Digital oscillator
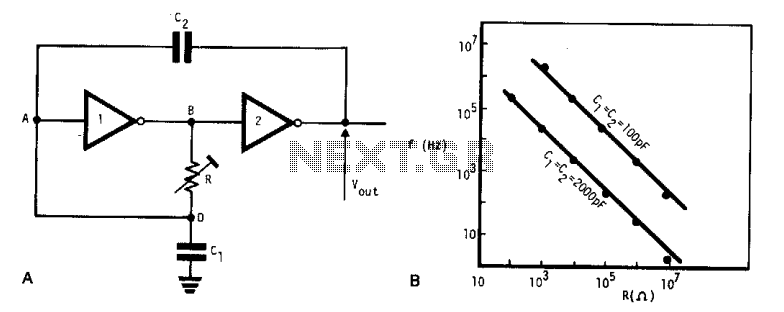
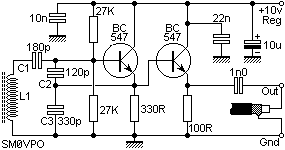
This simple, low-cost oscillator is constructed using two CMOS buffer inverters, two capacitors, and a variable resistor. The circuit operates with voltage levels ranging from 4 V to 18 V. When C1 equals C2, the frequency of oscillation is determined.
The described oscillator circuit utilizes two CMOS buffer inverters which serve as the primary active components for generating oscillations. The configuration of these inverters allows for feedback that sustains oscillation. The two capacitors (C1 and C2) are crucial for determining the timing characteristics of the oscillator. When both capacitors are equal in value, the frequency of oscillation can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2 \pi R C} \]
where \( R \) is the resistance set by the variable resistor and \( C \) is the capacitance value of either capacitor (since C1 = C2).
The variable resistor allows for fine-tuning of the oscillation frequency, providing flexibility in applications where different frequencies may be required. The operating voltage range of 4 V to 18 V indicates that this oscillator can be used in various low-power applications, making it suitable for battery-operated devices or low-voltage circuits.
In terms of input and output impedance, the circuit's performance may be influenced by these parameters. However, they are typically considered negligible for the basic operation of this oscillator. When implementing this circuit, it is essential to ensure that the power supply is stable and within the specified voltage range to maintain consistent oscillation performance.
Overall, this CMOS-based oscillator circuit is an efficient solution for generating square wave signals in various electronic applications, including timers, clock generators, and signal modulation systems. Its simplicity and low cost make it an attractive option for hobbyists and professionals alike.This very simple, low cost oscillator, is built with two CMOS buffer inverters, two capacitors and a variable resistance. The circuit can work with voltages ranging from 4 V up to 18 V. If Cl = C2, the frequency of oscillation. Ignoring the output and input impedance is given.
The described oscillator circuit utilizes two CMOS buffer inverters which serve as the primary active components for generating oscillations. The configuration of these inverters allows for feedback that sustains oscillation. The two capacitors (C1 and C2) are crucial for determining the timing characteristics of the oscillator. When both capacitors are equal in value, the frequency of oscillation can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2 \pi R C} \]
where \( R \) is the resistance set by the variable resistor and \( C \) is the capacitance value of either capacitor (since C1 = C2).
The variable resistor allows for fine-tuning of the oscillation frequency, providing flexibility in applications where different frequencies may be required. The operating voltage range of 4 V to 18 V indicates that this oscillator can be used in various low-power applications, making it suitable for battery-operated devices or low-voltage circuits.
In terms of input and output impedance, the circuit's performance may be influenced by these parameters. However, they are typically considered negligible for the basic operation of this oscillator. When implementing this circuit, it is essential to ensure that the power supply is stable and within the specified voltage range to maintain consistent oscillation performance.
Overall, this CMOS-based oscillator circuit is an efficient solution for generating square wave signals in various electronic applications, including timers, clock generators, and signal modulation systems. Its simplicity and low cost make it an attractive option for hobbyists and professionals alike.This very simple, low cost oscillator, is built with two CMOS buffer inverters, two capacitors and a variable resistance. The circuit can work with voltages ranging from 4 V up to 18 V. If Cl = C2, the frequency of oscillation. Ignoring the output and input impedance is given.