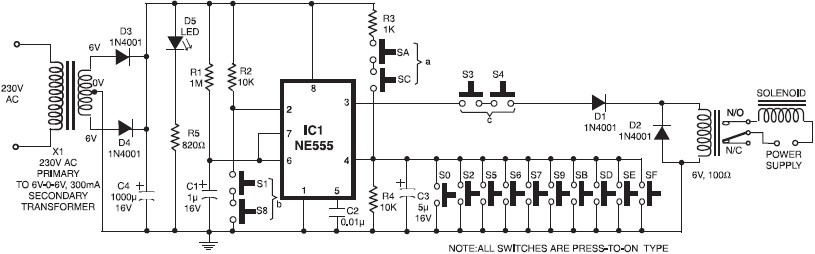
Digital Remote Thermometer circuit
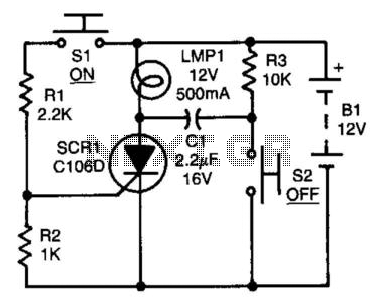
This circuit is designed for precise measurement of temperature in degrees Celsius. It features a transmitter section that converts the output voltage from the temperature sensor, which is proportional to the measured temperature, into a frequency signal. This frequency signal is transmitted through the mains supply cables. The receiver section counts the frequency bursts received from the mains supply and displays the count on three 7-segment LED displays. The least significant digit represents tenths of a degree, allowing for a temperature range of 00.0 to 99.9 °C. The distance between the transmitter and receiver can extend up to one hundred meters, provided both units are connected to the mains supply within the same light-meter control.
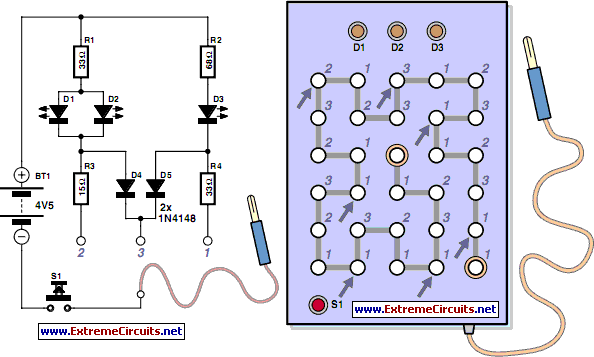
The circuit operates by utilizing a temperature sensor, such as a thermistor or an RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector), which generates a voltage that varies with temperature. This voltage is fed into a frequency-to-voltage converter circuit, which translates the analog voltage signal into a frequency output. This frequency output is then modulated and transmitted over the mains supply lines, leveraging existing electrical infrastructure for communication.
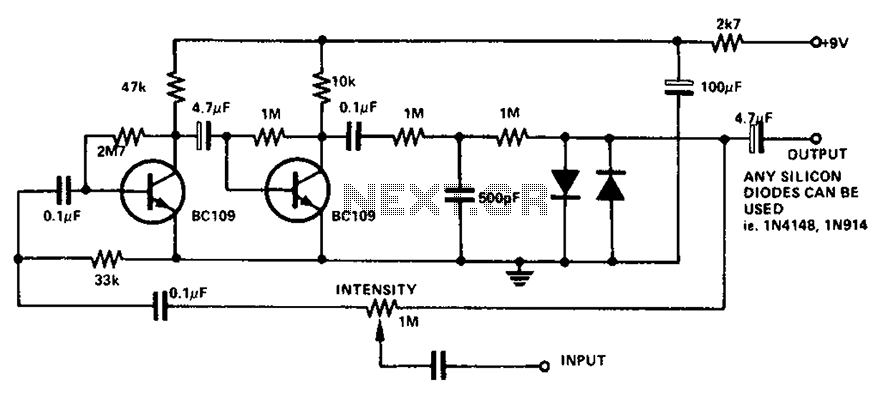
On the receiving end, a frequency counter is employed to detect the frequency bursts transmitted by the transmitter. The counter processes these bursts and converts them into a digital format suitable for display. The three 7-segment LED displays are configured to show the temperature reading in a clear and user-friendly manner, with the first two displays indicating whole degrees and the last display showing tenths of a degree.
