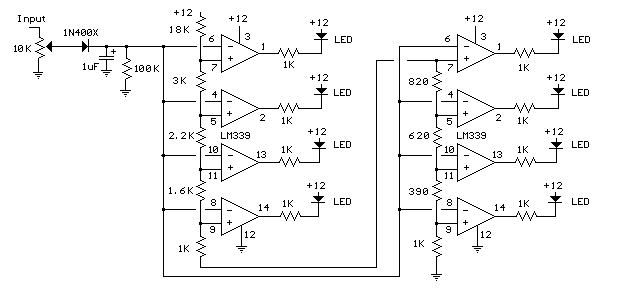
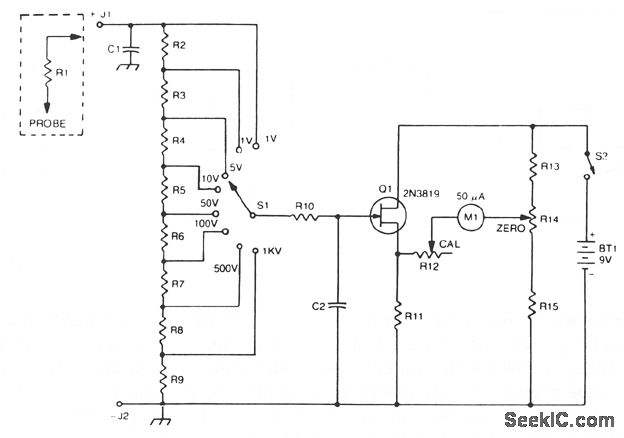
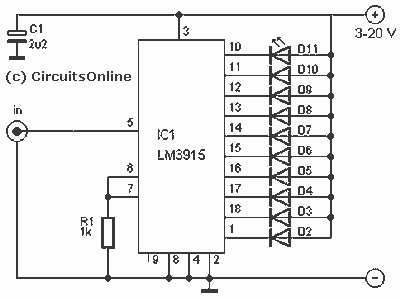
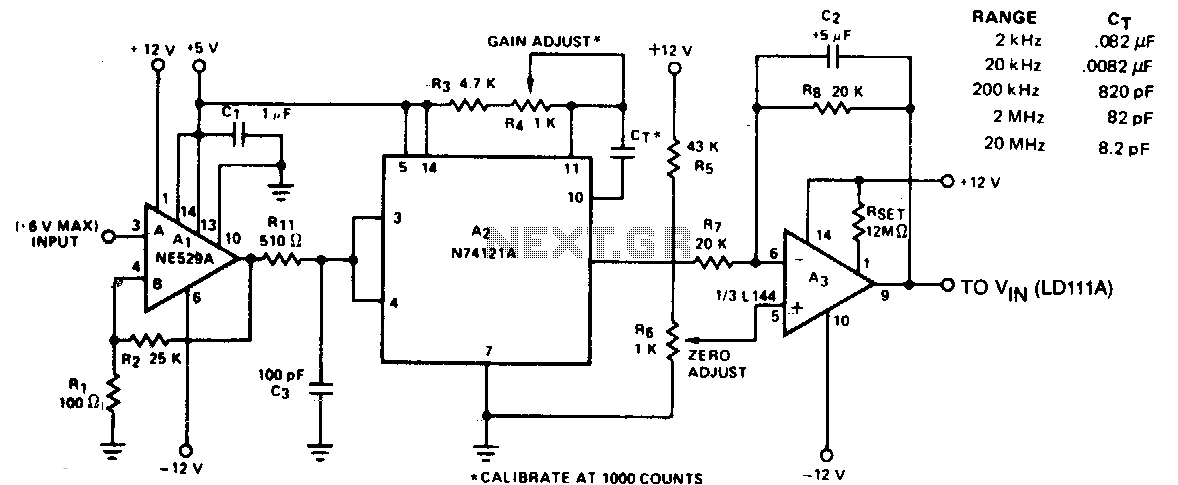
inductance meter
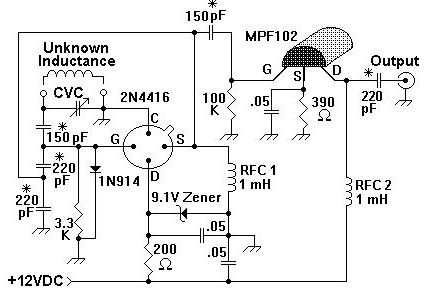
A device for measuring inductance. Over the years, articles describing devices for measuring inductance have appeared in QST and elsewhere, but none of them were suitable, so a new device has been developed.
The inductance measurement device is designed to provide accurate readings of inductance values across a range of inductive components. The core of the device typically consists of an oscillator circuit that generates a high-frequency signal. This signal is applied to the inductor under test, and the resulting current and voltage waveforms are analyzed to determine the inductance.
Key components of the circuit include an operational amplifier configured as a voltage comparator to measure the phase shift introduced by the inductor. A microcontroller or digital signal processor (DSP) can be used to process the signals and calculate the inductance based on the frequency response. The device may also incorporate a display module, such as an LCD or LED, to present the measured inductance value to the user.
Furthermore, a user interface comprising buttons or a touchscreen could allow the operator to select different measurement ranges or modes, enhancing the functionality of the device. Calibration features may also be included to ensure accuracy across a wide range of inductance values.
Power supply considerations are crucial, with options for battery operation or external power sources. Proper filtering and decoupling capacitors should be implemented to minimize noise and ensure stable operation of the measurement circuit.
Overall, this inductance measurement device represents a comprehensive solution for hobbyists and professionals alike, offering precision and versatility in the evaluation of inductive components.A device for measuring inductance Over the years, articles describing devices for measuring inductance have appeared in QST, and elsewhere, but none of them were just right for me, so I have developed .. 🔗 External reference
The inductance measurement device is designed to provide accurate readings of inductance values across a range of inductive components. The core of the device typically consists of an oscillator circuit that generates a high-frequency signal. This signal is applied to the inductor under test, and the resulting current and voltage waveforms are analyzed to determine the inductance.
Key components of the circuit include an operational amplifier configured as a voltage comparator to measure the phase shift introduced by the inductor. A microcontroller or digital signal processor (DSP) can be used to process the signals and calculate the inductance based on the frequency response. The device may also incorporate a display module, such as an LCD or LED, to present the measured inductance value to the user.
Furthermore, a user interface comprising buttons or a touchscreen could allow the operator to select different measurement ranges or modes, enhancing the functionality of the device. Calibration features may also be included to ensure accuracy across a wide range of inductance values.
Power supply considerations are crucial, with options for battery operation or external power sources. Proper filtering and decoupling capacitors should be implemented to minimize noise and ensure stable operation of the measurement circuit.
Overall, this inductance measurement device represents a comprehensive solution for hobbyists and professionals alike, offering precision and versatility in the evaluation of inductive components.A device for measuring inductance Over the years, articles describing devices for measuring inductance have appeared in QST, and elsewhere, but none of them were just right for me, so I have developed .. 🔗 External reference