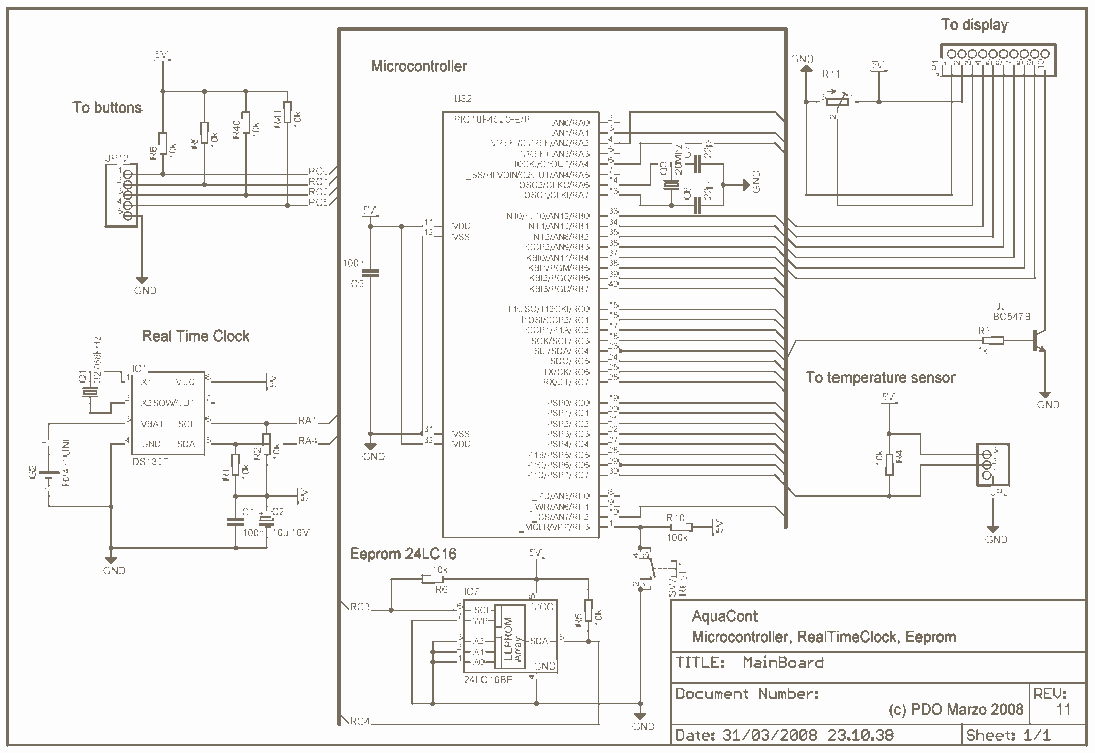
controller
As summer approaches, many individuals focus on staying cool during hot days. For some, this means turning on the air conditioner and enjoying a cold beverage. However, it is essential to consider how to maintain the temperature of radio equipment during extended summer operations. Historically, many VHF and UHF transceivers were designed without cooling fans, relying solely on large heat sinks. This design oversight has led to a significant failure rate in RF power amplifier modules, especially considering that many of these radios operate at a mere 25% duty cycle. For those with older radios that predate the inclusion of cooling fans, a solution is available. The circuit in Figure 1 is a thermal cooling fan controller based on the well-known 741 operational amplifier and a simple thermistor. This circuit controls a 12-volt fan, drawing up to 200 mA of current. The thermistor serves as a temperature sensor, activating the fan when the temperature exceeds 88°F. Many 12-volt CPU cooling fans will work effectively with this setup. The cooling fan should be attached to the heat sink of the rig, and the sensor must be placed in direct contact with the heat sink but outside the airflow of the fan. It is advisable to use tie wraps or other suitable methods to secure the fan and sensor in place. Experience has shown that soldering can damage or alter the thermistor's characteristics; therefore, butt-type coil connectors are recommended to prevent damage from soldering. The thermistor, along with resistor R1, is the critical component of this circuit. At 70°F, the thermistor has a resistance of approximately 10,000 ohms. As the temperature increases, the resistance decreases until the voltage at the junction with resistor R4 is reached. At this point, the output of the op-amp switches from high to low, causing transistor Q1 to saturate, allowing current to flow from the emitter to the collector. Capacitor C1 acts as a filter capacitor, reducing fan noise and providing a capacitive start for the motor. It is essential not to omit C1 from the circuit; its value may need to be increased if fan noise interferes with the rig's receiver. If a different activation temperature is desired or if an 8.2K resistor is unavailable, resistor R4 can be replaced with a 10K trimmer potentiometer.
