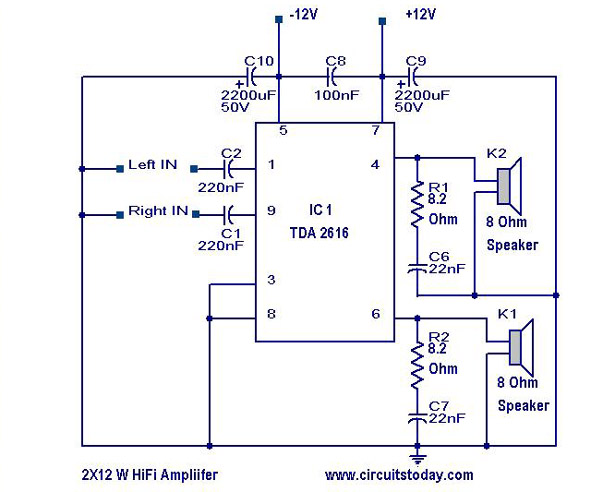
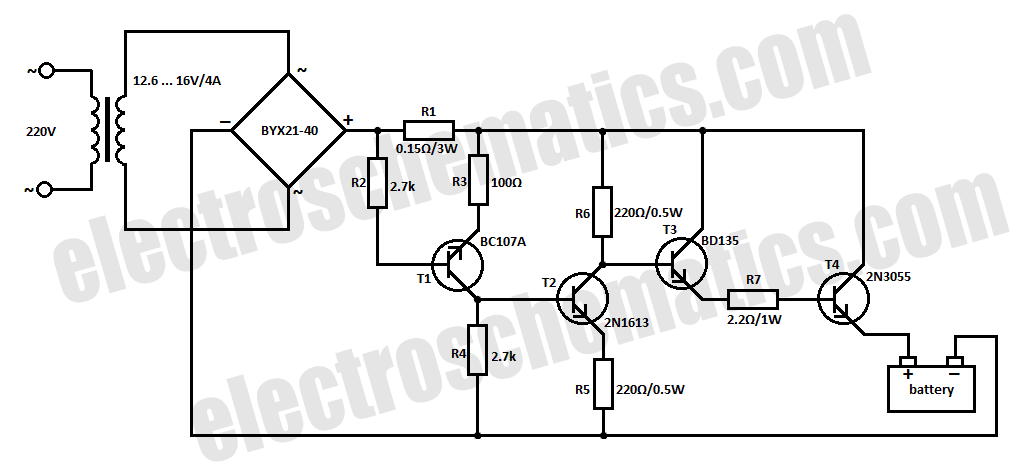
Delay circuit with NE555 timer
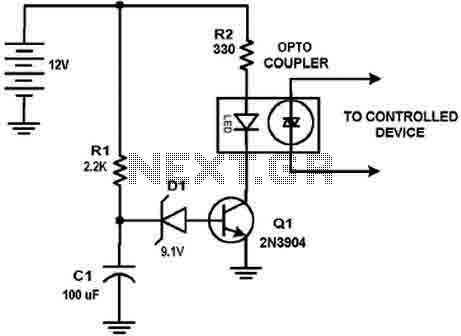
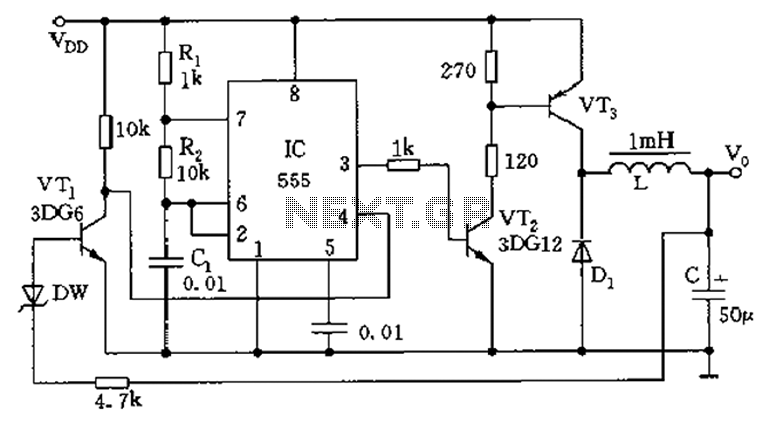
This circuit design was used to switch on device via a LED photocell arrangement (optocoupler) using components R1, C1, D1 and Q1. It produces a delay on powering up to ensure correct sequencing of certain equipment. A very simple delay timer using a single transistor and an R-C timing circuit. More: C1 charges toward the power supply voltage (12 volts) through R1. When the voltage reaches 9.1 volts, zener diode D1 conducts, forward biasing the transistor Q1, turning it on. At about 9.8 volts, the zener diode and base of Q1 conduct heavily, taking the charging current from C1. When power is turned off, the circuit is reset by C1 discharging through R1 into the now zero voltage supply. The time can be varied by changing R1, C1.
