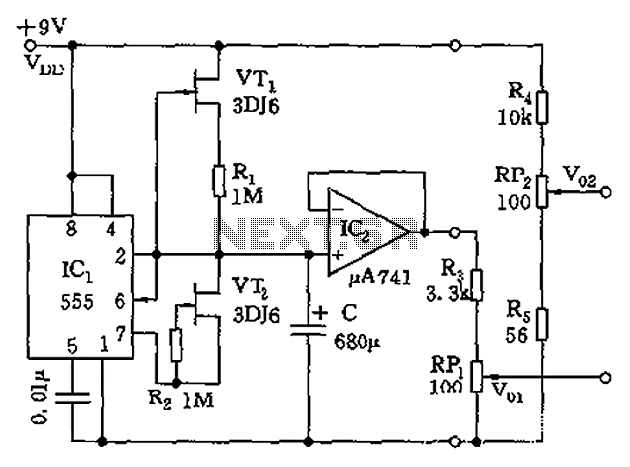
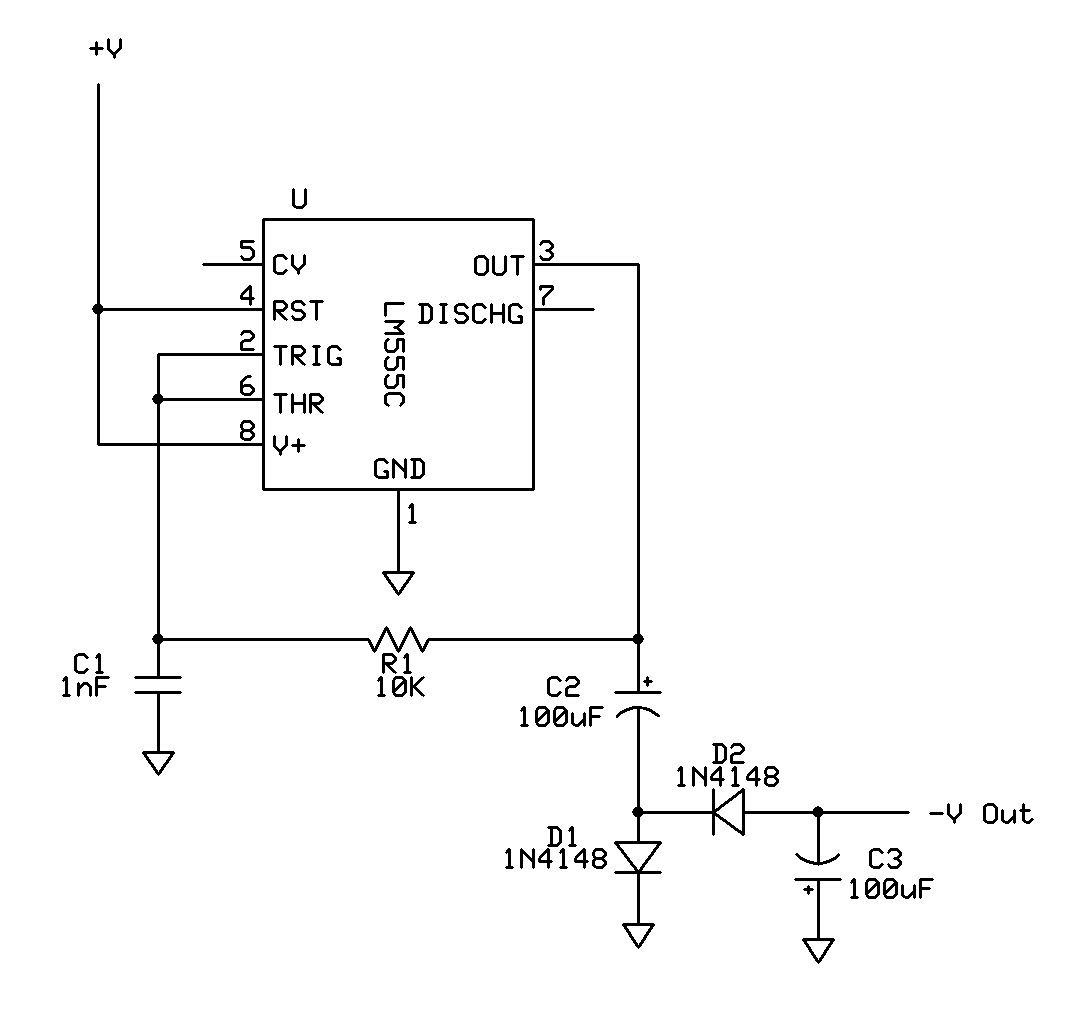
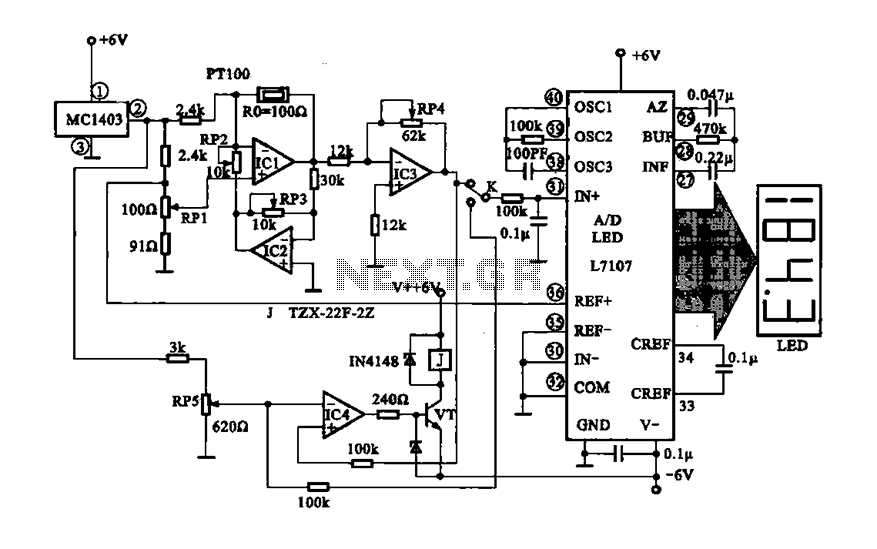
CMOS interface circuit with the PMOS cross-c
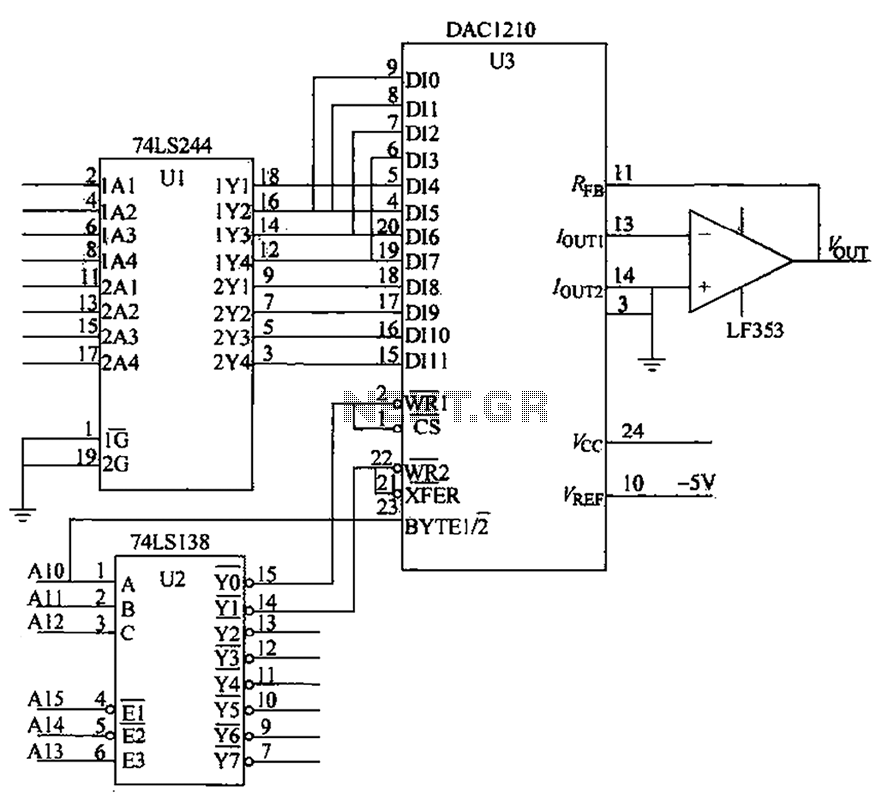
CMOS interface circuit with PMOS cross-coupled PMOS integrated circuit featuring high input impedance, where the input current can be ignored. The CMOS and PMOS interface circuit is illustrated in the accompanying figure.
The CMOS interface circuit utilizing PMOS cross-coupled configurations is designed to achieve high input impedance, making it suitable for applications where minimal loading on the preceding stage is critical. The PMOS transistors in this configuration operate in a complementary manner, allowing for enhanced performance in terms of noise margins and power consumption.
In this circuit, the PMOS transistors are arranged in a cross-coupled manner, which provides improved stability and reduces the susceptibility to variations in temperature and supply voltage. The high input impedance characteristic of this configuration is primarily due to the inherent properties of PMOS transistors, which exhibit low gate leakage currents. Consequently, the input current can be considered negligible, allowing for accurate signal processing without significant distortion or attenuation.
The CMOS interface circuit can be employed in various applications, including analog signal processing, sensor interfacing, and as part of more complex digital systems. The circuit's design typically includes biasing networks to ensure optimal operating conditions for the PMOS devices, as well as decoupling capacitors to filter out noise from the power supply.
In summary, the described CMOS interface circuit with PMOS cross-coupled transistors provides a robust solution for interfacing high-impedance sources while maintaining low power consumption and high signal integrity, making it an essential component in modern electronic designs. CMOS interface circuit with the PMOS cross-c PMOS integrated circuit high input impedance, input current can be ignored. CMOS and PMOS interface circuit shown in Figure