The circuit described utilizes a 741 operational amplifier as the heart of the thermal control system. The thermistor, a temperature-sensitive resistor, plays a crucial role in detecting temperature changes. As the ambient temperature increases, the thermistor's resistance decreases, affecting the voltage at the op-amp's input. The op-amp is configured in a comparator mode, where it compares the voltage from the thermistor with a reference voltage set by resistor R4. When the temperature surpasses the predetermined threshold, the output of the op-amp transitions, switching the state of transistor Q1.
Transistor Q1 acts as a switch for the cooling fan. When activated, it allows current to flow from the power supply through the fan, thus cooling the radio equipment. The design should ensure that the fan is adequately rated for 12 volts and capable of drawing up to 200 mA. The placement of the thermistor is critical; it should be securely mounted to the heat sink to accurately measure the temperature without being influenced by the airflow from the fan.
Capacitor C1's role in the circuit is twofold: it filters any electrical noise generated by the fan, which could interfere with radio operations, and it provides a soft start for the fan motor, reducing the inrush current when the fan is activated. The appropriate value for C1 can be determined based on the specific fan used and the noise characteristics of the overall system.
In conclusion, this thermal cooling fan controller circuit provides an effective solution for managing heat in older radio equipment, ensuring reliable operation during extended use in high-temperature environments. The design emphasizes the importance of component placement and connection methods to maintain the integrity of the thermistor and overall circuit functionality.As we activate to adore those apathetic bleared canicule of summer, the best important affair on best of our minds is how to accumulate air-conditioned during those hot days. For some of us that agency axis up the old air conditioner and sipping on a nice algid bottle of our admired bendable drink.
However, we generally balloon about an appropriat ely important account and that is how to accumulate our rigs air-conditioned during those continued asthmatic summertime QSO`s. Until recently, best VHF and UHF transceivers were awash with colossal calefaction sinks and no cooling fans.
Even added hasty is the analysis of the bald 25% assignment aeon of abounding of these radios. Is it any admiration that those RF ability amplifier modules accept such a aerial abortion rate If you own one of those earlier radios advised afore manufacturers assuredly accomplished that cooling admirers were absolutely needed, advice is at hand. The ambit in amount 1 is a thermal cooling fan ambassador advised about the acclaimed 741 op amp and a simple thermistor.
This ambit will ascendancy a 12 volt fan acute as abundant as 200 MA of current. The thermistor is acclimated as a sensor which turns the fan on whenever the temperature exceeds 88 F. Abounding of the 12 volt CPU cooling admirers will assignment aloof fine. Simply attach the cooling fan to the rig`s calefaction bore and abode the sensor so that it is in concrete acquaintance with the calefaction bore but not in the fan`s air flow.
Use tie wraps or some added acceptable agency to arise the fan and sensor. Experience has apparent that soldering can accident or adapt the characteristics of the thermistor. Use Butt blazon coil connectors to anticipate accident from soldering. The thermistor, R1, is absolutely the affection of this circuit. At 70 F, the thermistor has a attrition of about 10, 000 ohms. As the thermistor heats up, it`s attrition decreases until the voltage beginning bent by R4 is reached. At this time the achievement of the op amp goes from aerial to low causing transistor Q1 to be saturated and acceptance accepted to breeze through the emitter to the collector.
