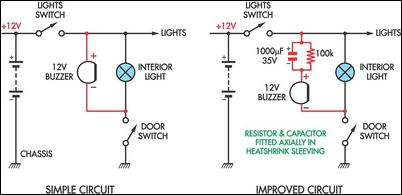
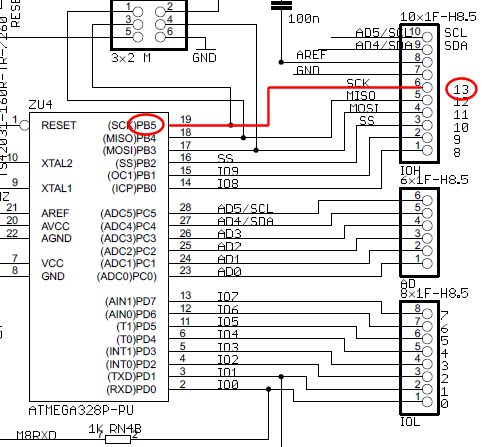
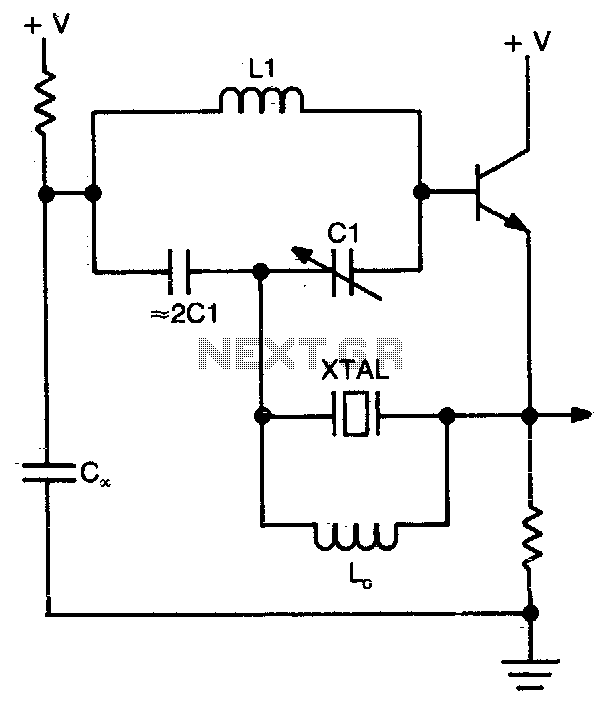
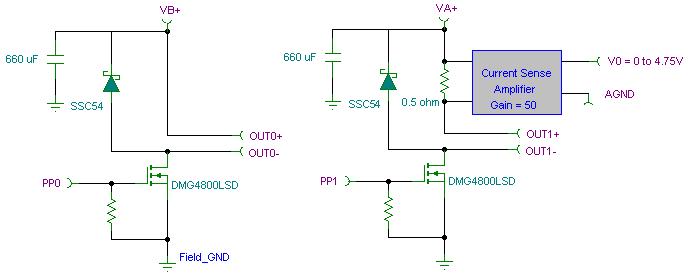
Correct Board Layout Lowers EMI of Switchmode Converters

This document outlines the layout considerations for switch-mode DC-DC converter printed circuit boards (PCBs) aimed at minimizing switching noise and electromagnetic interference (EMI).
The layout of switch-mode DC-DC converter PCBs is critical in ensuring efficient operation and compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. Key factors to consider include the placement of components, routing of traces, and the design of ground planes.
1. **Component Placement**: Components should be arranged to minimize the loop area of high-frequency current paths. The input and output capacitors should be placed as close as possible to the switching device to reduce parasitic inductance. Additionally, the placement of inductors and transformers should be optimized to prevent coupling of magnetic fields that can induce noise in adjacent circuits.
2. **Trace Routing**: High-frequency switching paths should be kept short and direct. Power traces must be wide enough to handle the current without excessive voltage drop or heating. It is advisable to use a star ground configuration to avoid ground loops, ensuring that return paths for high-frequency currents do not interfere with sensitive analog or digital signals.
3. **Ground Planes**: A solid ground plane is essential for minimizing EMI. The ground plane should be continuous and unbroken, providing a low-impedance return path for high-frequency currents. If multiple ground levels are necessary (e.g., digital and analog grounds), they should be connected at a single point to prevent ground loops.
4. **Decoupling Capacitors**: Placing decoupling capacitors as close as possible to the power pins of integrated circuits (ICs) helps to filter out high-frequency noise. The selection of capacitor types (ceramic, tantalum, etc.) and values should be based on the frequency characteristics of the circuit.
5. **Shielding and Filtering**: In cases where EMI is a significant concern, additional measures such as shielding enclosures or ferrite beads on power lines may be employed. Filters can also be integrated into the design to attenuate unwanted frequencies.
By adhering to these layout principles, the performance of switch-mode DC-DC converters can be optimized, leading to reduced noise and improved reliability in various applications.Describes how to layout switch-mode DC-DC converter printed circuit boards (PCBs) to minimize switching noise and EMI.. 🔗 External reference
The layout of switch-mode DC-DC converter PCBs is critical in ensuring efficient operation and compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. Key factors to consider include the placement of components, routing of traces, and the design of ground planes.
1. **Component Placement**: Components should be arranged to minimize the loop area of high-frequency current paths. The input and output capacitors should be placed as close as possible to the switching device to reduce parasitic inductance. Additionally, the placement of inductors and transformers should be optimized to prevent coupling of magnetic fields that can induce noise in adjacent circuits.
2. **Trace Routing**: High-frequency switching paths should be kept short and direct. Power traces must be wide enough to handle the current without excessive voltage drop or heating. It is advisable to use a star ground configuration to avoid ground loops, ensuring that return paths for high-frequency currents do not interfere with sensitive analog or digital signals.
3. **Ground Planes**: A solid ground plane is essential for minimizing EMI. The ground plane should be continuous and unbroken, providing a low-impedance return path for high-frequency currents. If multiple ground levels are necessary (e.g., digital and analog grounds), they should be connected at a single point to prevent ground loops.
4. **Decoupling Capacitors**: Placing decoupling capacitors as close as possible to the power pins of integrated circuits (ICs) helps to filter out high-frequency noise. The selection of capacitor types (ceramic, tantalum, etc.) and values should be based on the frequency characteristics of the circuit.
5. **Shielding and Filtering**: In cases where EMI is a significant concern, additional measures such as shielding enclosures or ferrite beads on power lines may be employed. Filters can also be integrated into the design to attenuate unwanted frequencies.
By adhering to these layout principles, the performance of switch-mode DC-DC converters can be optimized, leading to reduced noise and improved reliability in various applications.Describes how to layout switch-mode DC-DC converter printed circuit boards (PCBs) to minimize switching noise and EMI.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713