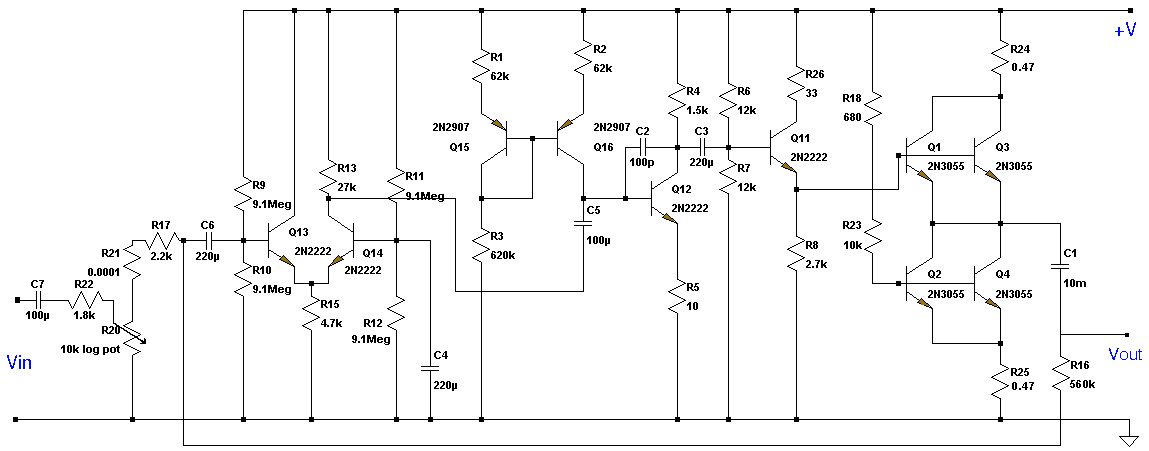
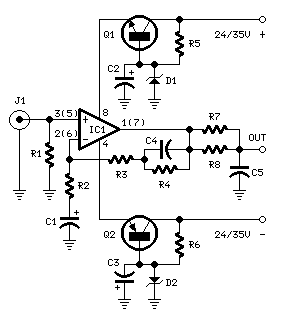
UHF Preamplifier
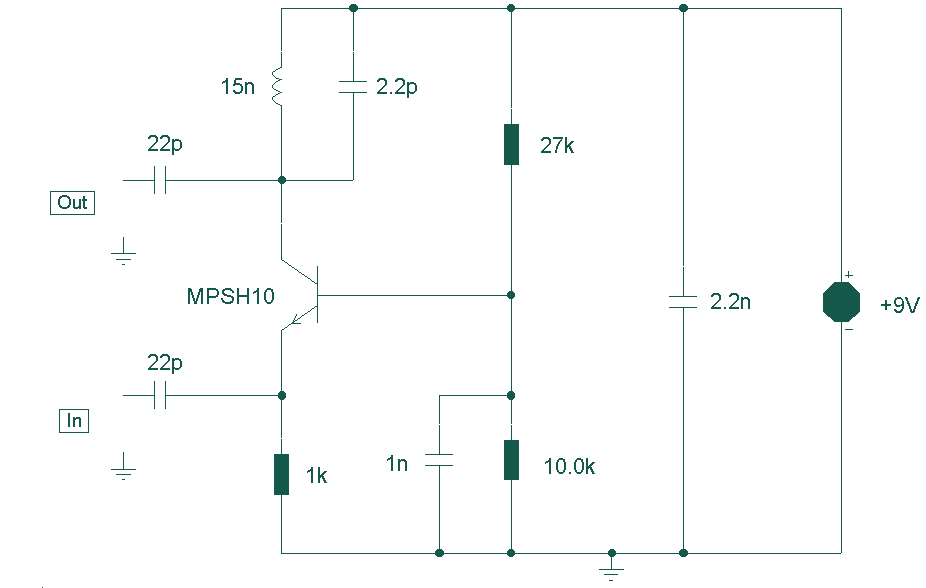
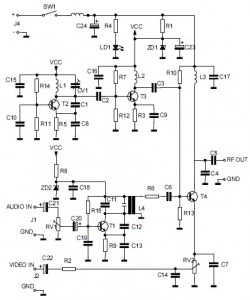
This circuit is designed to work at UHF frequencies in the range 450-800MHz. It has a gain of around 10dB and is suitable for boosting weak TV signals. The circuit is shown below.
The described circuit operates within the Ultra High Frequency (UHF) band, specifically targeting frequencies from 450 MHz to 800 MHz. This frequency range is commonly utilized for television broadcasting, particularly for digital and analog TV signals. The primary function of the circuit is to amplify weak signals to a more usable level, thereby improving the quality of reception.
The circuit achieves a gain of approximately 10 dB, which indicates a tenfold increase in signal power. This level of amplification is typically sufficient for compensating for signal losses that may occur due to distance from the transmission source, obstacles, or interference from other electronic devices.
Key components of the circuit likely include a low-noise amplifier (LNA) designed to minimize additional noise during the amplification process, ensuring that the integrity of the original signal is maintained. The LNA is typically followed by a matching network that optimizes the impedance to maximize power transfer between the circuit stages and the antenna.
Power supply considerations are also critical in the design. The circuit may utilize a regulated power supply to ensure stable operation, particularly since fluctuations in voltage can affect the performance of the amplifier. Additionally, bypass capacitors are often included to filter out any high-frequency noise from the power supply.
The circuit layout is crucial for performance, and careful attention should be paid to the placement of components to minimize parasitic inductance and capacitance. Shielding may also be implemented to protect the circuit from external electromagnetic interference (EMI), which is particularly important in the UHF range.
Overall, this circuit serves as an effective solution for enhancing the reception of UHF signals, making it a valuable component in television and communication systems where signal strength is a critical factor.This circuit is designed to work at UHF frequencies in the range 450-800MHz. It has a gain of around 10dB and is suitable for boosting weak TV signals. The circuit is shown below. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates within the Ultra High Frequency (UHF) band, specifically targeting frequencies from 450 MHz to 800 MHz. This frequency range is commonly utilized for television broadcasting, particularly for digital and analog TV signals. The primary function of the circuit is to amplify weak signals to a more usable level, thereby improving the quality of reception.
The circuit achieves a gain of approximately 10 dB, which indicates a tenfold increase in signal power. This level of amplification is typically sufficient for compensating for signal losses that may occur due to distance from the transmission source, obstacles, or interference from other electronic devices.
Key components of the circuit likely include a low-noise amplifier (LNA) designed to minimize additional noise during the amplification process, ensuring that the integrity of the original signal is maintained. The LNA is typically followed by a matching network that optimizes the impedance to maximize power transfer between the circuit stages and the antenna.
Power supply considerations are also critical in the design. The circuit may utilize a regulated power supply to ensure stable operation, particularly since fluctuations in voltage can affect the performance of the amplifier. Additionally, bypass capacitors are often included to filter out any high-frequency noise from the power supply.
The circuit layout is crucial for performance, and careful attention should be paid to the placement of components to minimize parasitic inductance and capacitance. Shielding may also be implemented to protect the circuit from external electromagnetic interference (EMI), which is particularly important in the UHF range.
Overall, this circuit serves as an effective solution for enhancing the reception of UHF signals, making it a valuable component in television and communication systems where signal strength is a critical factor.This circuit is designed to work at UHF frequencies in the range 450-800MHz. It has a gain of around 10dB and is suitable for boosting weak TV signals. The circuit is shown below. 🔗 External reference