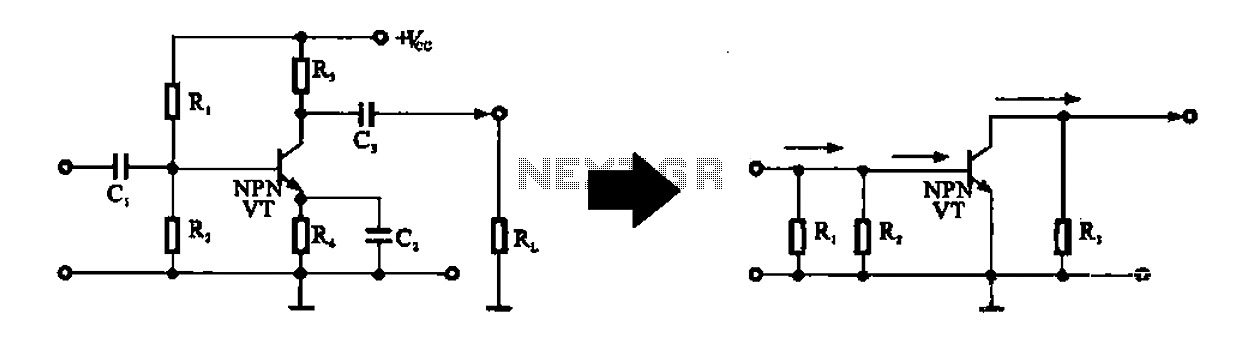
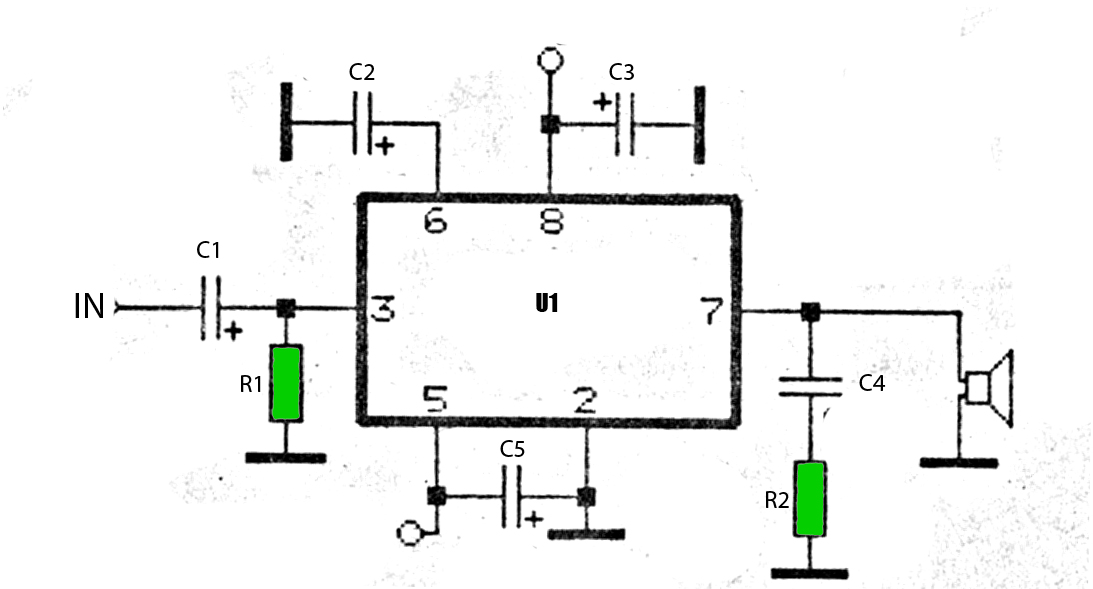
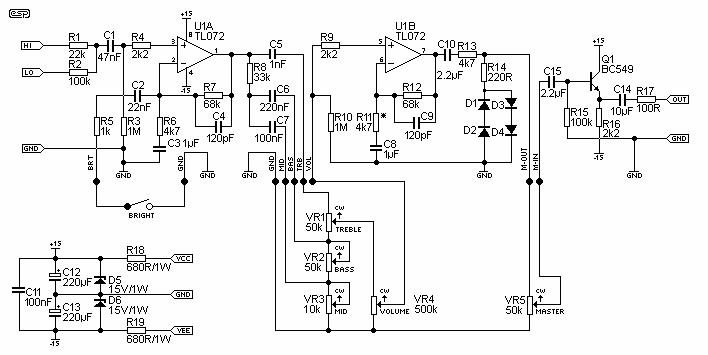
Combination of common-source grounded emitter amplifier
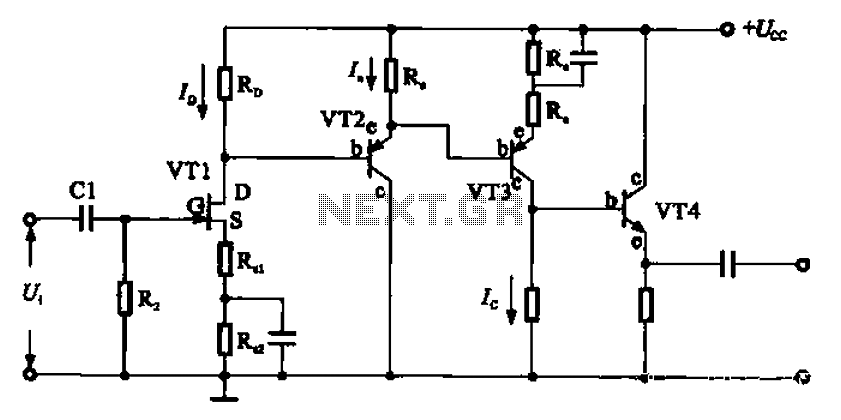
A combination of a common-source grounded emitter amplifier and a common emitter amplifier. The input impedance of the common emitter amplifier is in the range of 1.03 fl. Directly connecting the FET drive can be challenging; however, utilizing an emitter follower as illustrated allows for easier driving. The load resistance is connected to the common emitter amplifier, facilitating this integration. The output stage circuit incorporates the emitter follower to achieve current gain, exemplifying a typical low output impedance.
