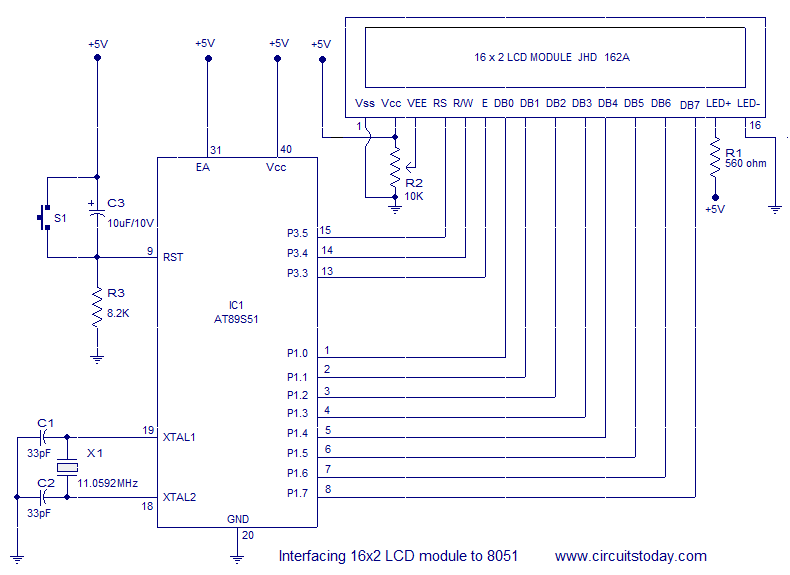
555 transistor characteristic curve tracer circuit diagram
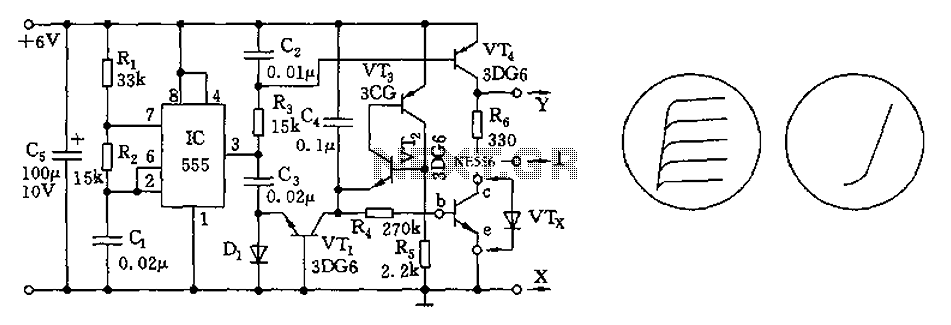
The transistor characteristic curve tracer circuit depicted in Figure 555 illustrates the characteristics of a transistor. It utilizes two voltages: a step wave applied to the base (b) to generate different base currents (Ib), and a sawtooth waveform at the collector (c) to represent the collector current (Ic) versus the supply voltage (Vcc) characteristic curve. The circuit incorporates a 555 timer and components R1, R2, and C1 to form an astable multivibrator, with an oscillation frequency calculated as f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2R2) * C1), where the parameter f is set to approximately 1100 Hz. The capacitor C2 and resistor R3 create an integrating circuit that generates a ramp signal, which is then output through the emitter follower VT4 to the vertical (Y) input of an oscilloscope, while also being applied to the collector (c) of the test transistor. Additional components, including C3, D1, VT1 to VT3, and C4, form a ladder wave generator. After every five oscillation cycles, the charging voltage on C4 causes VT3 to conduct, leading to the discharge of C4 and the formation of five distinct steps. A single charge on C4 results in a voltage drop at the emitter of VT2, creating a step wave that is applied to the base (b) of the test transistor. The oscilloscope is then connected to display the IV characteristic curve shown in Figure b.
The transistor characteristic curve tracer circuit is designed to provide a visual representation of a transistor's performance across various operating conditions. The astable multivibrator configuration formed by the 555 timer and passive components (R1, R2, and C1) generates a continuous square wave signal. This square wave signal modulates the base current (Ib) of the transistor under test, allowing for the examination of its response characteristics.
