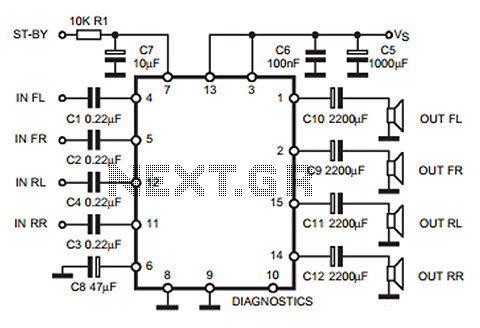
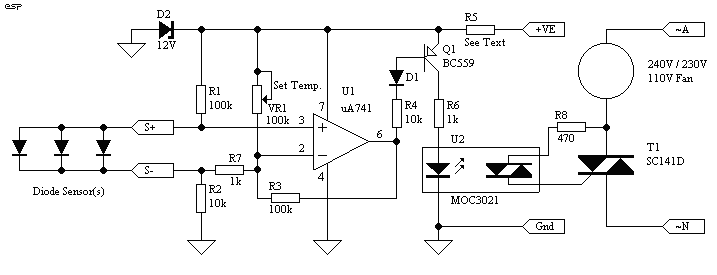
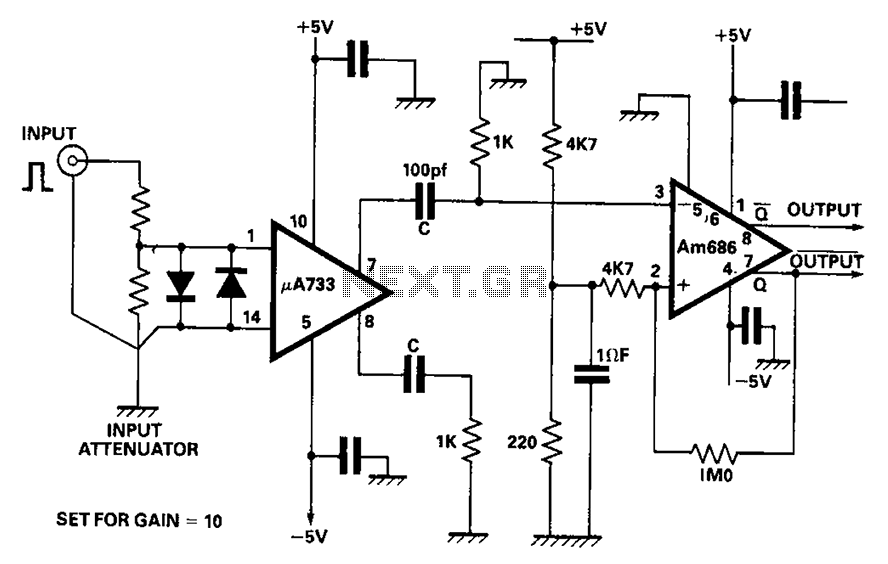
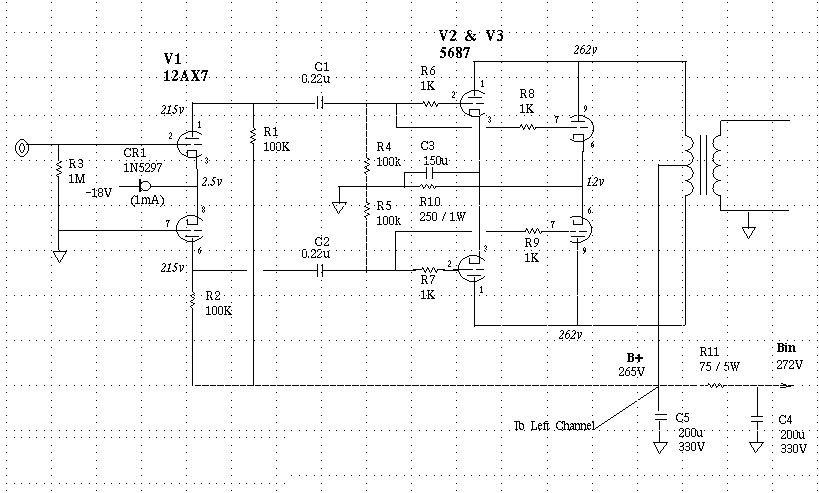
DIY Class-A 2SK1058 MOSFET Amplifier Project
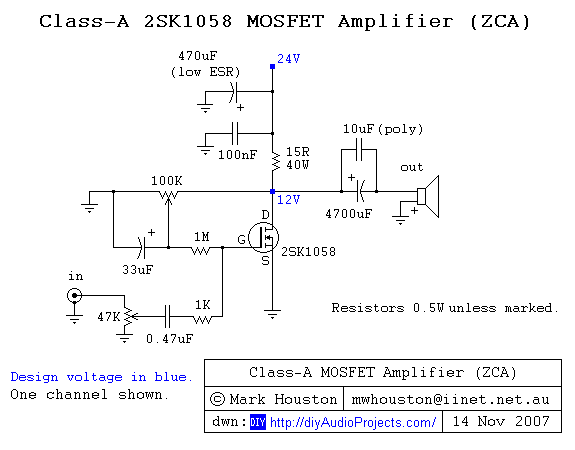
A straightforward DIY Class-A MOSFET amplifier project that utilizes a single Hitachi 2SK1058 N-channel MOSFET in a single-ended configuration.
