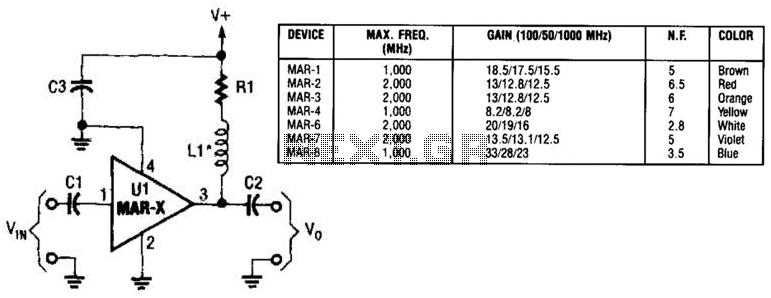
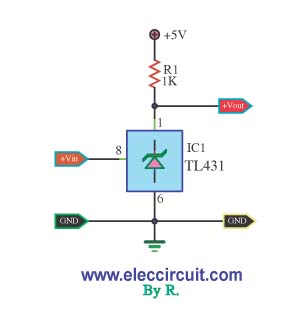
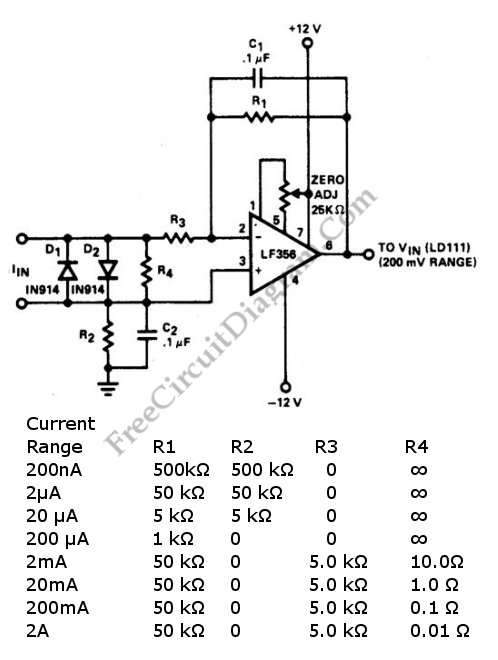
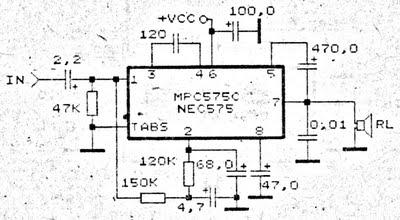
Alternating current voltage amplifier transistor
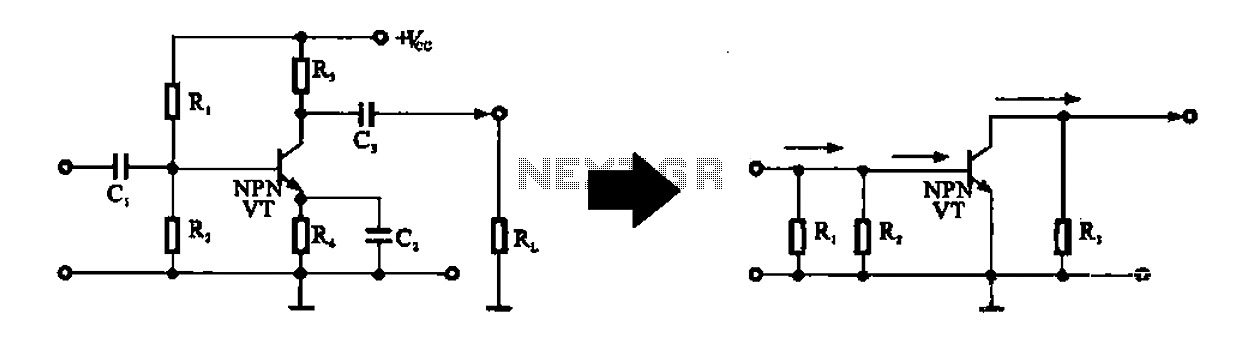
An alternating current voltage amplifier transistor AC path is described. In AC analysis, the internal resistance of the AC supply voltage source is low, which corresponds to a short circuit signal. Consequently, the alternating voltage terminal Vcc is considered to be at 0 volts, referred to as AC ground. AC ground and the actual ground can be treated as the same point. The emitter (e) connects to AC ground through capacitor C7.
The circuit described involves an AC voltage amplifier using a transistor, which is a fundamental component in analog electronics. The AC path indicates that the circuit is designed to amplify alternating current signals, which are characterized by their periodic nature. The low internal resistance of the AC supply voltage source suggests that it can effectively drive the circuit without significant voltage drop, allowing for accurate signal amplification.
In this configuration, the concept of AC ground is crucial. By defining the AC ground at the voltage terminal Vcc as 0 volts, the circuit can maintain a stable reference point for AC signals. This reference point is essential for ensuring that the amplified output accurately reflects the input signal variations. The emitter terminal (e) of the transistor plays a vital role in establishing this AC ground connection. The use of capacitor C7 facilitates this connection, allowing AC signals to pass while blocking any DC component that may be present.
Capacitor C7 serves as a coupling capacitor, which is critical in AC applications. It prevents DC bias from affecting the AC signal path while allowing the AC signals to flow from the emitter to the AC ground. This ensures that the transistor operates correctly within its active region, enhancing the linearity and fidelity of the amplification process.
Overall, the described circuit effectively utilizes an AC path for voltage amplification, leveraging the properties of the transistor and the strategic placement of capacitors to achieve optimal performance in AC signal processing.Alternating current voltage amplifier transistor AC path. In AC analysis, since the internal resistance of the AC supply voltage source is small, it corresponds to the short-ci rcuit signal, so that the alternating voltage terminal Vcc is ov, called AC ground. AC ground and the actual ground can be regarded as the same point, the emitter (e) via the capacitor C7 is AC ground,
The circuit described involves an AC voltage amplifier using a transistor, which is a fundamental component in analog electronics. The AC path indicates that the circuit is designed to amplify alternating current signals, which are characterized by their periodic nature. The low internal resistance of the AC supply voltage source suggests that it can effectively drive the circuit without significant voltage drop, allowing for accurate signal amplification.
In this configuration, the concept of AC ground is crucial. By defining the AC ground at the voltage terminal Vcc as 0 volts, the circuit can maintain a stable reference point for AC signals. This reference point is essential for ensuring that the amplified output accurately reflects the input signal variations. The emitter terminal (e) of the transistor plays a vital role in establishing this AC ground connection. The use of capacitor C7 facilitates this connection, allowing AC signals to pass while blocking any DC component that may be present.
Capacitor C7 serves as a coupling capacitor, which is critical in AC applications. It prevents DC bias from affecting the AC signal path while allowing the AC signals to flow from the emitter to the AC ground. This ensures that the transistor operates correctly within its active region, enhancing the linearity and fidelity of the amplification process.
Overall, the described circuit effectively utilizes an AC path for voltage amplification, leveraging the properties of the transistor and the strategic placement of capacitors to achieve optimal performance in AC signal processing.Alternating current voltage amplifier transistor AC path. In AC analysis, since the internal resistance of the AC supply voltage source is small, it corresponds to the short-ci rcuit signal, so that the alternating voltage terminal Vcc is ov, called AC ground. AC ground and the actual ground can be regarded as the same point, the emitter (e) via the capacitor C7 is AC ground,