Digital thermometer circuit based on CA3162 CA3162 and LM35
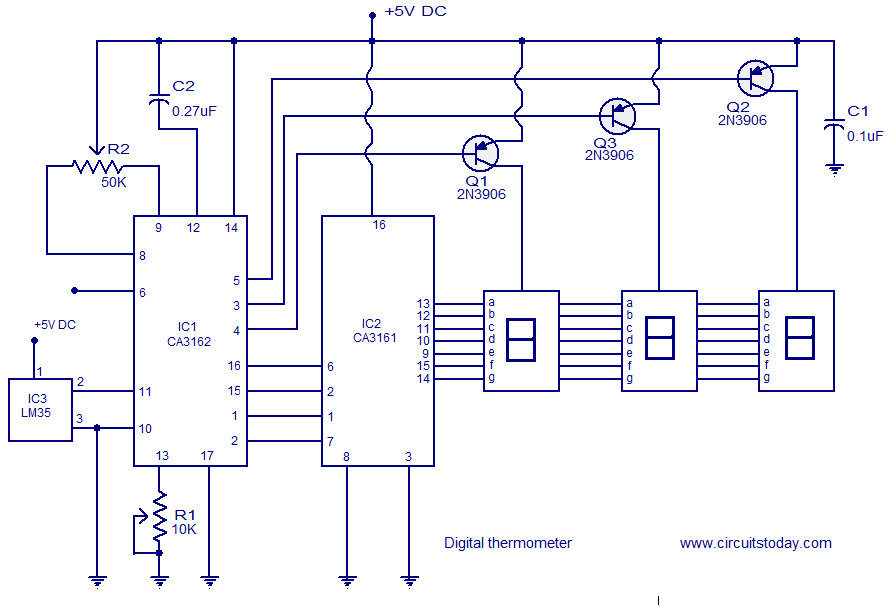
A simple digital thermometer circuit without a microcontroller and featuring a seven-segment LED readout is presented. The circuit utilizes three integrated circuits (ICs): CA3162, CA3161, and LM35. The CA3162 is a monolithic analog-to-digital (A/D) converter with a BCD output. This A/D converter is of the dual slope type with differential inputs, and it includes internal timing circuitry and a hold function. When the hold function is enabled, the output of the IC latches to its current state. The CA3161 is a monolithic BCD to seven-segment converter IC that can directly drive a seven-segment display without the need for current-limiting resistors. The LM35 is a three-terminal precision temperature sensor IC from National Semiconductor. Its output is highly linear, with a scale factor of 10 mV/°C, and it consumes only 60 µA in standby mode while being calibrated directly in degrees Celsius. The LM35 is employed for temperature sensing, providing a voltage proportional to the temperature at pin 2, which is connected to the high input pin (pin 11) of the CA3162. The CA3162 converts this analog voltage into BCD format. A potentiometer (POT) R1 connected to pin 13 of the CA3162 is used for gain adjustment, while POT R2 is for zero adjustment. Capacitor C2 serves as the integrating capacitor in the A/D converter circuitry. The operation of the CA3162 involves converting the voltage applied at input pin (pin 11) into a current using an internal voltage-to-current converter, which charges the integrating capacitor C2 for a predetermined duration. Once charged, the integrating capacitor is disconnected from the voltage/current converter, and a reference constant current source is applied to it. The time taken for the charge to return to its original value is measured, and the number of clock cycles during this period indicates the charge induced by the input voltage. An internal comparator senses the restoration point, latching the counter, which is then multiplexed to the BCD outputs, repeating the cycle. The hold pin (pin 6) of the CA3162 allows for different operational modes: grounding or leaving it open runs the IC in low-speed mode (sampling rate of 4 Hz), while applying +5V enables high-speed mode (sampling rate of 96 Hz). A fixed 1.2V on the hold pin latches the BCD output to the current state. Capacitor C1 acts as a power supply bypass capacitor, filtering any noise from the power supply line. The next section of the circuit consists of the BCD to seven-segment decoder and display driver, utilizing the CA3161. The BCD output pins from the CA3162 connect to the input pins of the CA3161. Transistors Q1, Q2, and Q3 control the common anode terminals of the respective seven-segment displays, driven by the digit driver pins (4, 3, and 5) of the CA3162.