This circuit employs a simple delay mechanism to control the activation of a device through an LED photocell arrangement, utilizing an optocoupler for isolation between the control and power circuits. The primary components involved in this design include a resistor (R1), a capacitor (C1), a zener diode (D1), and a transistor (Q1).
The operation begins with capacitor C1 charging through resistor R1 when power is applied. The circuit is designed for a nominal supply voltage of 12 volts. As C1 charges, the voltage across it gradually increases. Once this voltage reaches approximately 9.1 volts, zener diode D1 becomes conductive. This conduction forward-biases transistor Q1, allowing it to turn on and activate the connected load or device.
As the voltage continues to rise and reaches about 9.8 volts, both the zener diode and the base of transistor Q1 conduct heavily, diverting the charging current away from C1. This mechanism ensures that the circuit provides a delay before the output is activated, allowing for proper sequencing of connected equipment, which is crucial in applications where timing is essential.
When the power supply is turned off, the circuit resets itself. Capacitor C1 discharges through resistor R1, returning the voltage to zero and preparing the circuit for the next activation cycle. The time delay before the device is powered on can be adjusted by changing the values of R1 and C1, providing flexibility in the timing characteristics of the circuit.
This design exemplifies a straightforward yet effective approach to creating a delay timer using basic electronic components, making it suitable for various applications where controlled sequencing is required.This circuit design was used to switch on device via a LED photocell arrangement (optocoupler) using components R1, C1, D1 and Q1. It produces a delay on powering up to ensure correct sequencing of certain equipment. A very simple delay timer using a single transistor and an R-C timing circuit. C1 charges toward the power supply voltage (12 volts) through R1. When the voltage reaches 9.1 volts, zener diode D1 conducts, forward biasing the transistor Q1, turning it on. At about 9.8 volts, the zener diode and base of Q1 conduct heavily, taking the charging current from C1.
When power is turned off, the circuit is reset by C1 discharging through R1 into the now zero voltage supply. The time can be varied by changing R1, C1. 🔗 External reference
This circuit employs a simple delay mechanism to control the activation of a device through an LED photocell arrangement, utilizing an optocoupler for isolation between the control and power circuits. The primary components involved in this design include a resistor (R1), a capacitor (C1), a zener diode (D1), and a transistor (Q1).
The operation begins with capacitor C1 charging through resistor R1 when power is applied. The circuit is designed for a nominal supply voltage of 12 volts. As C1 charges, the voltage across it gradually increases. Once this voltage reaches approximately 9.1 volts, zener diode D1 becomes conductive. This conduction forward-biases transistor Q1, allowing it to turn on and activate the connected load or device.
As the voltage continues to rise and reaches about 9.8 volts, both the zener diode and the base of transistor Q1 conduct heavily, diverting the charging current away from C1. This mechanism ensures that the circuit provides a delay before the output is activated, allowing for proper sequencing of connected equipment, which is crucial in applications where timing is essential.
When the power supply is turned off, the circuit resets itself. Capacitor C1 discharges through resistor R1, returning the voltage to zero and preparing the circuit for the next activation cycle. The time delay before the device is powered on can be adjusted by changing the values of R1 and C1, providing flexibility in the timing characteristics of the circuit.
This design exemplifies a straightforward yet effective approach to creating a delay timer using basic electronic components, making it suitable for various applications where controlled sequencing is required.This circuit design was used to switch on device via a LED photocell arrangement (optocoupler) using components R1, C1, D1 and Q1. It produces a delay on powering up to ensure correct sequencing of certain equipment. A very simple delay timer using a single transistor and an R-C timing circuit. C1 charges toward the power supply voltage (12 volts) through R1. When the voltage reaches 9.1 volts, zener diode D1 conducts, forward biasing the transistor Q1, turning it on. At about 9.8 volts, the zener diode and base of Q1 conduct heavily, taking the charging current from C1.
When power is turned off, the circuit is reset by C1 discharging through R1 into the now zero voltage supply. The time can be varied by changing R1, C1. 🔗 External reference