DEVIATION METER
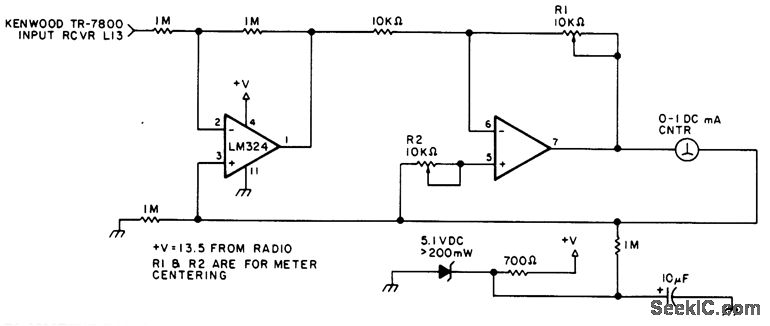
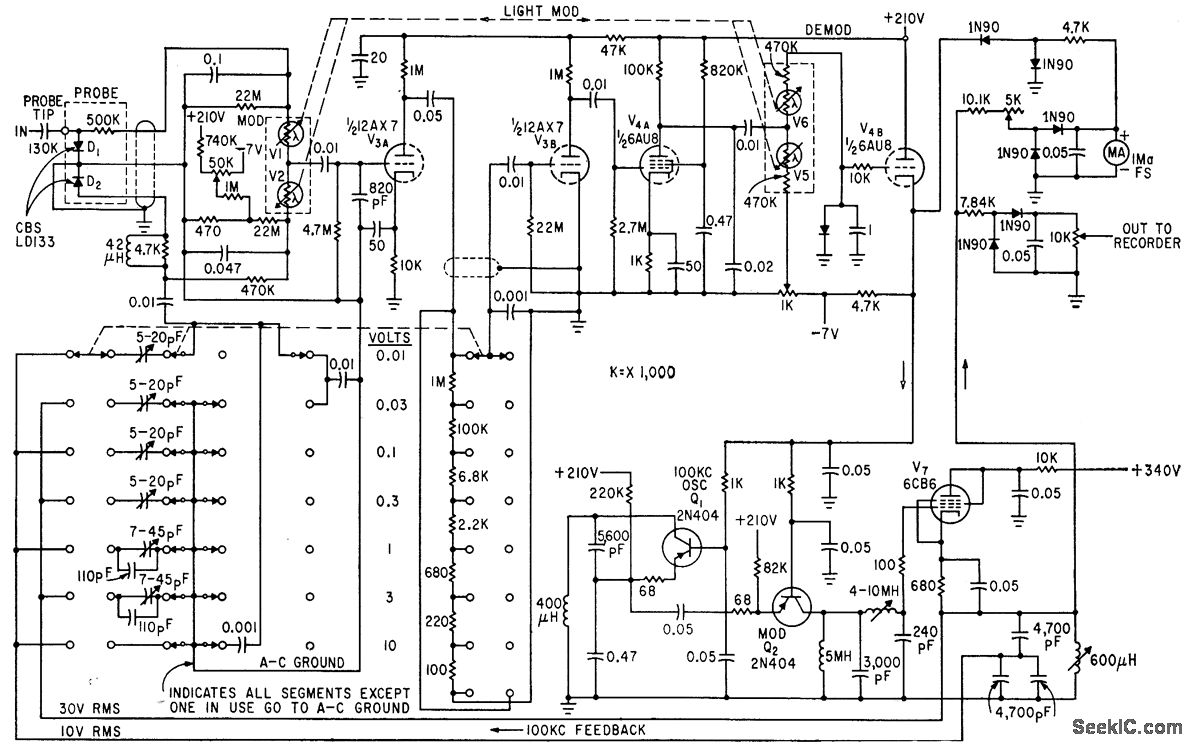
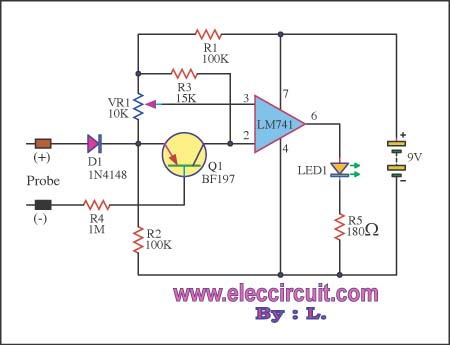
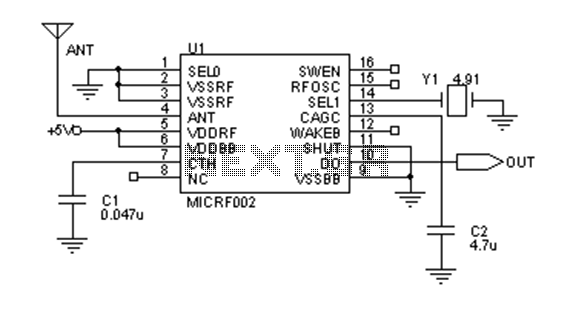
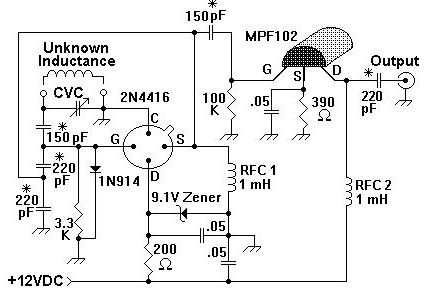
This circuit can be utilized in most FM VHF receivers, with the connection made from the FM discriminator. Each transmitted signal has a unique deviation signature, which can assist in identifying jammers.
The described circuit is designed for integration into FM VHF receivers, serving as a tool for signal analysis and jamming detection. The connection point is established at the FM discriminator, a critical component responsible for demodulating frequency-modulated signals. By tapping into this point, the circuit can monitor the deviation of incoming signals.
In FM communication, each transmitted signal is characterized by a specific deviation from the carrier frequency, which is determined by the modulation of the signal. This unique deviation signature allows for the differentiation of signals even in the presence of interference. The circuit exploits this property to detect and analyze the characteristics of various signals, making it particularly useful for identifying and locating jamming sources.
The circuit may incorporate elements such as bandpass filters to isolate the desired frequency range, amplifiers to boost the signal strength, and a microcontroller or dedicated processing unit to analyze the deviation signatures. The output can be visualized through an oscilloscope or transmitted to a computing device for further analysis.
In summary, this circuit provides a robust solution for monitoring FM VHF signals, enabling users to distinguish between legitimate transmissions and potential jamming attempts based on unique deviation signatures. Its application is essential in scenarios where signal integrity is critical and interference must be identified and mitigated.You can