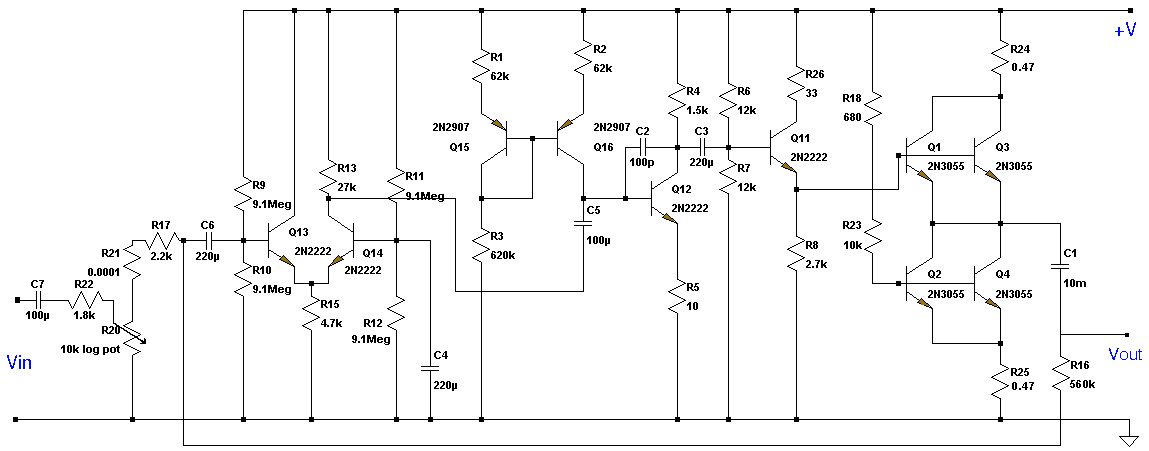
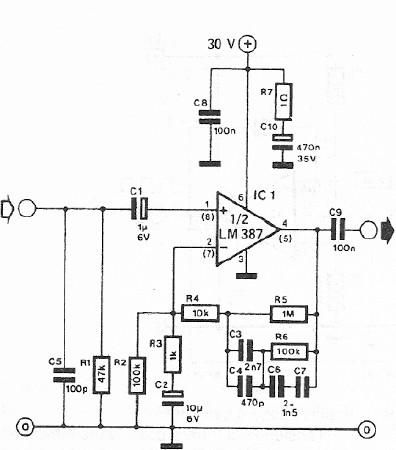
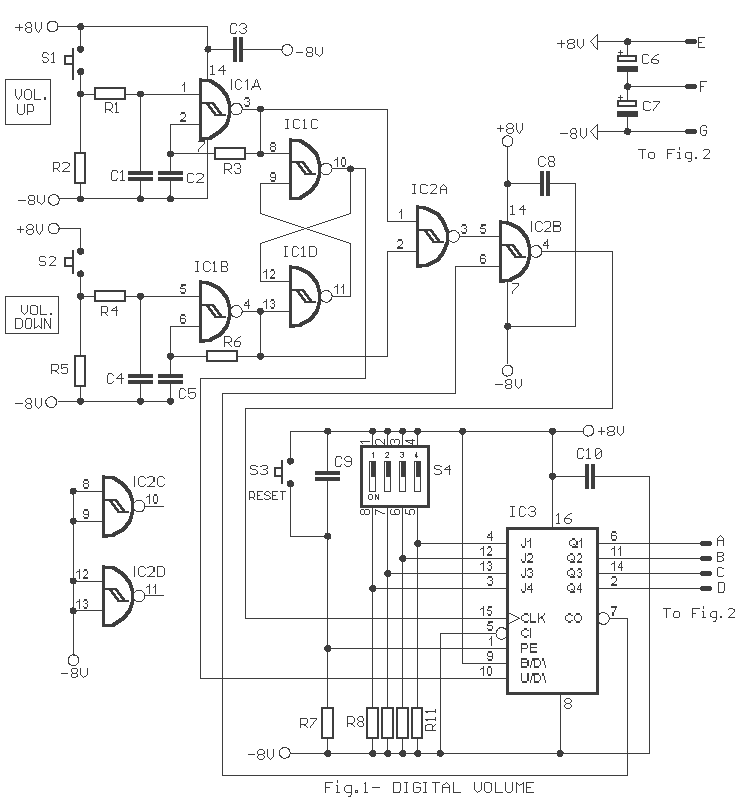
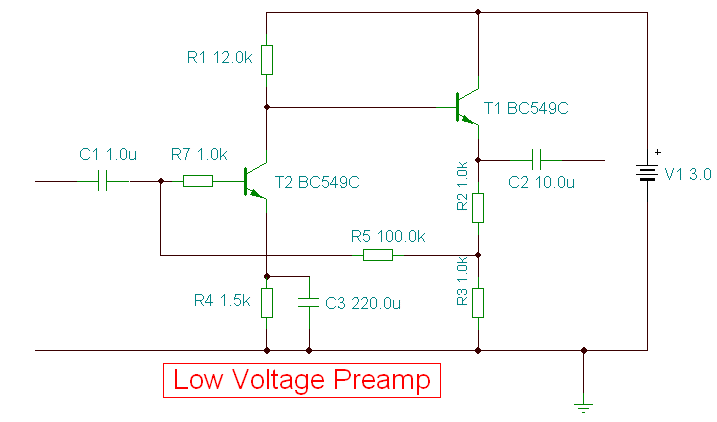
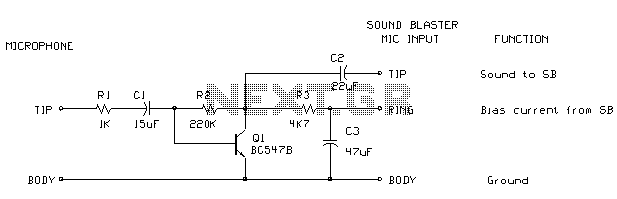
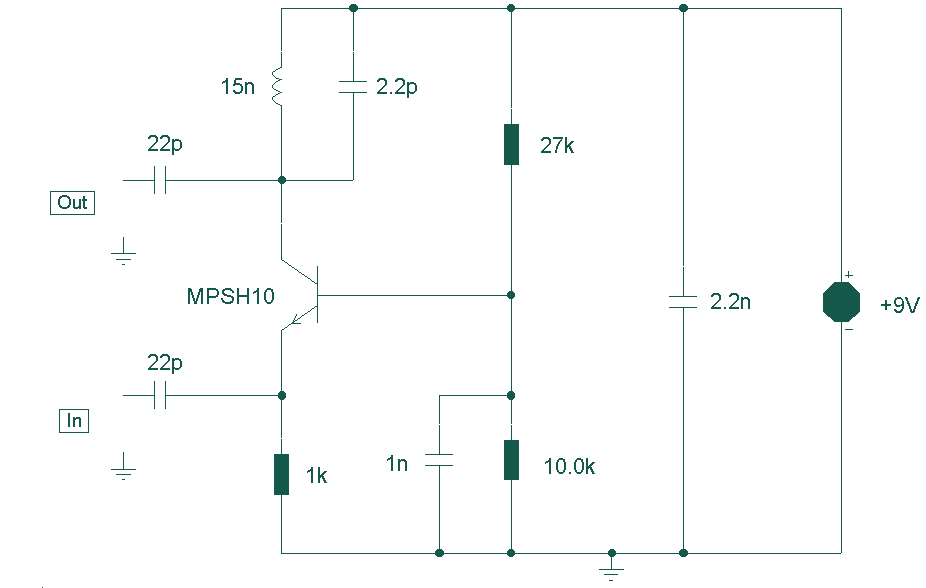
cm7777 preamp

The CM7777 preamp has failed. It is necessary to determine whether the failure is due to the power supply or the preamp itself. The focus is on verifying if the power supply outputs a DC voltage.
To troubleshoot the CM7777 preamp, it is essential to perform a systematic check of both the power supply and the preamp circuitry. Begin by measuring the output voltage of the power supply with a multimeter. Ensure that the power supply is connected correctly and powered on. The expected output voltage should align with the specifications provided in the CM7777 datasheet, typically around 12V DC for proper operation. If the voltage is absent or significantly lower than expected, this indicates a potential fault within the power supply.
Next, if the power supply is functioning correctly, the next step is to examine the preamp itself. This involves checking for any obvious signs of damage, such as burnt components or broken traces on the circuit board. Utilize the multimeter to test the continuity of critical components, including resistors, capacitors, and the integrated circuit. It may also be beneficial to inspect the power connections to the preamp to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion.
If the preamp is receiving the correct voltage but still fails to operate, further analysis of the internal components may be required. This could include testing the gain stages and verifying the integrity of any active components such as transistors or operational amplifiers within the preamp circuit.
