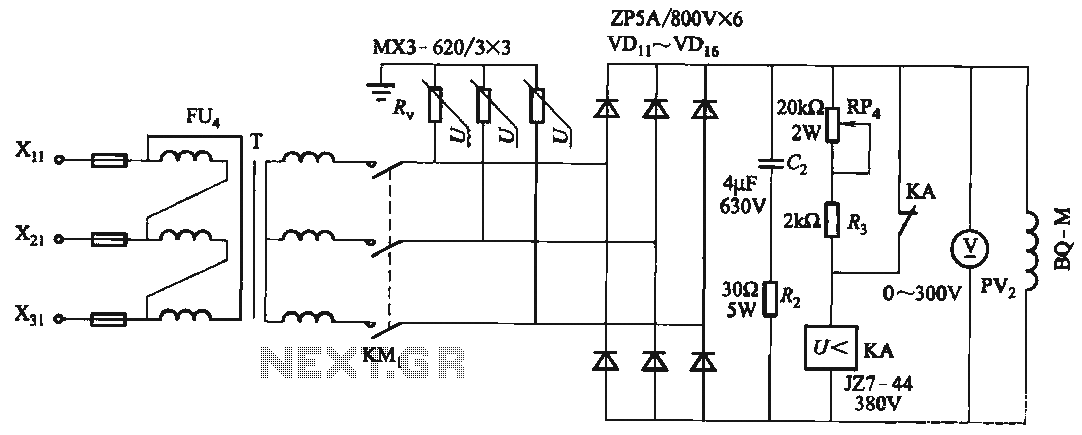
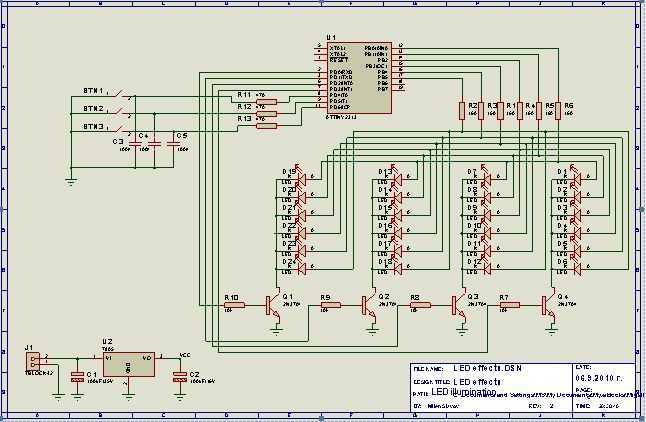
Constant Current LED Drive
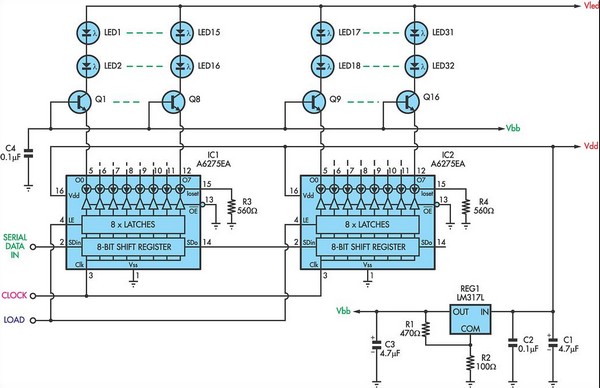
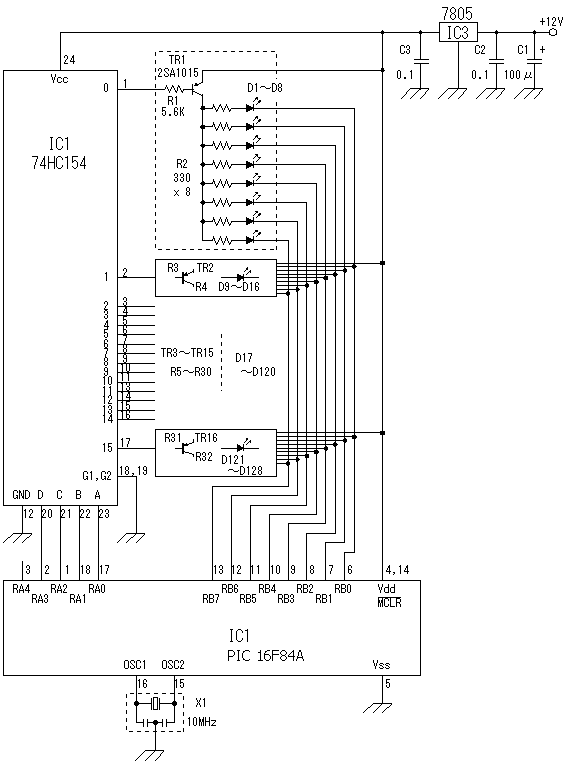
For applications requiring a large number of LEDs, traditional methods can become inefficient, prompting the need to minimize the voltage drop across the resistor. This approach can lead to inadequate current control. Integrated circuits (ICs) like the MM5450 and A6275 offer constant current outputs, ensuring stable current through the LEDs while maintaining a minimal voltage drop across the control circuit. However, these circuits face challenges due to the concentration of multiple constant current drivers in a compact package, which can lead to overheating and potential failure unless the supply voltage is kept low. To mitigate this issue, it is essential to maintain a small voltage across each constant current source. In this design, the LM317L (REG1) is utilized to provide a bias voltage of approximately 1.5V ±5%. Each transistor operates as an emitter-follower, supplying around 0.9V to the A6275 inputs. The LED supply voltage (Vled) must be sufficient to ensure at least 0.5V across each transistor, although it is permissible to exceed this requirement, and the supply does not need to be tightly regulated. General-purpose NPN transistors, such as the BC548, can be employed, and a single LM317L can easily handle a total LED current of at least 1A. The A6275 is produced by Allegro.
