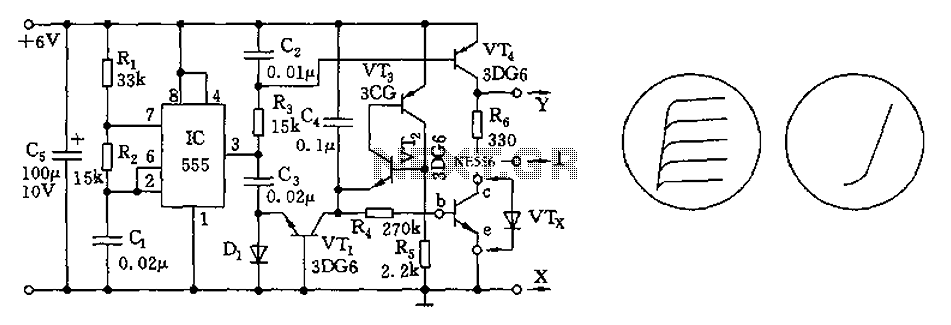
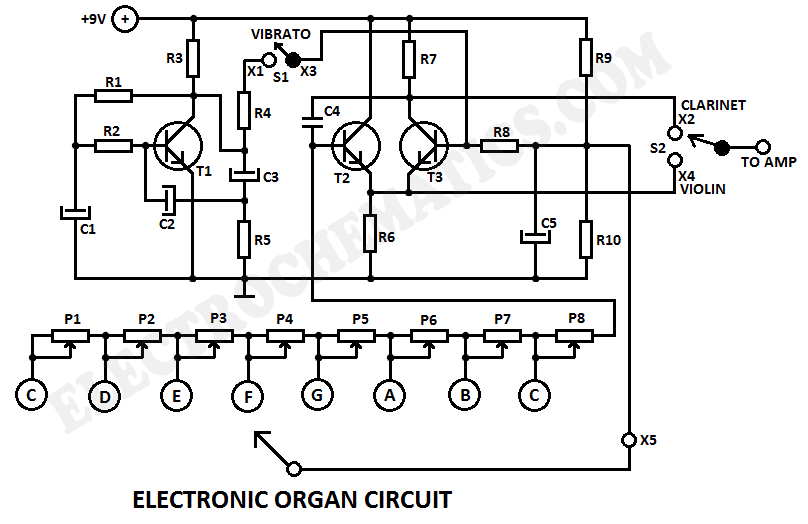
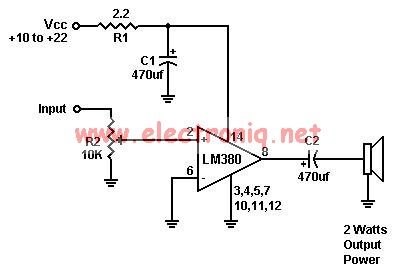
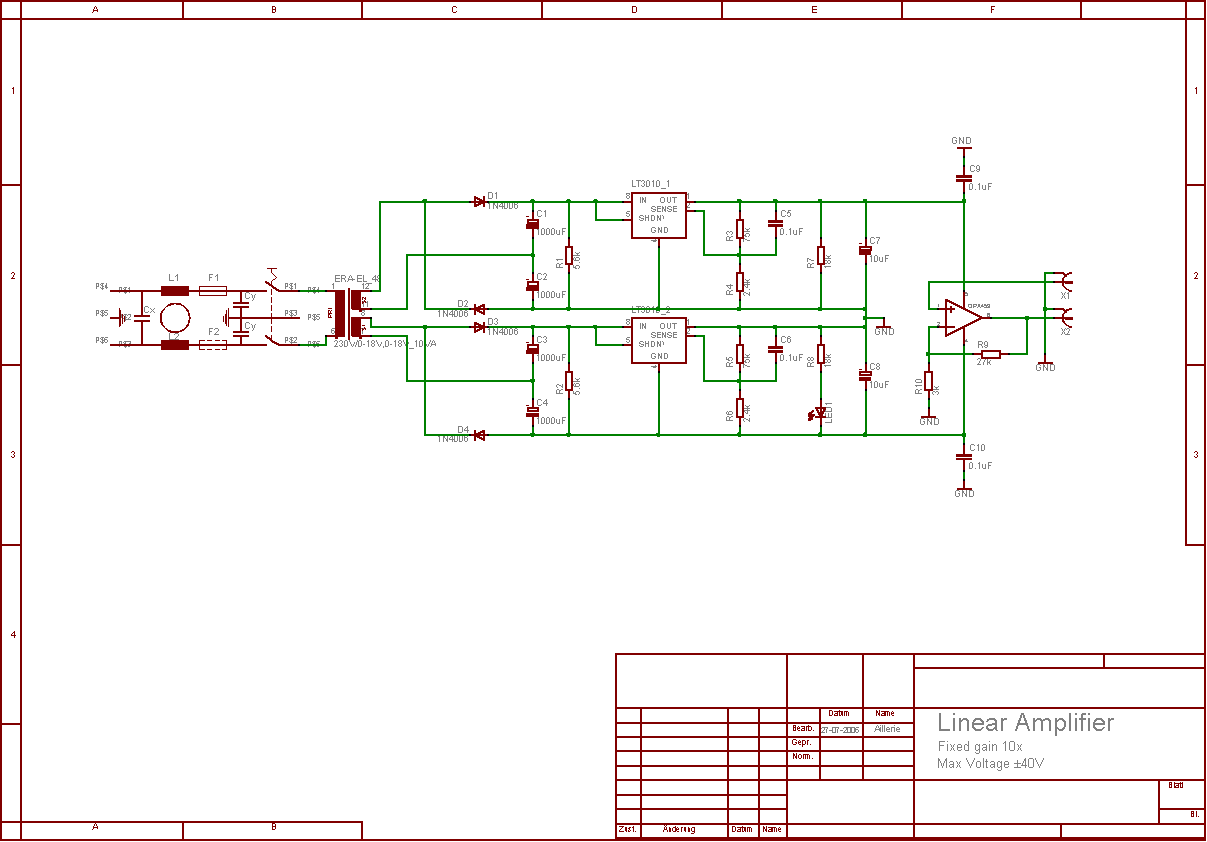
DC exciter excitation mode circuit
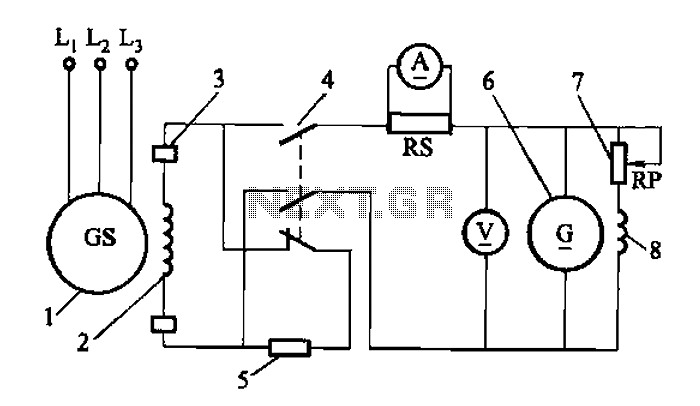
Adjust the exciter field rheostat RP to change the exciter output voltage, which in turn adjusts the generator excitation current, allowing for modifications to the generator output voltage for various purposes.
The exciter field rheostat (RP) is a critical component in the control of generator output voltage. By adjusting this rheostat, the resistance in the exciter circuit can be varied, which directly influences the voltage produced by the exciter. This change in exciter output voltage modifies the excitation current supplied to the generator's rotor, which is essential for maintaining stable voltage levels under varying load conditions.
In a typical setup, the exciter field rheostat is connected in series with the exciter field winding. When the rheostat is adjusted to a higher resistance, the current through the exciter winding decreases, leading to a lower magnetic field strength in the rotor. Consequently, this results in a decrease in the voltage output of the generator. Conversely, reducing the resistance of the rheostat increases the exciter output voltage, enhancing the excitation current and thereby increasing the generator's output voltage.
For effective operation, the exciter field rheostat should be calibrated correctly to ensure that the generator can respond adequately to load changes. It is important to monitor the excitation current and generator output voltage regularly to ensure that they remain within specified limits, preventing potential damage to the generator and connected systems. Additionally, the rheostat should be selected based on the rated capacity of the generator and the expected variations in load to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Proper maintenance and periodic testing of the rheostat's functionality are also essential to ensure long-term operational effectiveness.Adjust the exciter field rheostat RP, can change the exciter output voltage to adjust the generator excitation current section to achieve the change the generator output voltag e purposes.