use this circuit in most FM VHF receivers; the hookup is off the FM discriminator. Because every signal transmitted has its own deviation signature, this can be a red plusin hunting jammers 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is designed for integration into FM VHF receivers, serving as a tool for signal analysis and jamming detection. The connection point is established at the FM discriminator, a critical component responsible for demodulating frequency-modulated signals. By tapping into this point, the circuit can monitor the deviation of incoming signals.
In FM communication, each transmitted signal is characterized by a specific deviation from the carrier frequency, which is determined by the modulation of the signal. This unique deviation signature allows for the differentiation of signals even in the presence of interference. The circuit exploits this property to detect and analyze the characteristics of various signals, making it particularly useful for identifying and locating jamming sources.
The circuit may incorporate elements such as bandpass filters to isolate the desired frequency range, amplifiers to boost the signal strength, and a microcontroller or dedicated processing unit to analyze the deviation signatures. The output can be visualized through an oscilloscope or transmitted to a computing device for further analysis.
In summary, this circuit provides a robust solution for monitoring FM VHF signals, enabling users to distinguish between legitimate transmissions and potential jamming attempts based on unique deviation signatures. Its application is essential in scenarios where signal integrity is critical and interference must be identified and mitigated.You can use this circuit in most FM VHF receivers; the hookup is off the FM discriminator. Because every signal transmitted has its own deviation signature, this can be a red plusin hunting jammers 🔗 External reference