The described circuit integrates a common-source amplifier and a common emitter amplifier configuration to enhance the overall performance of the signal amplification process. The common-source amplifier, typically used in FET-based designs, provides high voltage gain, while the common emitter amplifier offers a balance of voltage and current gain with moderate input impedance.
In this configuration, the common emitter amplifier's input impedance is approximately 1.03 ohms, which presents a challenge for direct connections from the FET drive. To mitigate this issue, an emitter follower stage is introduced. The emitter follower, known for its high input impedance and low output impedance, serves as a buffer that allows for seamless interfacing between the FET and the common emitter amplifier. This configuration enhances the drive capability of the circuit, ensuring that the signal can be effectively transmitted without significant loss.
The load resistance (R_Tuen) is strategically connected to the common emitter amplifier to optimize the performance of the amplifier system. The inclusion of the emitter follower stage not only facilitates current gain but also stabilizes the output impedance, making it suitable for driving subsequent stages or loads that require a low impedance drive. This design exemplifies a robust approach to amplifier design, ensuring that both voltage and current gains are achieved while maintaining signal integrity and minimizing distortion.
Overall, this combination of amplifiers is ideal for applications requiring reliable amplification with efficient power handling, making it a valuable configuration in electronic circuit design. Combination of common-source grounded emitter amplifier A combination of common-source grounded pole radio amplifier. Common emitter amplifier input impedance in the range of l 03fl, it is difficult straight from the FET drive connected, however, if level through emitter follower, which as shown in FIG load R Tuen, connected to the common emitter amplifier the former, it is easy to drive, and as shown in FIG. The output stage circuit in front of the stage to join the emitter follower to get current gain, is an example of a typical low output impedance.
The described circuit integrates a common-source amplifier and a common emitter amplifier configuration to enhance the overall performance of the signal amplification process. The common-source amplifier, typically used in FET-based designs, provides high voltage gain, while the common emitter amplifier offers a balance of voltage and current gain with moderate input impedance.
In this configuration, the common emitter amplifier's input impedance is approximately 1.03 ohms, which presents a challenge for direct connections from the FET drive. To mitigate this issue, an emitter follower stage is introduced. The emitter follower, known for its high input impedance and low output impedance, serves as a buffer that allows for seamless interfacing between the FET and the common emitter amplifier. This configuration enhances the drive capability of the circuit, ensuring that the signal can be effectively transmitted without significant loss.
The load resistance (R_Tuen) is strategically connected to the common emitter amplifier to optimize the performance of the amplifier system. The inclusion of the emitter follower stage not only facilitates current gain but also stabilizes the output impedance, making it suitable for driving subsequent stages or loads that require a low impedance drive. This design exemplifies a robust approach to amplifier design, ensuring that both voltage and current gains are achieved while maintaining signal integrity and minimizing distortion.
Overall, this combination of amplifiers is ideal for applications requiring reliable amplification with efficient power handling, making it a valuable configuration in electronic circuit design. Combination of common-source grounded emitter amplifier A combination of common-source grounded pole radio amplifier. Common emitter amplifier input impedance in the range of l 03fl, it is difficult straight from the FET drive connected, however, if level through emitter follower, which as shown in FIG load R Tuen, connected to the common emitter amplifier the former, it is easy to drive, and as shown in FIG. The output stage circuit in front of the stage to join the emitter follower to get current gain, is an example of a typical low output impedance.