The exciter field rheostat (RP) is a critical component in the control of generator output voltage. By adjusting this rheostat, the resistance in the exciter circuit can be varied, which directly influences the voltage produced by the exciter. This change in exciter output voltage modifies the excitation current supplied to the generator's rotor, which is essential for maintaining stable voltage levels under varying load conditions.
In a typical setup, the exciter field rheostat is connected in series with the exciter field winding. When the rheostat is adjusted to a higher resistance, the current through the exciter winding decreases, leading to a lower magnetic field strength in the rotor. Consequently, this results in a decrease in the voltage output of the generator. Conversely, reducing the resistance of the rheostat increases the exciter output voltage, enhancing the excitation current and thereby increasing the generator's output voltage.
For effective operation, the exciter field rheostat should be calibrated correctly to ensure that the generator can respond adequately to load changes. It is important to monitor the excitation current and generator output voltage regularly to ensure that they remain within specified limits, preventing potential damage to the generator and connected systems. Additionally, the rheostat should be selected based on the rated capacity of the generator and the expected variations in load to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Proper maintenance and periodic testing of the rheostat's functionality are also essential to ensure long-term operational effectiveness.Adjust the exciter field rheostat RP, can change the exciter output voltage to adjust the generator excitation current section to achieve the change the generator output voltag e purposes.