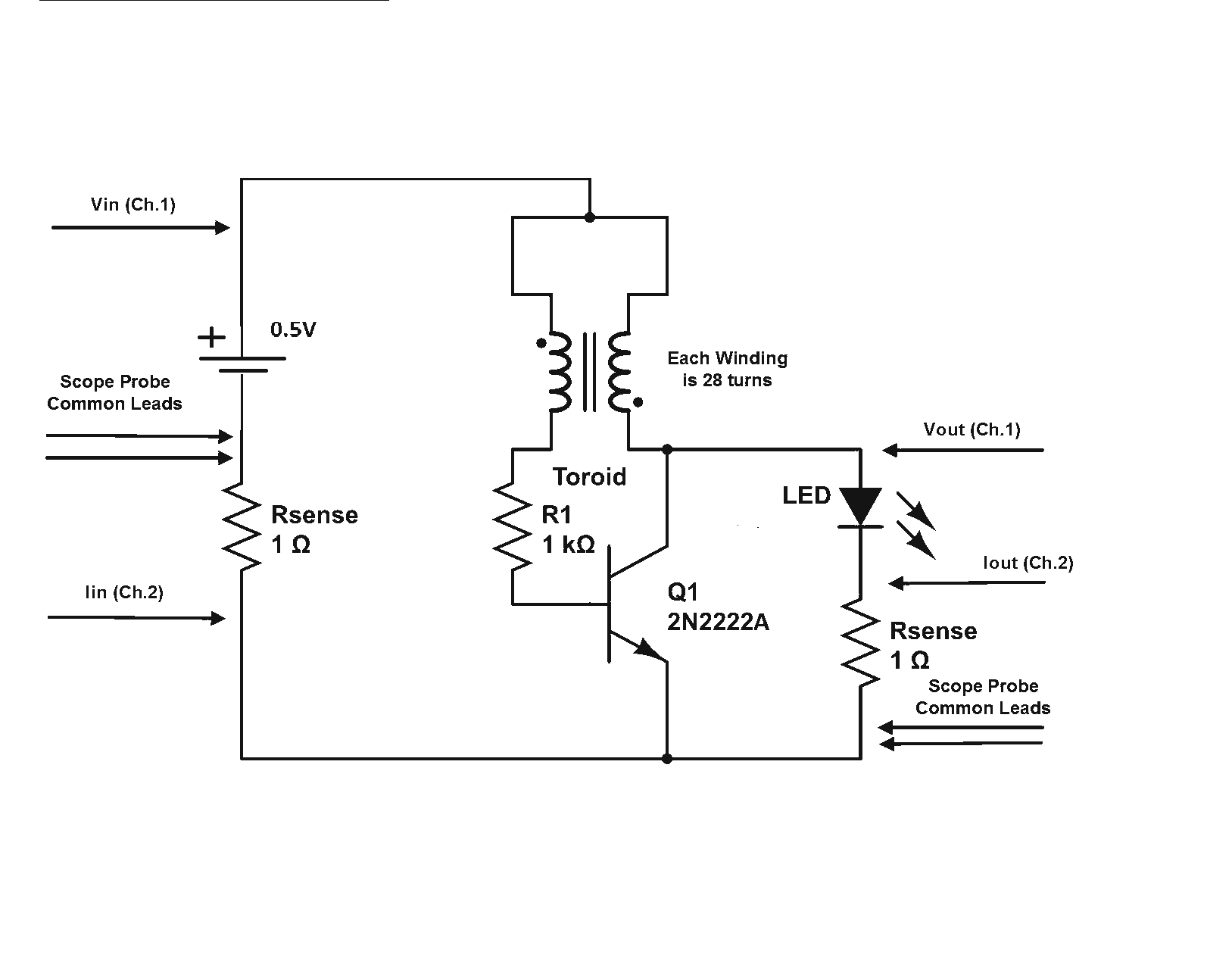
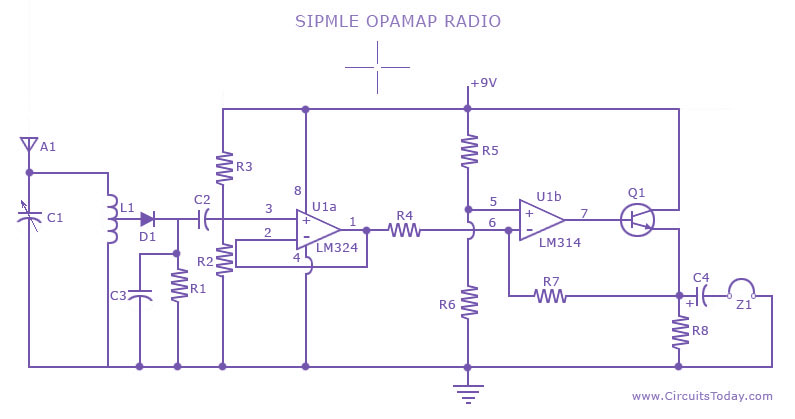
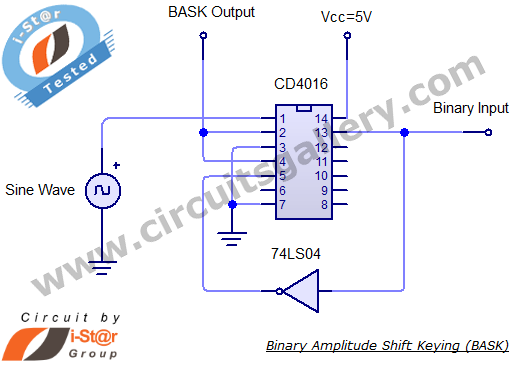
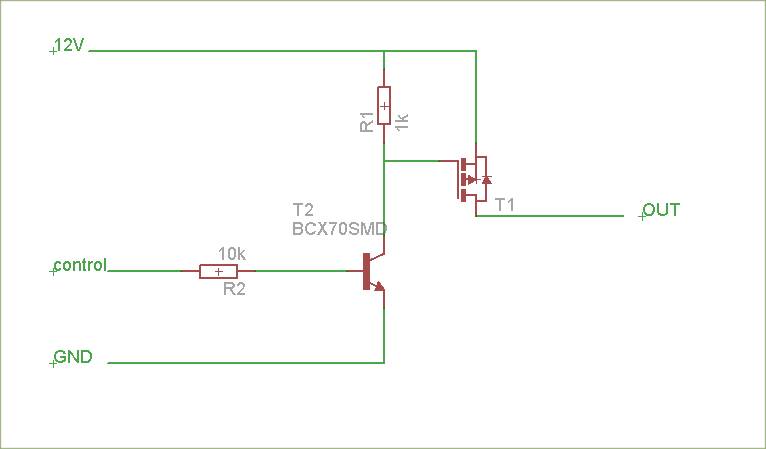
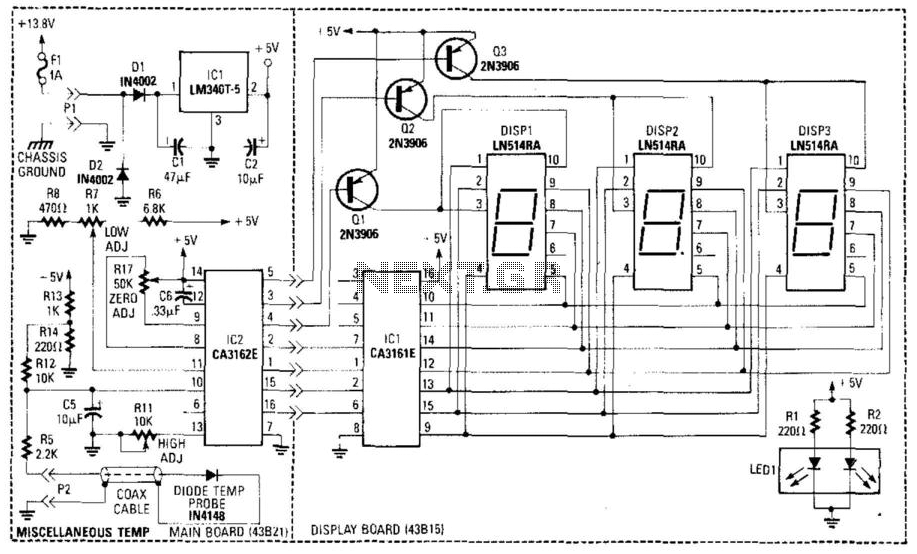
Digital Audio Selector Circuit
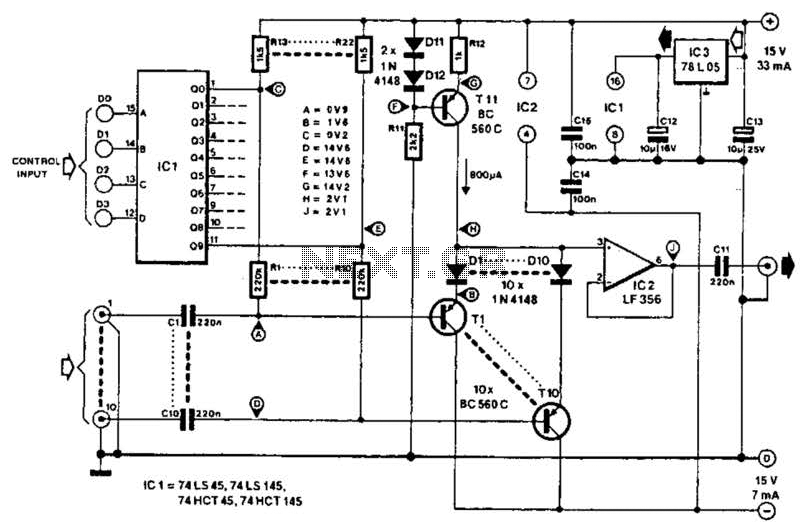
This circuit employs switched emitter followers instead of conventional analog switch CMOS chips, resulting in a more effective reduction of crosstalk between channels. It can manage up to 4 Vms with less than -80 dB crosstalk.
The circuit design utilizes switched emitter followers to achieve improved performance in signal integrity, particularly in applications where multiple channels operate simultaneously. Switched emitter followers are advantageous due to their ability to provide low output impedance and high linearity, which minimizes signal distortion and enhances the overall fidelity of the circuit.
In this configuration, each channel is isolated from the others, significantly reducing crosstalk, which is critical in multi-channel systems such as audio mixers or communication devices. The specification of handling up to 4 Vms indicates the circuit's robustness and capability to operate effectively within a wide voltage range while maintaining high performance.
