Code practice oscillator II
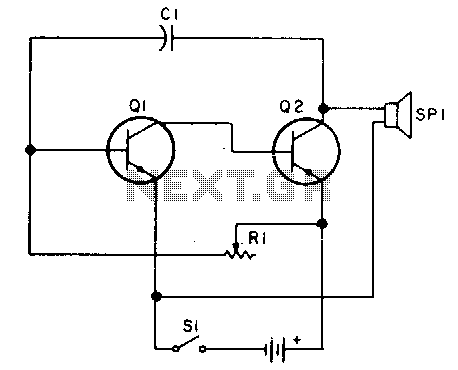
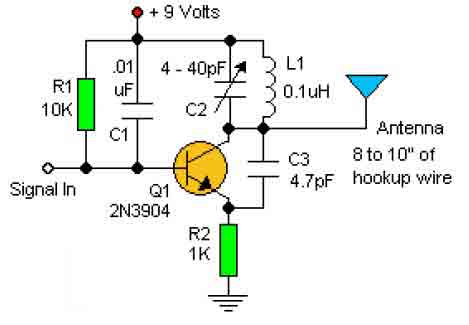
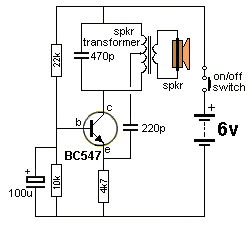
Oscillator, operates with 2 to 12 volts DC (optimal performance is achieved at 9 to 12 volts for maximum volume and clear keying). Additionally, R1 can be substituted with a 500K potentiometer, allowing the circuit to sweep across the entire audio frequency range.
The described oscillator circuit is designed to function within a voltage range of 2 to 12 volts DC, with a specific emphasis on achieving the best audio performance between 9 to 12 volts. This voltage range is critical for ensuring that the oscillator generates a clean and robust output signal, which is essential for applications requiring high-quality audio signals and precise keying.
In this circuit, R1 plays a pivotal role in determining the frequency of oscillation. By replacing R1 with a 500K potentiometer, the user can effectively adjust the resistance, thus enabling the circuit to sweep through a wide range of audio frequencies. This feature is particularly useful in applications such as audio synthesis, where varying the frequency can produce different tones and sound effects.
The oscillator circuit typically consists of active components like operational amplifiers or transistors, which work in conjunction with passive components such as resistors and capacitors to establish the desired frequency response. The configuration may include feedback loops that stabilize the oscillation and maintain consistent output levels.
To optimize performance, it is recommended to select high-quality components that can handle the specified voltage range and provide minimal distortion. Additionally, proper layout and grounding techniques should be employed to minimize noise and enhance the overall performance of the oscillator circuit.
This oscillator design is versatile and can be applied in various electronic projects, including signal generation, sound synthesis, and modulation applications. Adjusting the frequency range via the potentiometer allows for creative exploration within the audio spectrum, making it a valuable tool for engineers and hobbyists alike.Oscillator, works with2 to 12Tdc (but 9 to 12 volts gives best volume and clean keying) R1 can be replaced with a 500K pot and the circuit will sweep the entire audio frequency.
The described oscillator circuit is designed to function within a voltage range of 2 to 12 volts DC, with a specific emphasis on achieving the best audio performance between 9 to 12 volts. This voltage range is critical for ensuring that the oscillator generates a clean and robust output signal, which is essential for applications requiring high-quality audio signals and precise keying.
In this circuit, R1 plays a pivotal role in determining the frequency of oscillation. By replacing R1 with a 500K potentiometer, the user can effectively adjust the resistance, thus enabling the circuit to sweep through a wide range of audio frequencies. This feature is particularly useful in applications such as audio synthesis, where varying the frequency can produce different tones and sound effects.
The oscillator circuit typically consists of active components like operational amplifiers or transistors, which work in conjunction with passive components such as resistors and capacitors to establish the desired frequency response. The configuration may include feedback loops that stabilize the oscillation and maintain consistent output levels.
To optimize performance, it is recommended to select high-quality components that can handle the specified voltage range and provide minimal distortion. Additionally, proper layout and grounding techniques should be employed to minimize noise and enhance the overall performance of the oscillator circuit.
This oscillator design is versatile and can be applied in various electronic projects, including signal generation, sound synthesis, and modulation applications. Adjusting the frequency range via the potentiometer allows for creative exploration within the audio spectrum, making it a valuable tool for engineers and hobbyists alike.Oscillator, works with2 to 12Tdc (but 9 to 12 volts gives best volume and clean keying) R1 can be replaced with a 500K pot and the circuit will sweep the entire audio frequency.