The digital thermometer circuit described is designed to provide an accurate and efficient means of measuring temperature without the complexity of a microcontroller. The integration of the CA3162 A/D converter allows for precise conversion of the analog voltage from the LM35 temperature sensor into a digital format suitable for display. The dual slope A/D conversion method enhances measurement accuracy by averaging out noise and fluctuations in the input signal.
The CA3161 serves as an effective interface between the digital output from the CA3162 and the visual representation on the seven-segment display. By eliminating the need for additional current-limiting resistors, the CA3161 simplifies the circuit design and reduces component count, contributing to a more compact and efficient layout.
The use of potentiometers for gain and zero adjustments provides flexibility in calibrating the thermometer for different applications or environmental conditions. Additionally, the ability to switch between low-speed and high-speed modes allows the user to tailor the sampling rate according to the specific requirements of the measurement task, whether prioritizing power consumption or response time.
Overall, this digital thermometer circuit exemplifies a practical application of integrated circuit technology in temperature measurement, showcasing the synergy between analog sensing, digital processing, and user-friendly display.A simple digital thermometer circuit with out a micro controller and having a seven segment LED read out is shown here. The circuit is based on three ICs: CA3162, CA3161 and LM35. CA3162 is a monolithic analogue to digital (A/D) converter that has BCD output. The A/D converter inside the IC is a dual slope type with differential inputs. The IC has an internal timing circuitry and hold function. When the hold function is enables, the output IC latches itself to the present state. CA3161 is a monolithic BCD to seven segment converter IC. It can directly drive a seven segment display and there is no need for current limiting resistors. LM35 is a three terminal precision temperature sensor IC from National semiconductors. The output of LM35 is highly linear and has a scale factor of 10mV/C. The IC consumes only 60uA as standby current and is calibrated directly in degreeCelsius. IC LM35 is used for sensing the temperatures. A voltage proportional to the temperature will be available at pin 2 of the LM35 and this voltage is coupled to the high input pin (pin11) of the CA3162. CA3162 does the job of converting this analogue voltage in to a BCD format. POT R1 connected at pin 13 of the CA3162 is used for gain adjustment while POT R2 can be used for ZERO adjustment.
Capacitor C2 is the integrating capacitor of the A/D converter circuitry inside the IC. The working of the CA3162 is as follows, the voltage applied to the input pin (pin11) is converted into a current (using the built in V/I converter circuit) that charges the integrating capacitor C2 for a preset amount of them. Then the integrating is disconnected from the V/I converter circuit and a reference constant current source is connected to the integrating capacitor.
The time taken for the charge to restore to its original value is noted and the number of clock cycles elapsed during this time will be a measure of the charge induced by the input voltage (voltage applied to pin 11). The point of restoration is sensed using an internal comparator which latches the counter and the count is then multiplexed into the BCD outputs and the entire cycle is repeated.
The hold pin CA3162 (pin6) can be used for running the IC in different modes. When the hold pin is grounded or left open the IC runs in low speed mode (sampling rate is 4Hz). When hold pin is held at +5V, the IC runs in high speed mode i. e. a sampling rate of 96Hz. When the hold pin is held at a fixed 1. 2V, the BCD output latches to the current state. C1 is the power supply bypass capacitor whose job is to bypass noise if any from the power supply line. The next section of the circuit is the BCD to seven segment decoder plus display driver section. For that purpose CA3161 is used. The BCD output pins of the CA3162 are connected to the input pins of the CA3161. Transistors Q1, Q2, Q3 common anode terminals of the corresponding seven segments displays. Q1, Q2, Q3 are driven by the 4, 3, 5 pins (digit driver pins) of the CA3162 respectively. 🔗 External reference
The digital thermometer circuit described is designed to provide an accurate and efficient means of measuring temperature without the complexity of a microcontroller. The integration of the CA3162 A/D converter allows for precise conversion of the analog voltage from the LM35 temperature sensor into a digital format suitable for display. The dual slope A/D conversion method enhances measurement accuracy by averaging out noise and fluctuations in the input signal.
