Computer microphone circuit diagram
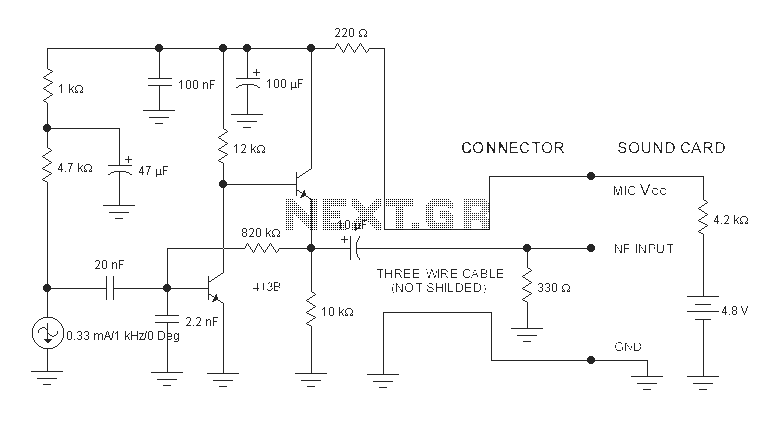
The sound card for a PC typically includes a microphone input, speaker output, and occasionally line inputs and outputs. The microphone input is specifically designed for dynamic microphones, accommodating an impedance range of 200 to 600 ohms. An adaptation has been made to the sound card to utilize a common electret microphone through a specific circuit. This adaptation features a composite amplifier constructed with two transistors. The BC413B transistor operates in a common emitter configuration, providing a slight boost to the microphone signal. This is followed by an emitter follower stage utilizing the BC547C transistor. The emitter follower stage is essential due to the distance between the microphone, circuit, and battery from the sound card. The low output impedance of the circuit, along with the use of screened cable, ensures a clean signal with minimal noise interference.
The circuit for adapting the sound card to accommodate an electret microphone involves a careful selection of components and configurations to ensure optimal performance. The BC413B transistor, functioning in a common emitter configuration, amplifies the low-level audio signal generated by the electret microphone. This configuration is advantageous as it provides voltage gain while also maintaining reasonable linearity, essential for accurate audio reproduction.
Following the common emitter stage, the BC547C transistor is employed in an emitter follower configuration. This configuration is critical for buffering the amplified signal and providing a low output impedance. The emitter follower allows the signal to drive long cable runs to the sound card without significant loss of quality or introduction of noise, which is particularly important in scenarios where the microphone and circuit are situated at a distance from the sound card.
To enhance the performance of the circuit, it is advisable to use high-quality screened cables for the connections between the microphone, circuit, and sound card. This will further reduce the potential for electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), which can degrade the audio signal quality.
Overall, the design of this circuit not only enables the use of a common electret microphone with a standard sound card but also ensures that the audio signal remains clean and robust throughout the transmission path. This adaptation is especially useful in applications where high-fidelity audio capture is required, such as in recording studios, broadcasting, or public speaking events.The sound card for a PC generally has a microphone input, speaker output and sometimes line inputs and outputs. The mic input is designed for dynamic microphones only in impedance range of 200 to 600 ohms. Lazar has adapted the sound card to use a common electret microphone using this circuit. He has made a composite amplifier using two transistors. The BC413B operates in common emitter to give a slight boost to the mic signal. This is followed by an emitter follower stage using the BC547C. This is necessary as the mic and circuit and battery will be some distance from the sound card, the low output impedance of the circuit and screened cable ensuring a clean signal with minimum noise pickup.
The circuit for adapting the sound card to accommodate an electret microphone involves a careful selection of components and configurations to ensure optimal performance. The BC413B transistor, functioning in a common emitter configuration, amplifies the low-level audio signal generated by the electret microphone. This configuration is advantageous as it provides voltage gain while also maintaining reasonable linearity, essential for accurate audio reproduction.
Following the common emitter stage, the BC547C transistor is employed in an emitter follower configuration. This configuration is critical for buffering the amplified signal and providing a low output impedance. The emitter follower allows the signal to drive long cable runs to the sound card without significant loss of quality or introduction of noise, which is particularly important in scenarios where the microphone and circuit are situated at a distance from the sound card.
To enhance the performance of the circuit, it is advisable to use high-quality screened cables for the connections between the microphone, circuit, and sound card. This will further reduce the potential for electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), which can degrade the audio signal quality.
Overall, the design of this circuit not only enables the use of a common electret microphone with a standard sound card but also ensures that the audio signal remains clean and robust throughout the transmission path. This adaptation is especially useful in applications where high-fidelity audio capture is required, such as in recording studios, broadcasting, or public speaking events.The sound card for a PC generally has a microphone input, speaker output and sometimes line inputs and outputs. The mic input is designed for dynamic microphones only in impedance range of 200 to 600 ohms. Lazar has adapted the sound card to use a common electret microphone using this circuit. He has made a composite amplifier using two transistors. The BC413B operates in common emitter to give a slight boost to the mic signal. This is followed by an emitter follower stage using the BC547C. This is necessary as the mic and circuit and battery will be some distance from the sound card, the low output impedance of the circuit and screened cable ensuring a clean signal with minimum noise pickup.