The sawtooth waveform produced by the integrating circuit (C2 and R3) is crucial in generating a linear ramp voltage that varies over time, which is then used to modulate the collector current (Ic) of the transistor. By connecting the output of the emitter follower (VT4) to an oscilloscope, the user can observe the changes in Ic as the base current is varied, effectively plotting the Ic-Vcc characteristic curve of the transistor.
The ladder wave generator, composed of capacitors (C3, C4) and transistors (VT1 to VT3), facilitates the creation of discrete voltage steps. These steps correspond to different operational states of the transistor, allowing for a detailed analysis of its switching behavior. The controlled charging and discharging of C4 ensure that the circuit can produce a series of well-defined steps, which are essential for accurately mapping the transistor's characteristics.
Finally, the circuit's output is designed to be connected to an oscilloscope, providing a clear visual representation of the IV characteristic curve. This setup allows engineers and technicians to evaluate the performance parameters of transistors, such as current gain, saturation voltages, and cutoff regions, aiding in the selection and application of transistors in various electronic designs. As shown in Figure 555 is the transistor characteristic curve tracer circuit depict transistor characteristics, to have two voltages, one step wave is applied b pole for genera ting different Ib, the second is on the sawtooth c pole, its period staircase corresponds to depict Ic-Vcc characteristic curve. As illustrated, 555 and R1, R2, C1 composition astable multivibrator, the oscillation frequency f 1.44 (R1 + 2R2) C1.
Illustration parameter f 1100Hz. C2, R3 composed of the integrating circuit for generating a ramp, through VT4 emitter follower output, added to the oscilloscope vertical Y and enter the test tube c pole. C3, D1, VT1 ~ VT3, C4 and other components ladder wave generator, every five oscillation cycles, charging voltage on C4 to make VT3 conduction, C4 discharge, formed five steps.
C4 on a single charge, VT2 emitter voltage drops that form a step. Step wave through R4 is added to the test tube b pole. The test tube is figure VTx. After the oscilloscope connected to an IV characteristic curve shown in Figure b.
The transistor characteristic curve tracer circuit is designed to provide a visual representation of a transistor's performance across various operating conditions. The astable multivibrator configuration formed by the 555 timer and passive components (R1, R2, and C1) generates a continuous square wave signal. This square wave signal modulates the base current (Ib) of the transistor under test, allowing for the examination of its response characteristics.
The sawtooth waveform produced by the integrating circuit (C2 and R3) is crucial in generating a linear ramp voltage that varies over time, which is then used to modulate the collector current (Ic) of the transistor. By connecting the output of the emitter follower (VT4) to an oscilloscope, the user can observe the changes in Ic as the base current is varied, effectively plotting the Ic-Vcc characteristic curve of the transistor.
The ladder wave generator, composed of capacitors (C3, C4) and transistors (VT1 to VT3), facilitates the creation of discrete voltage steps. These steps correspond to different operational states of the transistor, allowing for a detailed analysis of its switching behavior. The controlled charging and discharging of C4 ensure that the circuit can produce a series of well-defined steps, which are essential for accurately mapping the transistor's characteristics.
Finally, the circuit's output is designed to be connected to an oscilloscope, providing a clear visual representation of the IV characteristic curve. This setup allows engineers and technicians to evaluate the performance parameters of transistors, such as current gain, saturation voltages, and cutoff regions, aiding in the selection and application of transistors in various electronic designs. As shown in Figure 555 is the transistor characteristic curve tracer circuit depict transistor characteristics, to have two voltages, one step wave is applied b pole for genera ting different Ib, the second is on the sawtooth c pole, its period staircase corresponds to depict Ic-Vcc characteristic curve. As illustrated, 555 and R1, R2, C1 composition astable multivibrator, the oscillation frequency f 1.44 (R1 + 2R2) C1.
Illustration parameter f 1100Hz. C2, R3 composed of the integrating circuit for generating a ramp, through VT4 emitter follower output, added to the oscilloscope vertical Y and enter the test tube c pole. C3, D1, VT1 ~ VT3, C4 and other components ladder wave generator, every five oscillation cycles, charging voltage on C4 to make VT3 conduction, C4 discharge, formed five steps.
C4 on a single charge, VT2 emitter voltage drops that form a step. Step wave through R4 is added to the test tube b pole. The test tube is figure VTx. After the oscilloscope connected to an IV characteristic curve shown in Figure b.