In this circuit design, the use of constant current drivers is essential for maintaining consistent LED performance across various operating conditions. The integration of the LM317L voltage regulator plays a critical role in stabilizing the bias voltage, which is vital for the proper functioning of the constant current sources. By setting the bias to approximately 1.5V, the circuit ensures that the current remains within the desired range, preventing fluctuations that could lead to LED dimming or burnout.
The choice of transistors, such as the BC548, is important due to their general-purpose nature and ability to handle the required current levels efficiently. The emitter-follower configuration allows for effective voltage level shifting, ensuring that the A6275 receives the appropriate voltage for optimal operation. The design must also consider the thermal management of the ICs, as excessive heat can impair performance and reduce lifespan. Adequate heat dissipation strategies, such as using heat sinks or ensuring proper airflow, should be implemented to enhance reliability.
Overall, this schematic effectively balances the need for efficient LED control with the challenges posed by high current demands and thermal management. By carefully selecting components and configuring the circuit to maintain stable operating conditions, the design achieves a robust solution for applications that require multiple LEDs to operate reliably and efficiently.However, for applications needing many LEDs, this becomes extravagantly inefficient and it is tempting to keep the voltage drop across the resistor as small as possible. That leads to poor control of the current. ICs such as the MM5450 and its relatives and the A6275 and its relatives provide constant current outputs so that the current through the LEDs is well
controlled even though the voltage drop across the circuit doing the control is acceptably small. However, the difficulty with these circuits is that because they contain many constant current drivers crowded into a relatively small package, unless the supply voltage is small, they become too hot and can destroy themselves. This problem is not easy to solve. The solution is to maintain a small voltage across each constant current source. In this circuit, this is accomplished by REG1, the LM317L, which provides a bias of about 1. 5V ±5%. Each transistor works as an emitter-follower, presenting the A6275 inputs with about 0. 9V. Vled, the LED supply voltage, needs to be high enough to ensure that there will be at least 0. 5V across each transistor but it is safe to allow significantly more than this and the supply need not be well regulated.
The transistors can be general purpose NPN types such as BC548 and a single LM317L will easily supply a total LED current of at least 1A. A6275s are made by Allegro. 🔗 External reference
In this circuit design, the use of constant current drivers is essential for maintaining consistent LED performance across various operating conditions. The integration of the LM317L voltage regulator plays a critical role in stabilizing the bias voltage, which is vital for the proper functioning of the constant current sources. By setting the bias to approximately 1.5V, the circuit ensures that the current remains within the desired range, preventing fluctuations that could lead to LED dimming or burnout.
The choice of transistors, such as the BC548, is important due to their general-purpose nature and ability to handle the required current levels efficiently. The emitter-follower configuration allows for effective voltage level shifting, ensuring that the A6275 receives the appropriate voltage for optimal operation. The design must also consider the thermal management of the ICs, as excessive heat can impair performance and reduce lifespan. Adequate heat dissipation strategies, such as using heat sinks or ensuring proper airflow, should be implemented to enhance reliability.
Overall, this schematic effectively balances the need for efficient LED control with the challenges posed by high current demands and thermal management. By carefully selecting components and configuring the circuit to maintain stable operating conditions, the design achieves a robust solution for applications that require multiple LEDs to operate reliably and efficiently.However, for applications needing many LEDs, this becomes extravagantly inefficient and it is tempting to keep the voltage drop across the resistor as small as possible. That leads to poor control of the current. ICs such as the MM5450 and its relatives and the A6275 and its relatives provide constant current outputs so that the current through the LEDs is well
controlled even though the voltage drop across the circuit doing the control is acceptably small. However, the difficulty with these circuits is that because they contain many constant current drivers crowded into a relatively small package, unless the supply voltage is small, they become too hot and can destroy themselves. This problem is not easy to solve. The solution is to maintain a small voltage across each constant current source. In this circuit, this is accomplished by REG1, the LM317L, which provides a bias of about 1. 5V ±5%. Each transistor works as an emitter-follower, presenting the A6275 inputs with about 0. 9V. Vled, the LED supply voltage, needs to be high enough to ensure that there will be at least 0. 5V across each transistor but it is safe to allow significantly more than this and the supply need not be well regulated.
The transistors can be general purpose NPN types such as BC548 and a single LM317L will easily supply a total LED current of at least 1A. A6275s are made by Allegro. 🔗 External reference