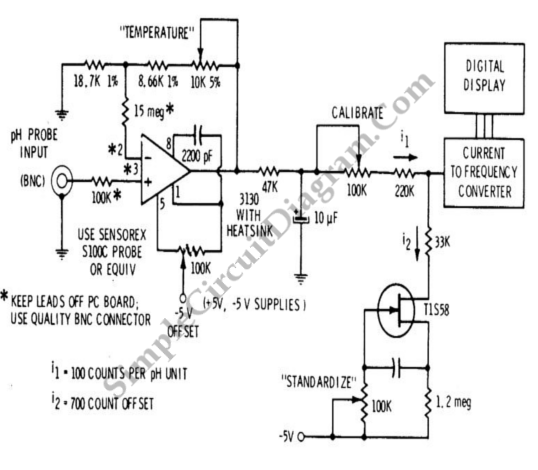
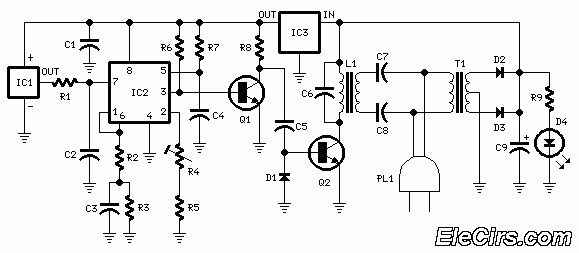
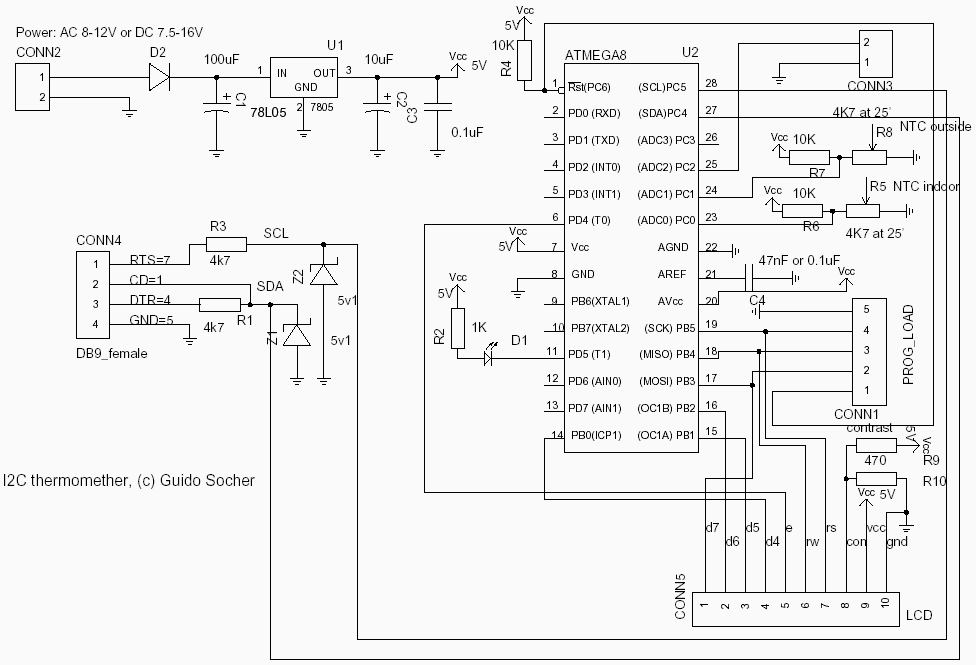
Coulomb meter
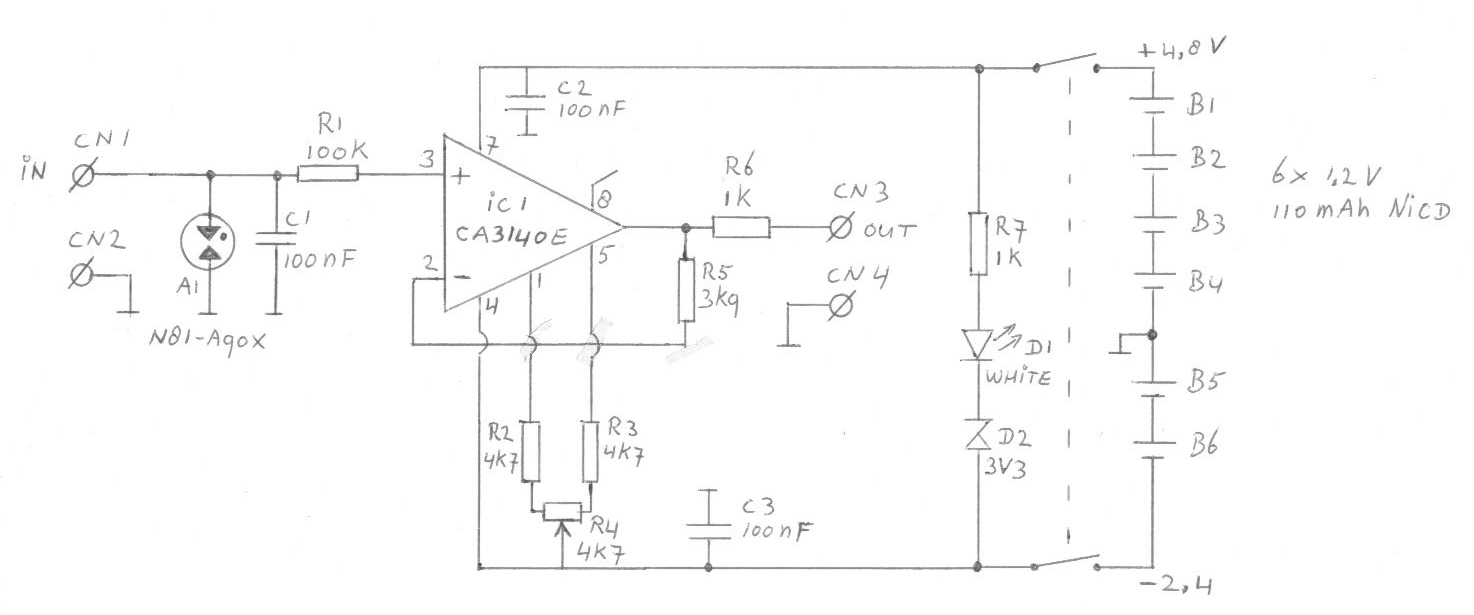
Another cause of voltage drift is the input current of IC1, which slowly charges capacitor C1. This effect is particularly noticeable when the output voltage is approximately 0 volts.
The circuit in question involves an integrated circuit (IC1) whose input current contributes to voltage drift. This phenomenon occurs as the input current gradually charges the capacitor (C1) over time. The charging process of capacitor C1 can lead to an increase in voltage across it, which may affect the overall performance of the circuit, especially when the output voltage is at or near 0 volts.
In practical applications, the behavior of IC1 can be influenced by the characteristics of the capacitor, including its capacitance value and equivalent series resistance (ESR). A capacitor with a higher capacitance may take longer to charge, resulting in a more pronounced voltage drift effect. Conversely, a capacitor with lower ESR can charge more quickly, potentially mitigating the drift.
To analyze this circuit further, it is essential to consider the time constant defined by the product of the resistance in the charging path and the capacitance of C1. This time constant determines how quickly the capacitor charges and can significantly impact the stability of the output voltage. If the time constant is too long, it may lead to instability in applications requiring rapid response times.
In designing circuits where voltage stability is critical, it may be beneficial to implement additional components, such as a feedback mechanism or a voltage regulator, to counteract the effects of the input current on the capacitor. This could help maintain a more stable output voltage across varying conditions and load scenarios.
Furthermore, careful selection of IC1 and C1, along with their respective parameters, can enhance circuit performance and minimize voltage drift, ensuring reliable operation in sensitive electronic applications.Another cause of voltage drift is the input current of IC1, which slowly charges capacitor C1, this can especially be seen when the output voltage is about 0 Volt. 🔗 External reference
