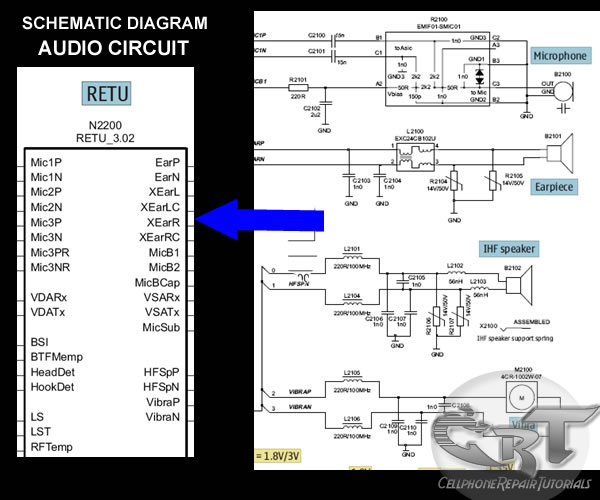
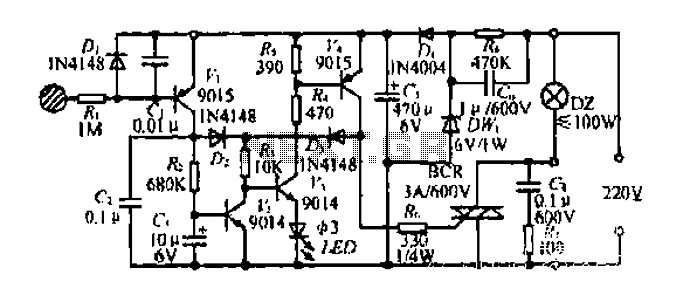
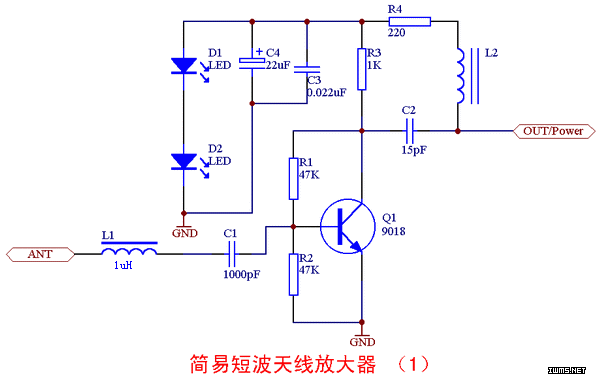
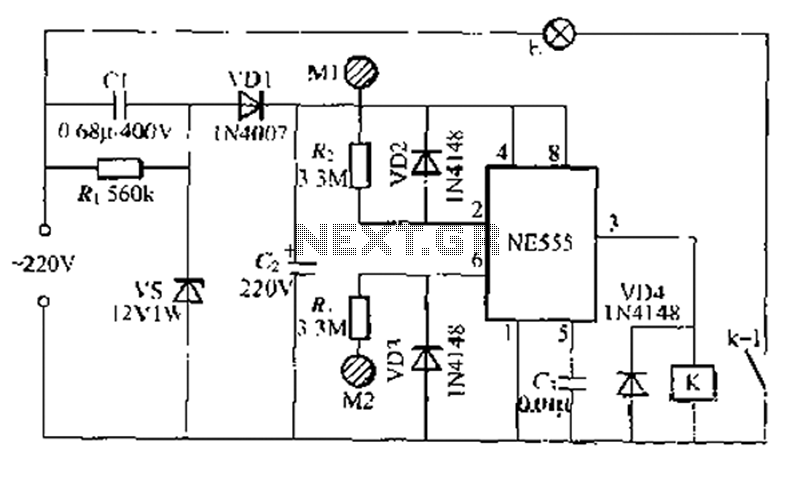
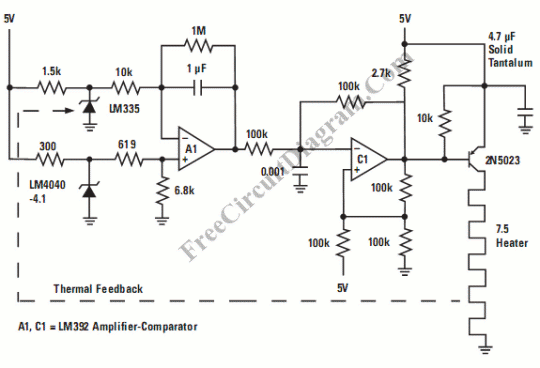
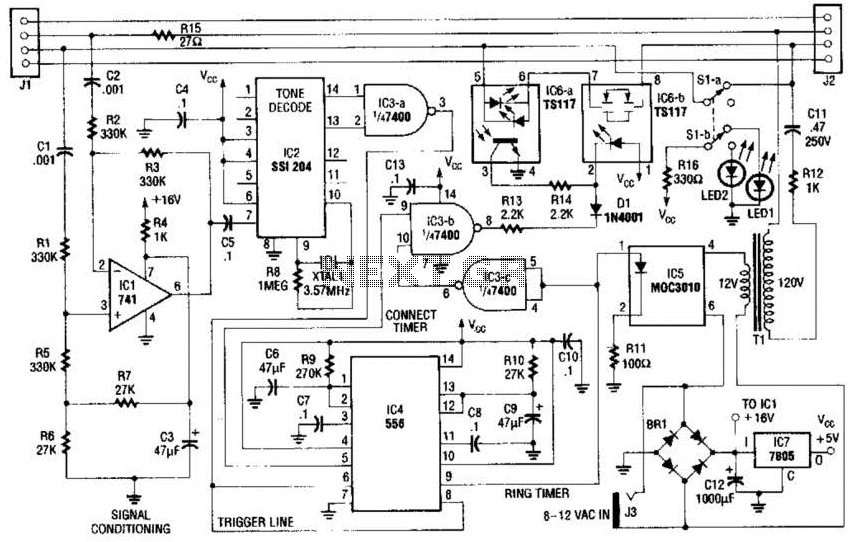
Crystal Oscillator Circuit
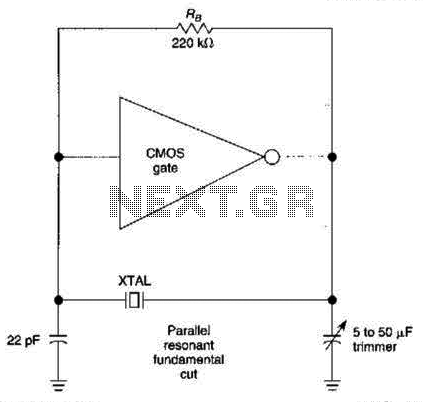
The CMOS amplifier is biased into the linear region by resistor RB. The pi-type crystal network (C1 and C2, and XTAL) provides the 180-degree phase shift at the resonant frequency, which causes the circuit to oscillate.
The described circuit utilizes a CMOS amplifier configured to operate within its linear region, facilitated by the biasing resistor RB. This configuration is essential for ensuring that the amplifier can effectively amplify signals without distortion. The pi-type crystal network comprises two capacitors (C1 and C2) and a crystal oscillator (XTAL), which collectively create a feedback loop that is critical for generating oscillations.
At the resonant frequency, the pi network achieves a 180-degree phase shift. This phase shift is a crucial requirement for sustaining oscillations, as it ensures that the output of the amplifier is in phase opposition to the input, thereby reinforcing the oscillatory behavior. The interaction between the capacitive elements and the crystal oscillator determines the frequency stability and the quality of the oscillation produced.
The design and selection of components within this circuit are vital. The values of capacitors C1 and C2 must be chosen to ensure that the resonant frequency aligns with the desired operating frequency of the oscillator. Additionally, the characteristics of the crystal (XTAL) should match the circuit requirements to provide accurate frequency control and stability.
