Dimming circuit using capacitance
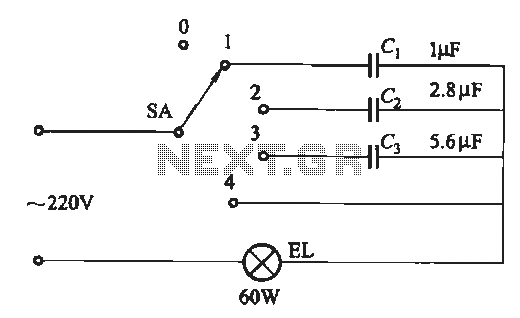
A dimming circuit capacitor circuit is illustrated in Figure 2-63. When the switch SA is moved from position "1" to "3," the capacitance increases in ascending order, resulting in the light bulb brightness also increasing correspondingly. When SA is set to position "0," the lamp is off, and when it is set to position "4," the lamp reaches its maximum brightness. The capacitance can be estimated using the formula: C = O i Lu kettle of 066 million pF, where P represents the lamp power rating in watts. Dimming occurs after power is applied, and it is recommended to use a voltage rating above 300V or a CJ41 CBB22 type capacitor.
A dimming circuit utilizing capacitors is commonly employed to control the brightness of incandescent lamps. The circuit operates by adjusting the capacitance in relation to the power supplied to the lamp. The switch SA serves as a variable control that allows the user to select different capacitance levels, thereby modulating the light output.
In position "1," the circuit connects to a minimal capacitance value, resulting in low brightness. As the switch is moved through the positions "2" and "3," the capacitance increases sequentially, allowing more current to flow to the lamp and thereby increasing the brightness. Position "0" effectively disconnects the circuit, turning the lamp off. Position "4" connects the circuit to its maximum capacitance, delivering the highest current and resulting in maximum brightness.
The formula provided for estimating capacitance, C = O i Lu kettle of 066 million pF, indicates that the capacitance value is directly influenced by the power rating of the lamp, denoted as P in watts. This relationship is crucial for ensuring that the circuit operates within safe limits, particularly when using components rated for higher voltages, such as those above 300V, which are necessary to handle the potential voltage spikes in the circuit. The CJ41 CBB22 type capacitor is recommended due to its reliability and performance characteristics in high-voltage applications.
This dimming circuit is an essential component in lighting control systems, providing flexibility and energy efficiency by allowing users to adjust the intensity of light according to their needs. Proper selection of capacitors and understanding of the circuit's operational principles are vital for optimal performance and safety.(1) dimming circuit capacitor circuit shown in Figure 2-63. When the switch SA from "1" hit "3" position, in ascending order of capacity, light bulb degree also in ascending order. When SA hit the "0" position, the lamp, and when SA hit the "4" position, the brightest. Capacitance can be estimated by the following formula: . C = O i Lu kettle of 066 million 'pF) ~ / formula P- lamp power rating. W ' P. - Dimming after power, w. Optional voltage above 300V or CJ41 CBB22 type capacitor.
A dimming circuit utilizing capacitors is commonly employed to control the brightness of incandescent lamps. The circuit operates by adjusting the capacitance in relation to the power supplied to the lamp. The switch SA serves as a variable control that allows the user to select different capacitance levels, thereby modulating the light output.
In position "1," the circuit connects to a minimal capacitance value, resulting in low brightness. As the switch is moved through the positions "2" and "3," the capacitance increases sequentially, allowing more current to flow to the lamp and thereby increasing the brightness. Position "0" effectively disconnects the circuit, turning the lamp off. Position "4" connects the circuit to its maximum capacitance, delivering the highest current and resulting in maximum brightness.
The formula provided for estimating capacitance, C = O i Lu kettle of 066 million pF, indicates that the capacitance value is directly influenced by the power rating of the lamp, denoted as P in watts. This relationship is crucial for ensuring that the circuit operates within safe limits, particularly when using components rated for higher voltages, such as those above 300V, which are necessary to handle the potential voltage spikes in the circuit. The CJ41 CBB22 type capacitor is recommended due to its reliability and performance characteristics in high-voltage applications.
This dimming circuit is an essential component in lighting control systems, providing flexibility and energy efficiency by allowing users to adjust the intensity of light according to their needs. Proper selection of capacitors and understanding of the circuit's operational principles are vital for optimal performance and safety.(1) dimming circuit capacitor circuit shown in Figure 2-63. When the switch SA from "1" hit "3" position, in ascending order of capacity, light bulb degree also in ascending order. When SA hit the "0" position, the lamp, and when SA hit the "4" position, the brightest. Capacitance can be estimated by the following formula: . C = O i Lu kettle of 066 million 'pF) ~ / formula P- lamp power rating. W ' P. - Dimming after power, w. Optional voltage above 300V or CJ41 CBB22 type capacitor.