In conclusion, a methodical approach to testing both the power supply and the preamp will help isolate the source of the failure, facilitating effective repairs or replacements as necessary.My CM7777 preamp has failed. I want to determine if the failure is due to the power supply or the preamp itself. Does the power supply output a DC voltage on the .. 🔗 External reference
To troubleshoot the CM7777 preamp, it is essential to perform a systematic check of both the power supply and the preamp circuitry. Begin by measuring the output voltage of the power supply with a multimeter. Ensure that the power supply is connected correctly and powered on. The expected output voltage should align with the specifications provided in the CM7777 datasheet, typically around 12V DC for proper operation. If the voltage is absent or significantly lower than expected, this indicates a potential fault within the power supply.
Next, if the power supply is functioning correctly, the next step is to examine the preamp itself. This involves checking for any obvious signs of damage, such as burnt components or broken traces on the circuit board. Utilize the multimeter to test the continuity of critical components, including resistors, capacitors, and the integrated circuit. It may also be beneficial to inspect the power connections to the preamp to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion.
If the preamp is receiving the correct voltage but still fails to operate, further analysis of the internal components may be required. This could include testing the gain stages and verifying the integrity of any active components such as transistors or operational amplifiers within the preamp circuit.
In conclusion, a methodical approach to testing both the power supply and the preamp will help isolate the source of the failure, facilitating effective repairs or replacements as necessary.My CM7777 preamp has failed. I want to determine if the failure is due to the power supply or the preamp itself. Does the power supply output a DC voltage on the .. 🔗 External reference