The implementation of this circuit may involve transistors configured as emitter followers, where the input signal is fed to the base of the transistor, and the output is taken from the emitter. The switching mechanism can be achieved using control signals that turn the transistors on or off, thus allowing or blocking the signal path. This design choice leads to a more straightforward and reliable operation compared to traditional CMOS switches, which may introduce additional complexities and potential points of failure.
To further enhance performance, careful attention should be paid to the layout and grounding techniques to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can contribute to crosstalk and signal degradation. Overall, this circuit is well-suited for applications requiring high fidelity and low interference between channels. This circuit, uses switched emitter followers, rather than the usual analog switch CMOS chips. This yields better reduction of crosstalk between channels. This circuit can handle up to 4 Vms with less than -80-dB crosstalk.
The circuit design utilizes switched emitter followers to achieve improved performance in signal integrity, particularly in applications where multiple channels operate simultaneously. Switched emitter followers are advantageous due to their ability to provide low output impedance and high linearity, which minimizes signal distortion and enhances the overall fidelity of the circuit.
In this configuration, each channel is isolated from the others, significantly reducing crosstalk, which is critical in multi-channel systems such as audio mixers or communication devices. The specification of handling up to 4 Vms indicates the circuit's robustness and capability to operate effectively within a wide voltage range while maintaining high performance.
The implementation of this circuit may involve transistors configured as emitter followers, where the input signal is fed to the base of the transistor, and the output is taken from the emitter. The switching mechanism can be achieved using control signals that turn the transistors on or off, thus allowing or blocking the signal path. This design choice leads to a more straightforward and reliable operation compared to traditional CMOS switches, which may introduce additional complexities and potential points of failure.
To further enhance performance, careful attention should be paid to the layout and grounding techniques to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can contribute to crosstalk and signal degradation. Overall, this circuit is well-suited for applications requiring high fidelity and low interference between channels. This circuit, uses switched emitter followers, rather than the usual analog switch CMOS chips. This yields better reduction of crosstalk between channels. This circuit can handle up to 4 Vms with less than -80-dB crosstalk.