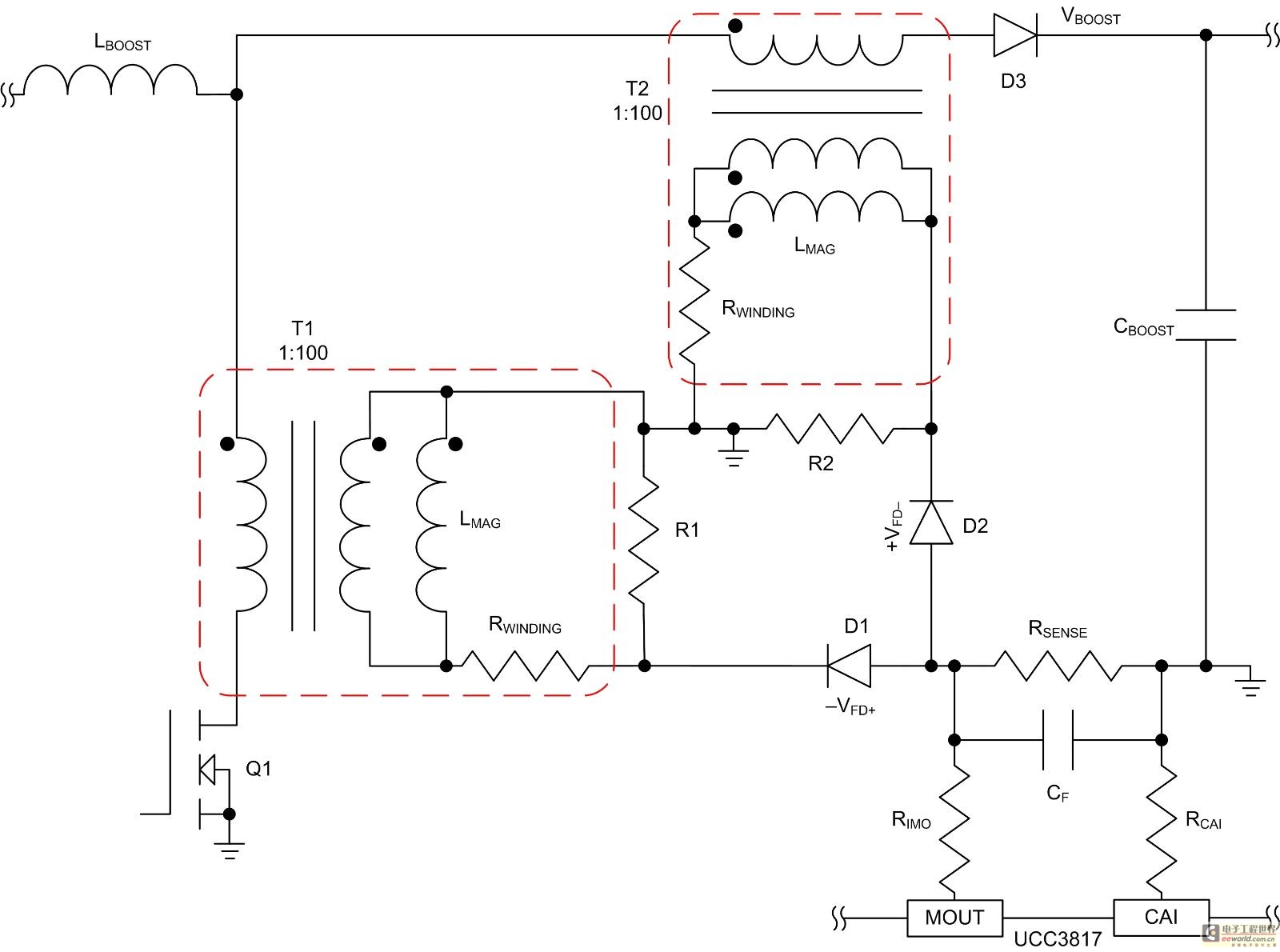
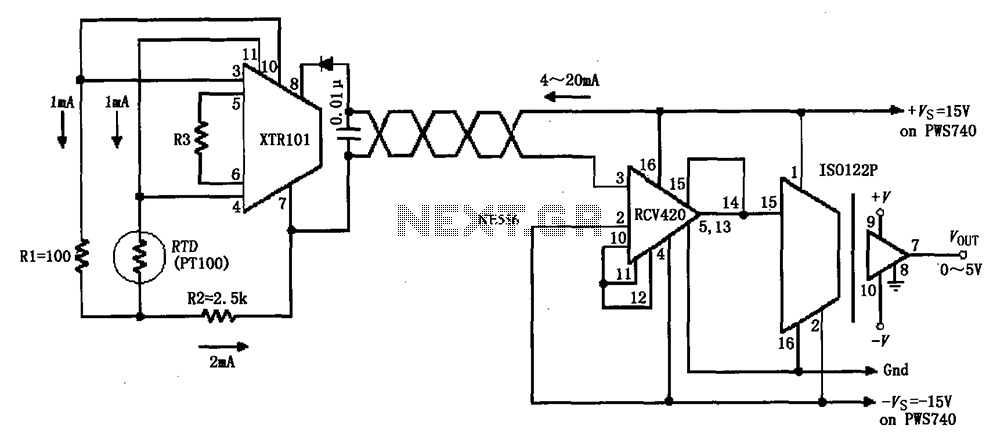
Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit waveform pulse wave oscillator blocking oscillator transformer
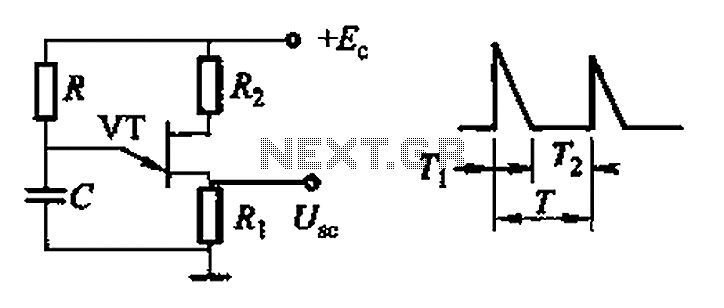
Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit, waveform and frequency formula - pulse wave oscillator - blocking oscillator transformer
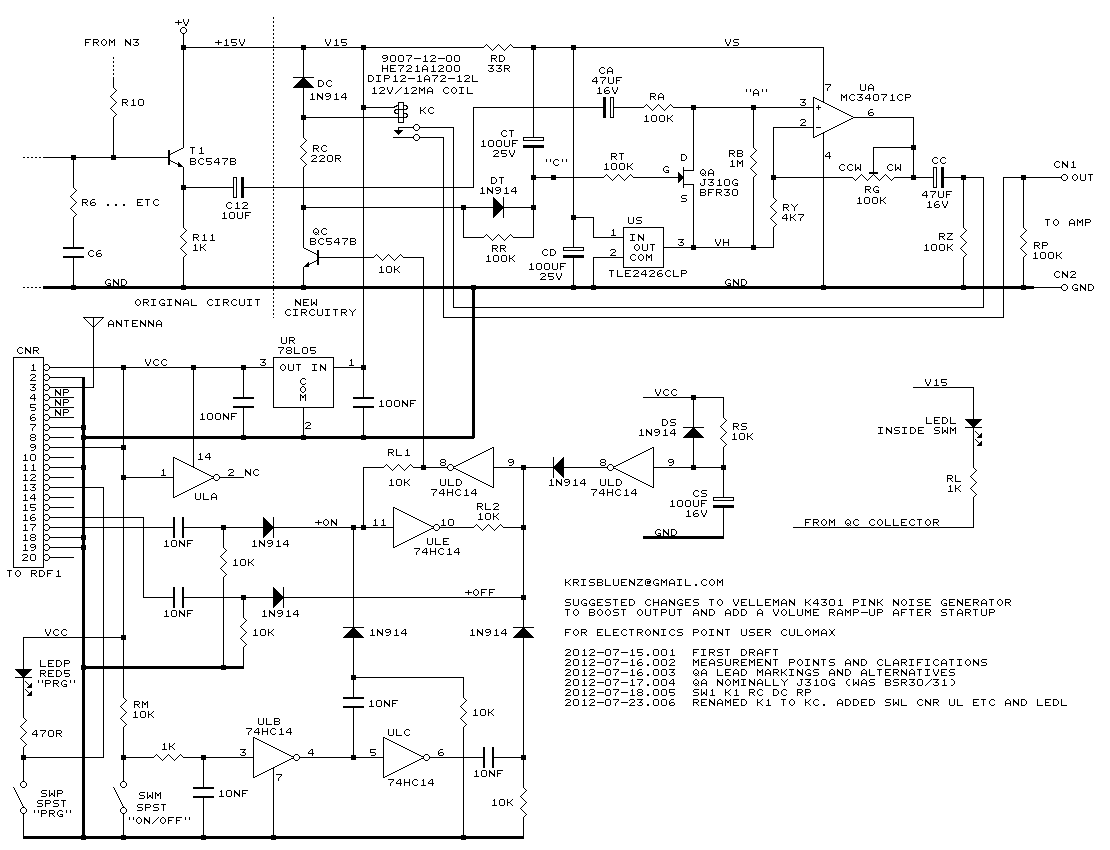
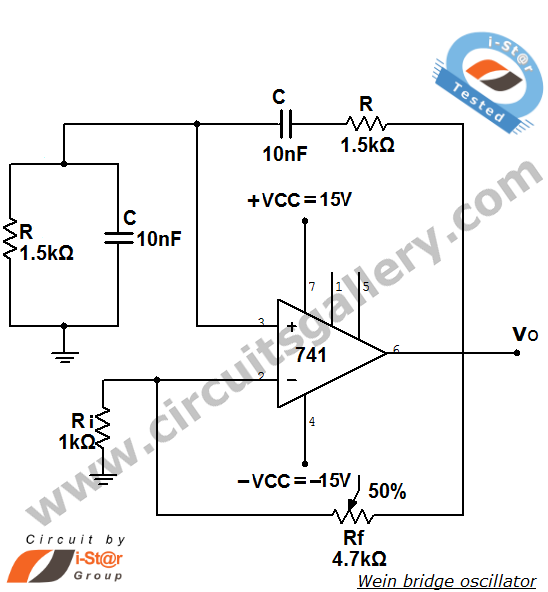
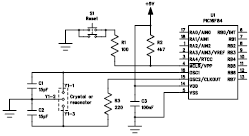
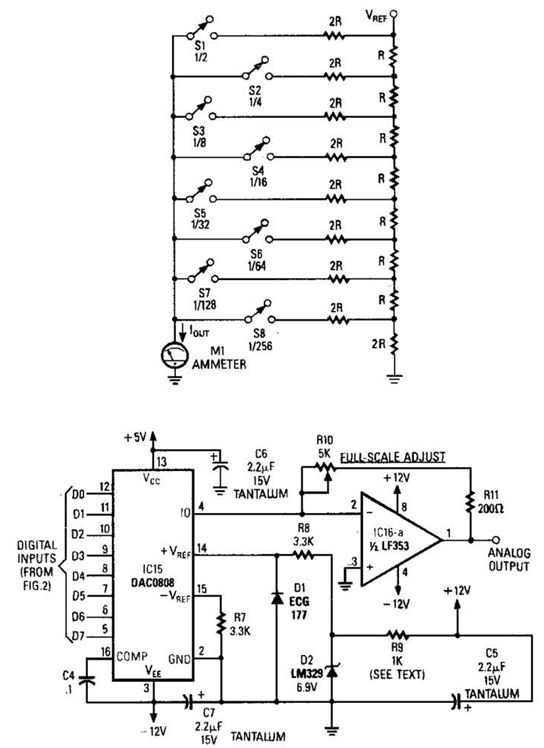
The common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit is designed to generate pulse waveforms, which are characterized by their square or rectangular shape. These oscillators are essential in various electronic applications, including clock generation, signal modulation, and timing circuits. The pulse wave oscillator operates by utilizing a feedback mechanism that allows the circuit to switch between high and low states rapidly, resulting in a periodic output waveform.
The frequency of the pulse waveform generated by a blocking oscillator can be determined using specific formulas that take into account the values of the circuit components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. In a typical blocking oscillator configuration, a transformer is employed to provide feedback to the transistor or active device, enabling it to oscillate. The frequency of oscillation is influenced by the inductance of the transformer and the capacitance in the circuit.
