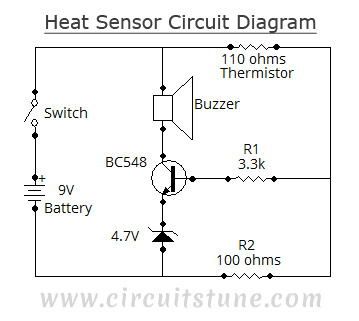
Differential Temperature Sensor
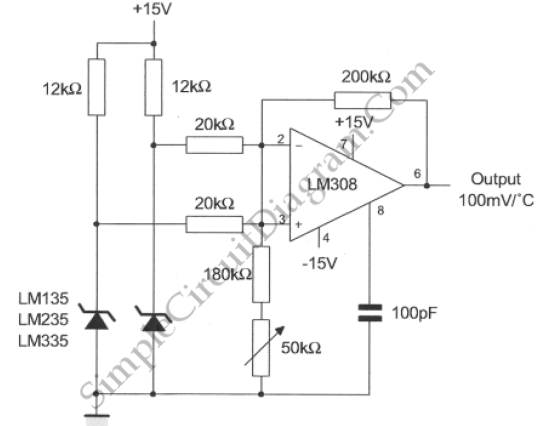
A differential temperature sensor is employed to measure the temperature difference between two distinct areas. The schematic diagram of the circuit is provided for reference.
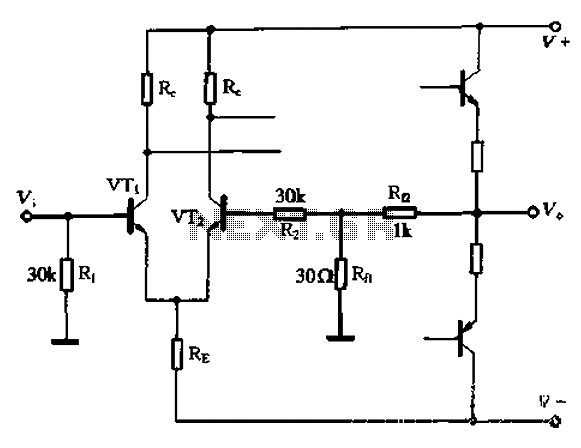
The differential temperature sensor circuit typically consists of two temperature sensing elements, such as thermocouples or thermistors, positioned in separate locations. These sensors generate voltage outputs that are proportional to the temperature of their respective environments. The circuit is designed to amplify the difference in voltage between the two sensors, effectively providing a measurement of the temperature differential.
In a typical configuration, the outputs from the temperature sensors are fed into a differential amplifier. This amplifier is configured to subtract one voltage from the other, allowing for precise measurement of the temperature difference. The gain of the amplifier can be adjusted to ensure that the output signal is within a usable range for further processing or display.
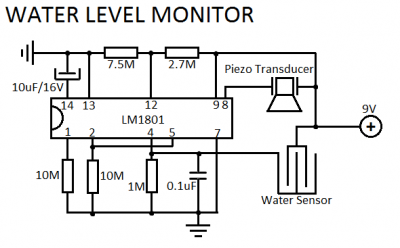
Additional components may include resistors for biasing, capacitors for filtering noise, and possibly a microcontroller or analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital output. The output from the differential amplifier can be displayed on an LCD or sent to a data acquisition system for monitoring and analysis.
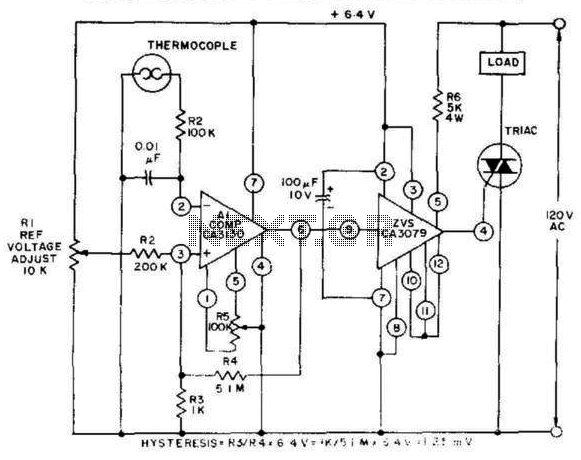
The schematic diagram would illustrate the connections between the sensors, the differential amplifier, and any additional circuitry necessary for the operation of the sensor system. Proper layout and component selection are critical for minimizing errors due to noise and ensuring accurate temperature measurements.Differential temperature sensor is used to measure temperature difference in two different area. Here is the schematic diagram of the circuit: Please note.. 🔗 External reference
The differential temperature sensor circuit typically consists of two temperature sensing elements, such as thermocouples or thermistors, positioned in separate locations. These sensors generate voltage outputs that are proportional to the temperature of their respective environments. The circuit is designed to amplify the difference in voltage between the two sensors, effectively providing a measurement of the temperature differential.
In a typical configuration, the outputs from the temperature sensors are fed into a differential amplifier. This amplifier is configured to subtract one voltage from the other, allowing for precise measurement of the temperature difference. The gain of the amplifier can be adjusted to ensure that the output signal is within a usable range for further processing or display.
Additional components may include resistors for biasing, capacitors for filtering noise, and possibly a microcontroller or analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital output. The output from the differential amplifier can be displayed on an LCD or sent to a data acquisition system for monitoring and analysis.
The schematic diagram would illustrate the connections between the sensors, the differential amplifier, and any additional circuitry necessary for the operation of the sensor system. Proper layout and component selection are critical for minimizing errors due to noise and ensuring accurate temperature measurements.Differential temperature sensor is used to measure temperature difference in two different area. Here is the schematic diagram of the circuit: Please note.. 🔗 External reference