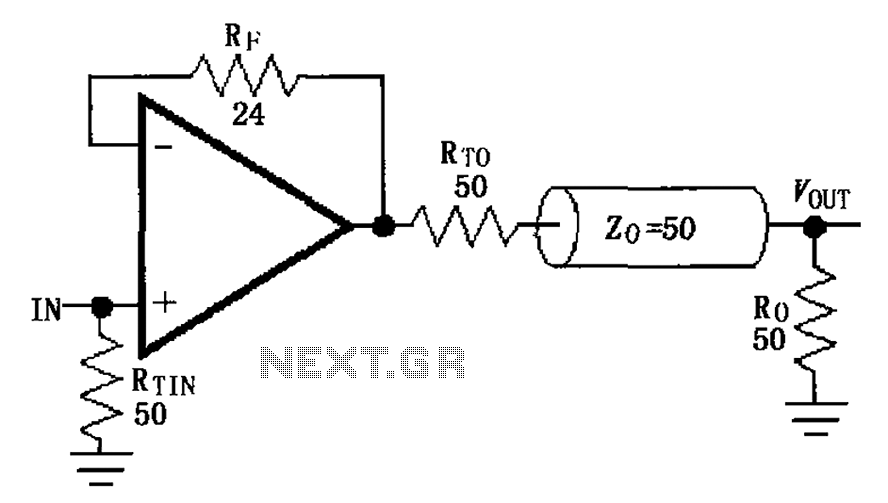
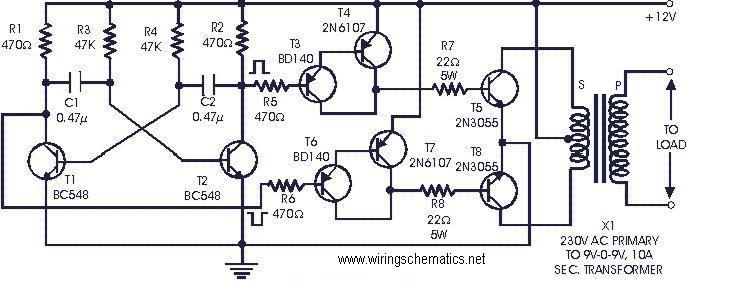
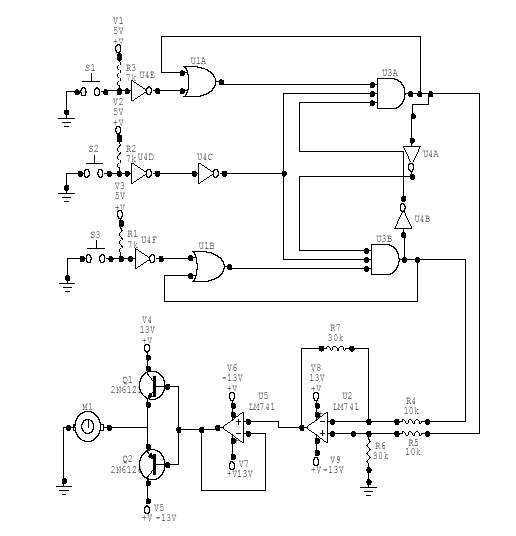
DC Motor speed control circuit
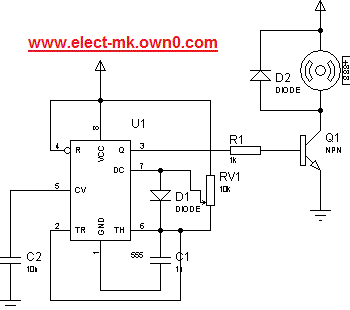
Provision in the speed of a small engine DC motor speed control circuit using a small rheostat for control in the DC motor circuit diagram.
The circuit for controlling the speed of a small DC motor typically incorporates a rheostat as a variable resistor, allowing for manual adjustment of the motor's speed. The basic configuration includes a DC motor, a power supply, and a rheostat connected in series with the motor.
When the rheostat is adjusted, it alters the resistance in the circuit, which in turn modifies the voltage across the motor. As the resistance increases, the voltage supplied to the motor decreases, resulting in a reduction of the motor's speed. Conversely, reducing the resistance allows more voltage to reach the motor, increasing its speed.
In a typical schematic, the DC motor is represented by a circle with terminals labeled accordingly, while the rheostat is depicted as a resistor symbol with an adjustable slider. The power supply is often represented by a pair of parallel lines, indicating the positive and negative terminals.
It is important to consider the specifications of the rheostat to ensure it can handle the current required by the motor without overheating. Additionally, the power supply voltage should match the motor's rated voltage to prevent damage.
For applications requiring more precise speed control or efficiency, alternatives such as pulse width modulation (PWM) circuits can be implemented. However, for basic speed control needs, a simple rheostat in series with the motor provides an effective and straightforward solution.Provision in the speed of a small engine DC Motor speed control circuit of Service By a small rheostat control In DC motor Circuit diagram. 🔗 External reference
The circuit for controlling the speed of a small DC motor typically incorporates a rheostat as a variable resistor, allowing for manual adjustment of the motor's speed. The basic configuration includes a DC motor, a power supply, and a rheostat connected in series with the motor.
When the rheostat is adjusted, it alters the resistance in the circuit, which in turn modifies the voltage across the motor. As the resistance increases, the voltage supplied to the motor decreases, resulting in a reduction of the motor's speed. Conversely, reducing the resistance allows more voltage to reach the motor, increasing its speed.
In a typical schematic, the DC motor is represented by a circle with terminals labeled accordingly, while the rheostat is depicted as a resistor symbol with an adjustable slider. The power supply is often represented by a pair of parallel lines, indicating the positive and negative terminals.
It is important to consider the specifications of the rheostat to ensure it can handle the current required by the motor without overheating. Additionally, the power supply voltage should match the motor's rated voltage to prevent damage.
For applications requiring more precise speed control or efficiency, alternatives such as pulse width modulation (PWM) circuits can be implemented. However, for basic speed control needs, a simple rheostat in series with the motor provides an effective and straightforward solution.Provision in the speed of a small engine DC Motor speed control circuit of Service By a small rheostat control In DC motor Circuit diagram. 🔗 External reference