In summary, this CMOS amplifier circuit exemplifies a classic oscillator design, leveraging the properties of a pi-type network to achieve the necessary phase shift for oscillation, while the biasing provided by resistor RB ensures optimal performance in the linear operating region of the amplifier. The CMOS amplifier is biased into the linear region by resistor RB. The pi-type crystal network (CI and C2, and XTAL) provides the 180 phase shift at the resonant frequency which causes the circuit to oscillate.
The described circuit utilizes a CMOS amplifier configured to operate within its linear region, facilitated by the biasing resistor RB. This configuration is essential for ensuring that the amplifier can effectively amplify signals without distortion. The pi-type crystal network comprises two capacitors (C1 and C2) and a crystal oscillator (XTAL), which collectively create a feedback loop that is critical for generating oscillations.
At the resonant frequency, the pi network achieves a 180-degree phase shift. This phase shift is a crucial requirement for sustaining oscillations, as it ensures that the output of the amplifier is in phase opposition to the input, thereby reinforcing the oscillatory behavior. The interaction between the capacitive elements and the crystal oscillator determines the frequency stability and the quality of the oscillation produced.
The design and selection of components within this circuit are vital. The values of capacitors C1 and C2 must be chosen to ensure that the resonant frequency aligns with the desired operating frequency of the oscillator. Additionally, the characteristics of the crystal (XTAL) should match the circuit requirements to provide accurate frequency control and stability.
In summary, this CMOS amplifier circuit exemplifies a classic oscillator design, leveraging the properties of a pi-type network to achieve the necessary phase shift for oscillation, while the biasing provided by resistor RB ensures optimal performance in the linear operating region of the amplifier. The CMOS amplifier is biased into the linear region by resistor RB. The pi-type crystal network (CI and C2, and XTAL) provides the 180 phase shift at the resonant frequency which causes the circuit to oscillate.