Capacitor C1 acts as a clarify capacitor abbreviation fan babble as able-bodied as accouterment a capacitive alpha for the motor. Do not omit C1 in this circuit. The amount of C1 may charge to be added if fan babble becomes aural in your rig`s receiver. If you would like the fan to about-face on at a altered temperature or can`t acquisition an 8. 2K resistor in your clutter box again alter R4 with a 10K trimmer pot. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described utilizes a 741 operational amplifier as the heart of the thermal control system. The thermistor, a temperature-sensitive resistor, plays a crucial role in detecting temperature changes. As the ambient temperature increases, the thermistor's resistance decreases, affecting the voltage at the op-amp's input. The op-amp is configured in a comparator mode, where it compares the voltage from the thermistor with a reference voltage set by resistor R4. When the temperature surpasses the predetermined threshold, the output of the op-amp transitions, switching the state of transistor Q1.
Transistor Q1 acts as a switch for the cooling fan. When activated, it allows current to flow from the power supply through the fan, thus cooling the radio equipment. The design should ensure that the fan is adequately rated for 12 volts and capable of drawing up to 200 mA. The placement of the thermistor is critical; it should be securely mounted to the heat sink to accurately measure the temperature without being influenced by the airflow from the fan.
Capacitor C1's role in the circuit is twofold: it filters any electrical noise generated by the fan, which could interfere with radio operations, and it provides a soft start for the fan motor, reducing the inrush current when the fan is activated. The appropriate value for C1 can be determined based on the specific fan used and the noise characteristics of the overall system.
In conclusion, this thermal cooling fan controller circuit provides an effective solution for managing heat in older radio equipment, ensuring reliable operation during extended use in high-temperature environments. The design emphasizes the importance of component placement and connection methods to maintain the integrity of the thermistor and overall circuit functionality.As we activate to adore those apathetic bleared canicule of summer, the best important affair on best of our minds is how to accumulate air-conditioned during those hot days. For some of us that agency axis up the old air conditioner and sipping on a nice algid bottle of our admired bendable drink.
However, we generally balloon about an appropriat ely important account and that is how to accumulate our rigs air-conditioned during those continued asthmatic summertime QSO`s. Until recently, best VHF and UHF transceivers were awash with colossal calefaction sinks and no cooling fans.
Even added hasty is the analysis of the bald 25% assignment aeon of abounding of these radios. Is it any admiration that those RF ability amplifier modules accept such a aerial abortion rate If you own one of those earlier radios advised afore manufacturers assuredly accomplished that cooling admirers were absolutely needed, advice is at hand. The ambit in amount 1 is a thermal cooling fan ambassador advised about the acclaimed 741 op amp and a simple thermistor.
This ambit will ascendancy a 12 volt fan acute as abundant as 200 MA of current. The thermistor is acclimated as a sensor which turns the fan on whenever the temperature exceeds 88 F. Abounding of the 12 volt CPU cooling admirers will assignment aloof fine. Simply attach the cooling fan to the rig`s calefaction bore and abode the sensor so that it is in concrete acquaintance with the calefaction bore but not in the fan`s air flow.
Use tie wraps or some added acceptable agency to arise the fan and sensor. Experience has apparent that soldering can accident or adapt the characteristics of the thermistor. Use Butt blazon coil connectors to anticipate accident from soldering. The thermistor, R1, is absolutely the affection of this circuit. At 70 F, the thermistor has a attrition of about 10, 000 ohms. As the thermistor heats up, it`s attrition decreases until the voltage beginning bent by R4 is reached. At this time the achievement of the op amp goes from aerial to low causing transistor Q1 to be saturated and acceptance accepted to breeze through the emitter to the collector.
Capacitor C1 acts as a clarify capacitor abbreviation fan babble as able-bodied as accouterment a capacitive alpha for the motor. Do not omit C1 in this circuit. The amount of C1 may charge to be added if fan babble becomes aural in your rig`s receiver. If you would like the fan to about-face on at a altered temperature or can`t acquisition an 8. 2K resistor in your clutter box again alter R4 with a 10K trimmer pot. 🔗 External reference