DIGITAL LOCK CIRCUIT
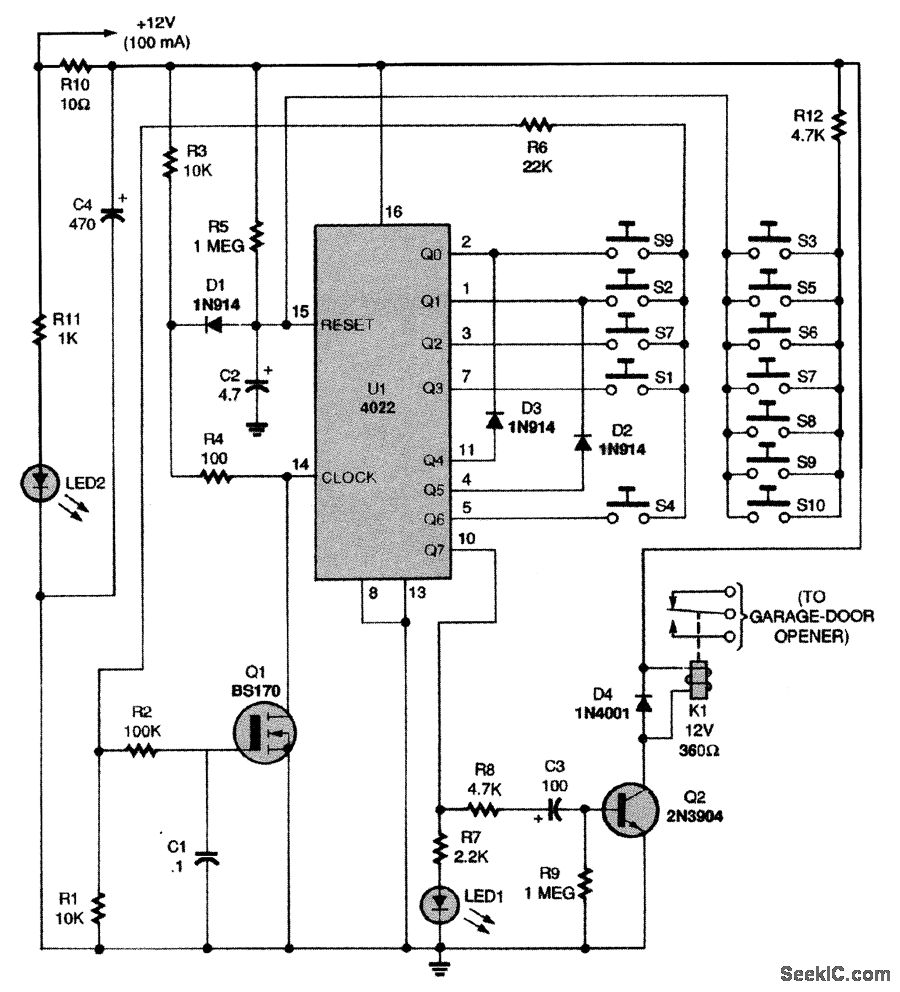
This circuit relies on the input of a correct sequence code. An incorrect number that is not part of the code triggers a reset of the circuit. When the correct code is entered, Q2 activates relay K1 for a brief period, determined by capacitor C3.
The circuit functions as a basic code entry system, utilizing a combination of digital logic and analog components to ensure that only a specific sequence of inputs can trigger the relay operation. The primary components include a microcontroller or a simple logic gate arrangement to evaluate the entered code, a transistor (Q2) to switch the relay, and a timing capacitor (C3) that defines the duration of the relay activation.
Upon entering a sequence, the system checks each digit against a predefined code stored in memory. If an incorrect digit is detected, the circuit resets, ensuring that no unauthorized access is granted. This reset mechanism can be implemented using a flip-flop or a simple reset line that is activated by the incorrect input.
When the correct sequence is entered, Q2 is triggered, allowing current to flow through relay K1. The relay then closes its contacts, which can be used to control various external devices, such as alarms, locks, or indicators. The duration of this activation is governed by the charge time of capacitor C3, which can be calculated based on the RC time constant, where the resistance in the circuit and the capacitance determine how long the relay remains activated before returning to its default state.
The design of this circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating features such as debounce logic for the input keys to prevent false triggering, as well as visual indicators (LEDs) to provide feedback on the status of the code entry process. Additionally, the circuit could be expanded with security features, such as a lockout period after multiple incorrect attempts, to increase its robustness against unauthorized access attempts.This circuit depends on the entry of a correct sequence code. An incorrect number that is not part of the code causes the circuit to reset. When the correct code is entered, Q2 operates relay K1 for a short time, depending on C3. 🔗 External reference
The circuit functions as a basic code entry system, utilizing a combination of digital logic and analog components to ensure that only a specific sequence of inputs can trigger the relay operation. The primary components include a microcontroller or a simple logic gate arrangement to evaluate the entered code, a transistor (Q2) to switch the relay, and a timing capacitor (C3) that defines the duration of the relay activation.
Upon entering a sequence, the system checks each digit against a predefined code stored in memory. If an incorrect digit is detected, the circuit resets, ensuring that no unauthorized access is granted. This reset mechanism can be implemented using a flip-flop or a simple reset line that is activated by the incorrect input.
When the correct sequence is entered, Q2 is triggered, allowing current to flow through relay K1. The relay then closes its contacts, which can be used to control various external devices, such as alarms, locks, or indicators. The duration of this activation is governed by the charge time of capacitor C3, which can be calculated based on the RC time constant, where the resistance in the circuit and the capacitance determine how long the relay remains activated before returning to its default state.
The design of this circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating features such as debounce logic for the input keys to prevent false triggering, as well as visual indicators (LEDs) to provide feedback on the status of the code entry process. Additionally, the circuit could be expanded with security features, such as a lockout period after multiple incorrect attempts, to increase its robustness against unauthorized access attempts.This circuit depends on the entry of a correct sequence code. An incorrect number that is not part of the code causes the circuit to reset. When the correct code is entered, Q2 operates relay K1 for a short time, depending on C3. 🔗 External reference