The output waveform of a pulse wave oscillator can be visualized as a series of sharp transitions between the high and low voltage levels, with a duty cycle that can be adjusted based on the circuit design. The duty cycle is defined as the ratio of the time the output is in the high state to the total period of the waveform. This characteristic makes pulse wave oscillators particularly useful in applications where precise timing and control of signal duration are required.
In summary, the common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit, specifically the pulse wave oscillator and blocking oscillator transformer configuration, is a fundamental component in electronic design, providing essential timing and waveform generation capabilities. Understanding the underlying principles and formulas governing these circuits is crucial for engineers working in the field of electronics. Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit, waveform and frequency formula - pulse wave oscillator - blocking oscillator transformer
The common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit is designed to generate pulse waveforms, which are characterized by their square or rectangular shape. These oscillators are essential in various electronic applications, including clock generation, signal modulation, and timing circuits. The pulse wave oscillator operates by utilizing a feedback mechanism that allows the circuit to switch between high and low states rapidly, resulting in a periodic output waveform.
The frequency of the pulse waveform generated by a blocking oscillator can be determined using specific formulas that take into account the values of the circuit components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. In a typical blocking oscillator configuration, a transformer is employed to provide feedback to the transistor or active device, enabling it to oscillate. The frequency of oscillation is influenced by the inductance of the transformer and the capacitance in the circuit.
The output waveform of a pulse wave oscillator can be visualized as a series of sharp transitions between the high and low voltage levels, with a duty cycle that can be adjusted based on the circuit design. The duty cycle is defined as the ratio of the time the output is in the high state to the total period of the waveform. This characteristic makes pulse wave oscillators particularly useful in applications where precise timing and control of signal duration are required.
In summary, the common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit, specifically the pulse wave oscillator and blocking oscillator transformer configuration, is a fundamental component in electronic design, providing essential timing and waveform generation capabilities. Understanding the underlying principles and formulas governing these circuits is crucial for engineers working in the field of electronics. Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit, waveform and frequency formula - pulse wave oscillator - blocking oscillator transformer