The circuit in question involves an integrated circuit (IC1) whose input current contributes to voltage drift. This phenomenon occurs as the input current gradually charges the capacitor (C1) over time. The charging process of capacitor C1 can lead to an increase in voltage across it, which may affect the overall performance of the circuit, especially when the output voltage is at or near 0 volts.
In practical applications, the behavior of IC1 can be influenced by the characteristics of the capacitor, including its capacitance value and equivalent series resistance (ESR). A capacitor with a higher capacitance may take longer to charge, resulting in a more pronounced voltage drift effect. Conversely, a capacitor with lower ESR can charge more quickly, potentially mitigating the drift.
To analyze this circuit further, it is essential to consider the time constant defined by the product of the resistance in the charging path and the capacitance of C1. This time constant determines how quickly the capacitor charges and can significantly impact the stability of the output voltage. If the time constant is too long, it may lead to instability in applications requiring rapid response times.
In designing circuits where voltage stability is critical, it may be beneficial to implement additional components, such as a feedback mechanism or a voltage regulator, to counteract the effects of the input current on the capacitor. This could help maintain a more stable output voltage across varying conditions and load scenarios.
Furthermore, careful selection of IC1 and C1, along with their respective parameters, can enhance circuit performance and minimize voltage drift, ensuring reliable operation in sensitive electronic applications.Another cause of voltage drift is the input current of IC1, which slowly charges capacitor C1, this can especially be seen when the output voltage is about 0 Volt. 🔗 External reference