Cmos Pair 2-Mhz Crystal Oscillator
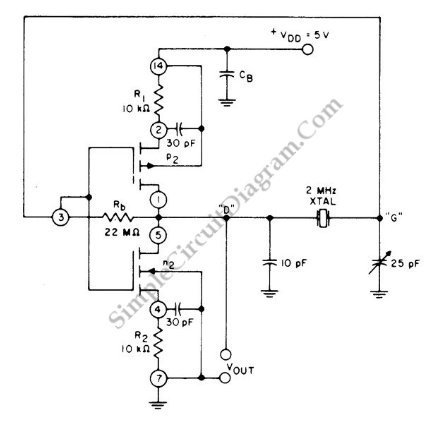
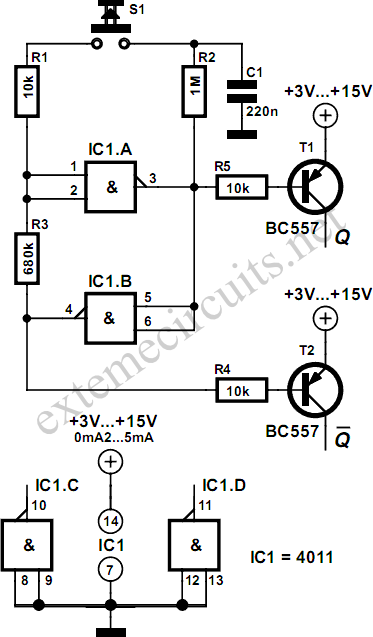
This is a 2 MHz crystal circuit utilizing a CMOS pair. This circuit is suitable for applications in digital watches and clocks due to its low power consumption.
The 2 MHz crystal oscillator circuit employs complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology, which is known for its low power consumption and high noise immunity. The core of the circuit consists of a quartz crystal that provides a stable frequency reference, ensuring precise timekeeping in digital watches and clocks.
The CMOS pair in the circuit typically includes two transistors configured in an inverter arrangement. This configuration allows for efficient oscillation, with one transistor driving the other, creating a feedback loop that sustains the oscillation at the desired frequency. The choice of a 2 MHz frequency is particularly advantageous for timekeeping applications, as it strikes a balance between accuracy and power efficiency.
Additionally, the circuit may incorporate passive components such as resistors and capacitors to fine-tune the oscillation characteristics and stabilize the output signal. The low power drain characteristic of this circuit is essential for battery-operated devices, extending the operational life of digital watches and clocks.
In summary, the 2 MHz CMOS crystal oscillator circuit is an effective solution for timekeeping applications, combining low power consumption with reliable frequency generation, making it an ideal choice for modern digital timepieces.This is a 2 MHz crystal circuit using CMOS pair. This circuit is ideal for uses in digital watches and clock because this circuit has low power drain. The.. 🔗 External reference
The 2 MHz crystal oscillator circuit employs complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology, which is known for its low power consumption and high noise immunity. The core of the circuit consists of a quartz crystal that provides a stable frequency reference, ensuring precise timekeeping in digital watches and clocks.
The CMOS pair in the circuit typically includes two transistors configured in an inverter arrangement. This configuration allows for efficient oscillation, with one transistor driving the other, creating a feedback loop that sustains the oscillation at the desired frequency. The choice of a 2 MHz frequency is particularly advantageous for timekeeping applications, as it strikes a balance between accuracy and power efficiency.
Additionally, the circuit may incorporate passive components such as resistors and capacitors to fine-tune the oscillation characteristics and stabilize the output signal. The low power drain characteristic of this circuit is essential for battery-operated devices, extending the operational life of digital watches and clocks.
In summary, the 2 MHz CMOS crystal oscillator circuit is an effective solution for timekeeping applications, combining low power consumption with reliable frequency generation, making it an ideal choice for modern digital timepieces.This is a 2 MHz crystal circuit using CMOS pair. This circuit is ideal for uses in digital watches and clock because this circuit has low power drain. The.. 🔗 External reference