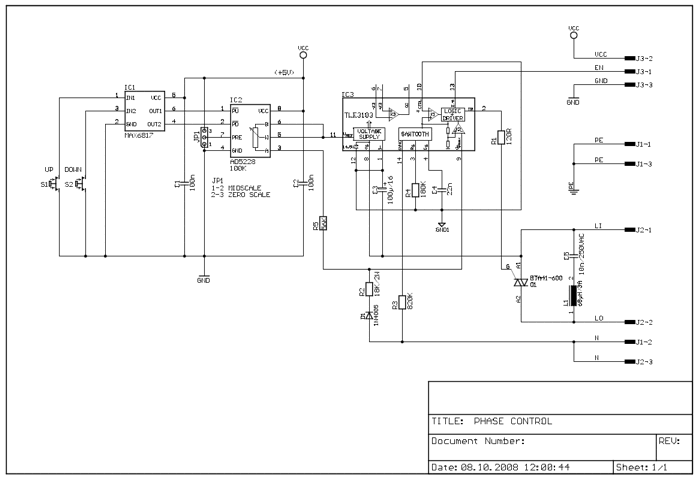
Power supply considerations for both the transmitter and receiver are critical, as they must operate reliably over potentially long distances. The use of appropriate filtering and signal conditioning techniques is essential to minimize noise and interference from other devices connected to the mains supply. Additionally, the circuit can be designed to include features such as calibration adjustments to ensure accuracy and precision in temperature measurements.
Overall, this circuit provides a robust solution for remote temperature monitoring, suitable for various applications where wired connections are impractical or undesirable, while maintaining high accuracy and reliability in temperature measurement.This circuit is intended for precision centigrade temperature measurement, with a transmitter section converting to frequency the sensor`s output voltage, which is proportional to the measured temperature. The output frequency bursts are conveyed into the mains supply cables. The receiver section counts the bursts coming from mains supply and shows the counting on three 7-segment LED displays.
The least significant digit displays tenths of degree and then a 00.0 to 99.9 °C range is obtained. Transmitter-receiver distance can reach hundred meters, provided both units are connected to the mains supply within the control of the same light-meter.. 🔗 External reference
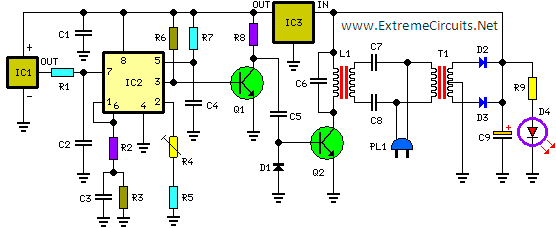
The circuit operates by utilizing a temperature sensor, such as a thermistor or an RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector), which generates a voltage that varies with temperature. This voltage is fed into a frequency-to-voltage converter circuit, which translates the analog voltage signal into a frequency output. This frequency output is then modulated and transmitted over the mains supply lines, leveraging existing electrical infrastructure for communication.
On the receiving end, a frequency counter is employed to detect the frequency bursts transmitted by the transmitter. The counter processes these bursts and converts them into a digital format suitable for display. The three 7-segment LED displays are configured to show the temperature reading in a clear and user-friendly manner, with the first two displays indicating whole degrees and the last display showing tenths of a degree.
Power supply considerations for both the transmitter and receiver are critical, as they must operate reliably over potentially long distances. The use of appropriate filtering and signal conditioning techniques is essential to minimize noise and interference from other devices connected to the mains supply. Additionally, the circuit can be designed to include features such as calibration adjustments to ensure accuracy and precision in temperature measurements.
Overall, this circuit provides a robust solution for remote temperature monitoring, suitable for various applications where wired connections are impractical or undesirable, while maintaining high accuracy and reliability in temperature measurement.This circuit is intended for precision centigrade temperature measurement, with a transmitter section converting to frequency the sensor`s output voltage, which is proportional to the measured temperature. The output frequency bursts are conveyed into the mains supply cables. The receiver section counts the bursts coming from mains supply and shows the counting on three 7-segment LED displays.
The least significant digit displays tenths of degree and then a 00.0 to 99.9 °C range is obtained. Transmitter-receiver distance can reach hundred meters, provided both units are connected to the mains supply within the control of the same light-meter.. 🔗 External reference