The CA3161 serves as an effective interface between the digital output from the CA3162 and the visual representation on the seven-segment display. By eliminating the need for additional current-limiting resistors, the CA3161 simplifies the circuit design and reduces component count, contributing to a more compact and efficient layout.
The use of potentiometers for gain and zero adjustments provides flexibility in calibrating the thermometer for different applications or environmental conditions. Additionally, the ability to switch between low-speed and high-speed modes allows the user to tailor the sampling rate according to the specific requirements of the measurement task, whether prioritizing power consumption or response time.
Overall, this digital thermometer circuit exemplifies a practical application of integrated circuit technology in temperature measurement, showcasing the synergy between analog sensing, digital processing, and user-friendly display.A simple digital thermometer circuit with out a micro controller and having a seven segment LED read out is shown here. The circuit is based on three ICs: CA3162, CA3161 and LM35. CA3162 is a monolithic analogue to digital (A/D) converter that has BCD output. The A/D converter inside the IC is a dual slope type with differential inputs. The IC has an internal timing circuitry and hold function. When the hold function is enables, the output IC latches itself to the present state. CA3161 is a monolithic BCD to seven segment converter IC. It can directly drive a seven segment display and there is no need for current limiting resistors. LM35 is a three terminal precision temperature sensor IC from National semiconductors. The output of LM35 is highly linear and has a scale factor of 10mV/C. The IC consumes only 60uA as standby current and is calibrated directly in degreeCelsius. IC LM35 is used for sensing the temperatures. A voltage proportional to the temperature will be available at pin 2 of the LM35 and this voltage is coupled to the high input pin (pin11) of the CA3162. CA3162 does the job of converting this analogue voltage in to a BCD format. POT R1 connected at pin 13 of the CA3162 is used for gain adjustment while POT R2 can be used for ZERO adjustment.
Capacitor C2 is the integrating capacitor of the A/D converter circuitry inside the IC. The working of the CA3162 is as follows, the voltage applied to the input pin (pin11) is converted into a current (using the built in V/I converter circuit) that charges the integrating capacitor C2 for a preset amount of them. Then the integrating is disconnected from the V/I converter circuit and a reference constant current source is connected to the integrating capacitor.
The time taken for the charge to restore to its original value is noted and the number of clock cycles elapsed during this time will be a measure of the charge induced by the input voltage (voltage applied to pin 11). The point of restoration is sensed using an internal comparator which latches the counter and the count is then multiplexed into the BCD outputs and the entire cycle is repeated.
The hold pin CA3162 (pin6) can be used for running the IC in different modes. When the hold pin is grounded or left open the IC runs in low speed mode (sampling rate is 4Hz). When hold pin is held at +5V, the IC runs in high speed mode i. e. a sampling rate of 96Hz. When the hold pin is held at a fixed 1. 2V, the BCD output latches to the current state. C1 is the power supply bypass capacitor whose job is to bypass noise if any from the power supply line. The next section of the circuit is the BCD to seven segment decoder plus display driver section. For that purpose CA3161 is used. The BCD output pins of the CA3162 are connected to the input pins of the CA3161. Transistors Q1, Q2, Q3 common anode terminals of the corresponding seven segments displays. Q1, Q2, Q3 are driven by the 4, 3, 5 pins (digit driver pins) of the CA3162 respectively. 🔗 External reference