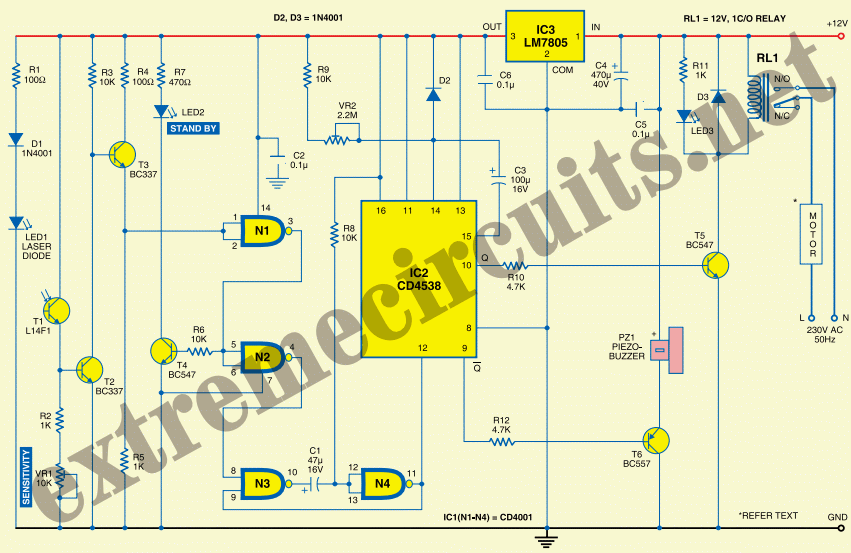
DOOR AJAR MONITOR

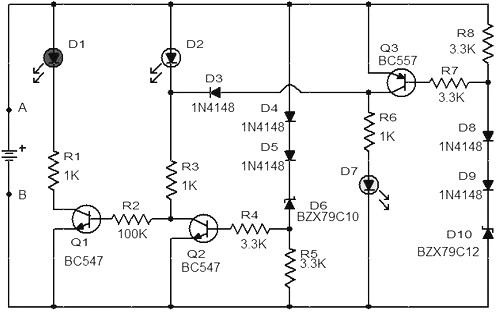
The monitor detects an open door, and if the condition is not rectified within 20 seconds, it triggers a beeping alarm. The circuit operates using a magnetic reed switch and a magnet positioned on the door. When the door is closed, the switch remains closed, and the alarm is disabled. Upon opening the door, the switch opens, allowing capacitor C1 to charge through resistor R1. Approximately 20 seconds later, the alarm activates.
The circuit design involves a magnetic reed switch (SW1) that is mounted on the door frame, aligned with a magnet (M1) attached to the door itself. When the door is closed, the magnet holds the reed switch in a closed position, preventing current from flowing to the alarm (A1). In this state, the capacitor (C1) remains discharged, and the alarm is inactive.
When the door is opened, the magnetic field is disrupted, causing the reed switch to open. This action initiates the charging of capacitor C1 through resistor R1, which is connected in series with the switch. The time constant of the RC circuit formed by R1 and C1 determines the delay before the alarm activates. The time constant (τ) can be calculated using the formula τ = R1 × C1, where R1 is the resistance in ohms and C1 is the capacitance in farads.
After approximately 20 seconds, once the voltage across C1 reaches a threshold level, it triggers the alarm circuit, causing the beeping sound to alert individuals nearby. The alarm will continue to sound until the door is closed again, which will reset the circuit by closing the reed switch and discharging the capacitor.
This design offers a simple yet effective solution for monitoring door status and ensuring security by providing an audible alert in the event of unauthorized access. The components used in this circuit should be selected based on the required voltage and current ratings to ensure reliable operation. Additionally, the circuit can be powered using a low-voltage DC supply, making it suitable for battery-operated applications.The monitor senses an ajar door and, if the situation isn`t corrected within 20 seconds, sounds a beeping alarm. The circuit is controlled by a magnetic reed switch and magnet on the door. With the door closed, the switch is closed and the alarm is disarmed. Opening the door opens switch, C1 starts charging up through R1. Approximately 20 seconds later, th.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design involves a magnetic reed switch (SW1) that is mounted on the door frame, aligned with a magnet (M1) attached to the door itself. When the door is closed, the magnet holds the reed switch in a closed position, preventing current from flowing to the alarm (A1). In this state, the capacitor (C1) remains discharged, and the alarm is inactive.
When the door is opened, the magnetic field is disrupted, causing the reed switch to open. This action initiates the charging of capacitor C1 through resistor R1, which is connected in series with the switch. The time constant of the RC circuit formed by R1 and C1 determines the delay before the alarm activates. The time constant (τ) can be calculated using the formula τ = R1 × C1, where R1 is the resistance in ohms and C1 is the capacitance in farads.
After approximately 20 seconds, once the voltage across C1 reaches a threshold level, it triggers the alarm circuit, causing the beeping sound to alert individuals nearby. The alarm will continue to sound until the door is closed again, which will reset the circuit by closing the reed switch and discharging the capacitor.
This design offers a simple yet effective solution for monitoring door status and ensuring security by providing an audible alert in the event of unauthorized access. The components used in this circuit should be selected based on the required voltage and current ratings to ensure reliable operation. Additionally, the circuit can be powered using a low-voltage DC supply, making it suitable for battery-operated applications.The monitor senses an ajar door and, if the situation isn`t corrected within 20 seconds, sounds a beeping alarm. The circuit is controlled by a magnetic reed switch and magnet on the door. With the door closed, the switch is closed and the alarm is disarmed. Opening the door opens switch, C1 starts charging up through R1. Approximately 20 seconds later, th.. 🔗 External reference