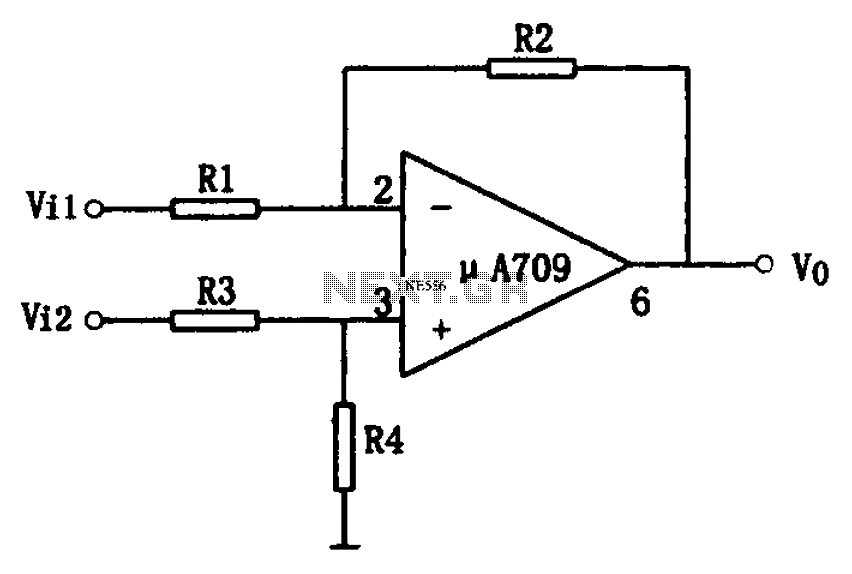
DIY Digital Thermometer Circuit
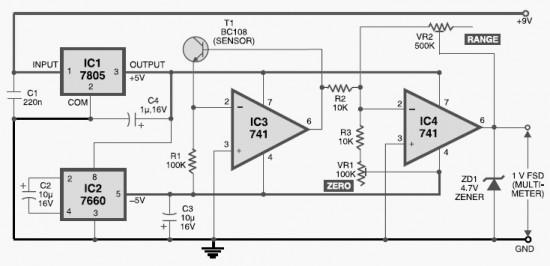
This DIY digital thermometer circuit can measure temperatures up to 150°C with an accuracy of ±1°C. The temperature is displayed on a 1V full scale deflection.
The digital thermometer circuit is designed to provide accurate temperature readings within a specified range, utilizing a temperature sensor such as the LM35 or a thermistor, which converts temperature changes into an electrical signal. The sensor output is then fed into an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), which digitizes the analog signal for processing.
The circuit typically includes a microcontroller, such as an Arduino or PIC, which receives the digital signal from the ADC. The microcontroller processes the data and converts it into a readable format, displaying the temperature on a digital display, such as a 7-segment LED display or an LCD.
To ensure accuracy, the circuit may incorporate calibration features, allowing adjustments to account for sensor discrepancies. Power supply considerations are also crucial; the circuit can be powered by a standard battery or an external power source, with voltage regulation components included to maintain stable operation.
Additional features may include temperature logging capabilities, where the microcontroller stores temperature data over time, and an interface for connecting to a computer or smartphone for data analysis. Overall, this DIY digital thermometer circuit is a versatile project suitable for various applications, including home automation, environmental monitoring, and educational purposes.This diy digital thermometer circuit can measure temperatures up to 150?C with an accuracy of ?1?C. The temperature is read on a 1V full scale-deflectio. 🔗 External reference
The digital thermometer circuit is designed to provide accurate temperature readings within a specified range, utilizing a temperature sensor such as the LM35 or a thermistor, which converts temperature changes into an electrical signal. The sensor output is then fed into an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), which digitizes the analog signal for processing.
The circuit typically includes a microcontroller, such as an Arduino or PIC, which receives the digital signal from the ADC. The microcontroller processes the data and converts it into a readable format, displaying the temperature on a digital display, such as a 7-segment LED display or an LCD.
To ensure accuracy, the circuit may incorporate calibration features, allowing adjustments to account for sensor discrepancies. Power supply considerations are also crucial; the circuit can be powered by a standard battery or an external power source, with voltage regulation components included to maintain stable operation.
Additional features may include temperature logging capabilities, where the microcontroller stores temperature data over time, and an interface for connecting to a computer or smartphone for data analysis. Overall, this DIY digital thermometer circuit is a versatile project suitable for various applications, including home automation, environmental monitoring, and educational purposes.This diy digital thermometer circuit can measure temperatures up to 150?C with an accuracy of ?1?C. The temperature is read on a 1V full scale-deflectio. 🔗 External reference