This Class-A MOSFET amplifier design is characterized by its simplicity and effectiveness, making it suitable for audio amplification applications. The core component, the Hitachi 2SK1058, is a high-performance N-channel MOSFET known for its low on-resistance and high-speed switching capabilities. In a single-ended configuration, the amplifier operates with a single active device, which simplifies the circuit and reduces the component count.
The circuit typically consists of the following key elements: the 2SK1058 MOSFET, a biasing network, an input coupling capacitor, and an output coupling capacitor. The biasing network is crucial for establishing the proper operating point of the MOSFET, ensuring it operates in the linear region for optimal audio fidelity. Resistors are used to set the gate voltage, while a source resistor may be included to stabilize the operating point against variations in temperature and device characteristics.
The input signal is coupled to the gate of the MOSFET through a capacitor, which blocks any DC offset and allows only the AC audio signal to pass. The output is taken from the drain of the MOSFET, also through a coupling capacitor, which prevents any DC component from reaching the load, such as a speaker.
Power supply considerations are essential, with a well-regulated DC voltage source required to power the amplifier. The choice of power supply voltage will affect the output power and linearity of the amplifier. Additionally, proper heat dissipation measures, such as a heat sink, should be implemented to manage the thermal performance of the MOSFET during operation.
Overall, this DIY Class-A MOSFET amplifier project offers a practical introduction to audio amplification, showcasing the fundamental principles of MOSFET operation while providing a platform for further experimentation and enhancement.A very simple DIY Class-A MOSFET Amplifier Project that uses only a one Hitachi 2SK1058 N-Channel MOSFET in a single-ended circuit 🔗 External reference
This Class-A MOSFET amplifier design is characterized by its simplicity and effectiveness, making it suitable for audio amplification applications. The core component, the Hitachi 2SK1058, is a high-performance N-channel MOSFET known for its low on-resistance and high-speed switching capabilities. In a single-ended configuration, the amplifier operates with a single active device, which simplifies the circuit and reduces the component count.
The circuit typically consists of the following key elements: the 2SK1058 MOSFET, a biasing network, an input coupling capacitor, and an output coupling capacitor. The biasing network is crucial for establishing the proper operating point of the MOSFET, ensuring it operates in the linear region for optimal audio fidelity. Resistors are used to set the gate voltage, while a source resistor may be included to stabilize the operating point against variations in temperature and device characteristics.
The input signal is coupled to the gate of the MOSFET through a capacitor, which blocks any DC offset and allows only the AC audio signal to pass. The output is taken from the drain of the MOSFET, also through a coupling capacitor, which prevents any DC component from reaching the load, such as a speaker.
Power supply considerations are essential, with a well-regulated DC voltage source required to power the amplifier. The choice of power supply voltage will affect the output power and linearity of the amplifier. Additionally, proper heat dissipation measures, such as a heat sink, should be implemented to manage the thermal performance of the MOSFET during operation.
Overall, this DIY Class-A MOSFET amplifier project offers a practical introduction to audio amplification, showcasing the fundamental principles of MOSFET operation while providing a platform for further experimentation and enhancement.A very simple DIY Class-A MOSFET Amplifier Project that uses only a one Hitachi 2SK1058 N-Channel MOSFET in a single-ended circuit 🔗 External reference