The CMOS interface circuit utilizing PMOS cross-coupled configurations is designed to achieve high input impedance, making it suitable for applications where minimal loading on the preceding stage is critical. The PMOS transistors in this configuration operate in a complementary manner, allowing for enhanced performance in terms of noise margins and power consumption.
In this circuit, the PMOS transistors are arranged in a cross-coupled manner, which provides improved stability and reduces the susceptibility to variations in temperature and supply voltage. The high input impedance characteristic of this configuration is primarily due to the inherent properties of PMOS transistors, which exhibit low gate leakage currents. Consequently, the input current can be considered negligible, allowing for accurate signal processing without significant distortion or attenuation.
The CMOS interface circuit can be employed in various applications, including analog signal processing, sensor interfacing, and as part of more complex digital systems. The circuit's design typically includes biasing networks to ensure optimal operating conditions for the PMOS devices, as well as decoupling capacitors to filter out noise from the power supply.
In summary, the described CMOS interface circuit with PMOS cross-coupled transistors provides a robust solution for interfacing high-impedance sources while maintaining low power consumption and high signal integrity, making it an essential component in modern electronic designs. CMOS interface circuit with the PMOS cross-c PMOS integrated circuit high input impedance, input current can be ignored. CMOS and PMOS interface circuit shown in Figure