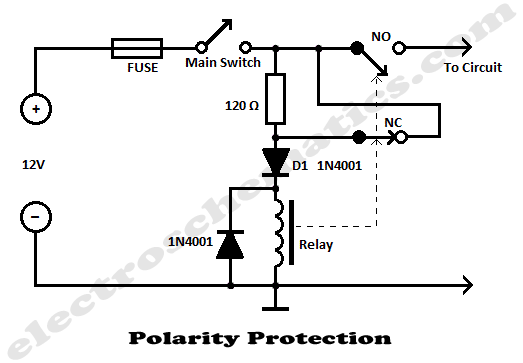
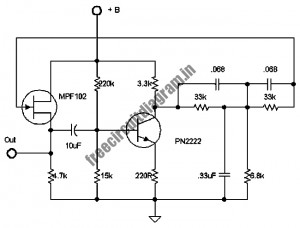
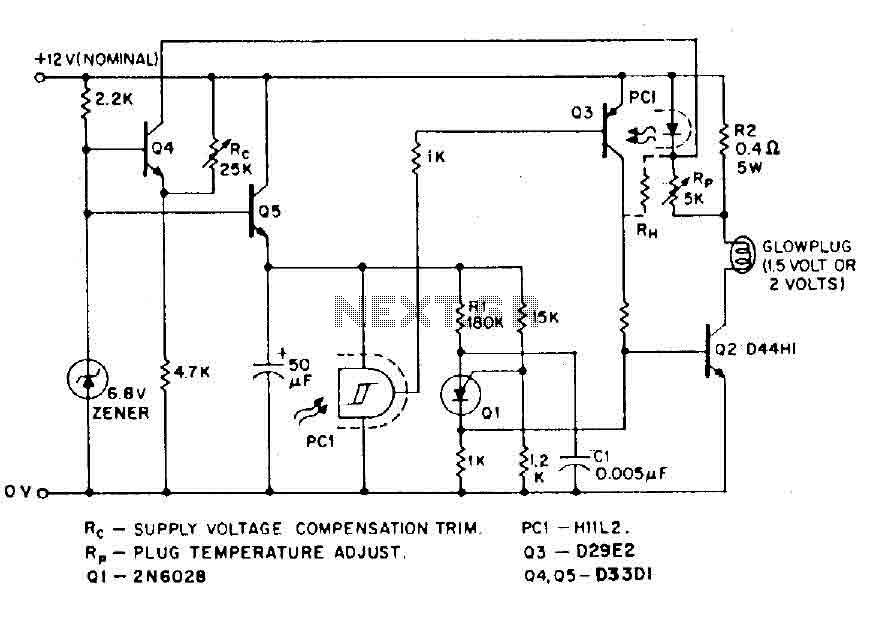
An estimate of the load current monitor circuit rod
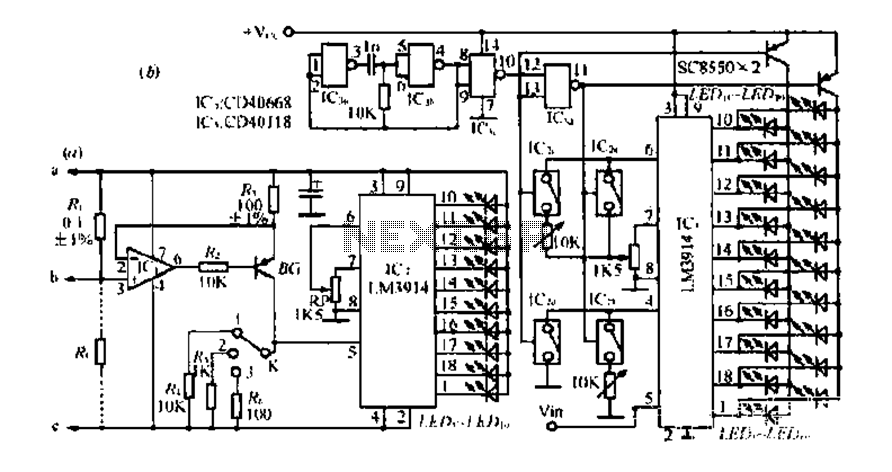
Figure A, B, and C illustrate the test rod end clip, with a positive power supply terminating test equipment. The B and C ends are connected in series with the load, where C represents the negative side of the device. The sensing resistance measurements indicate that the load current can be directly perceived due to its string loop configuration. The product features low resistance, ensuring that the load operates effectively without disruption. An operational amplifier integrated circuit (IC) functions as a voltage follower, allowing the current flowing through resistor R to generate a voltage drop equivalent to that across R3. The current flowing through R3, R4, R5, and R6 provides a current-to-voltage conversion ratio. For instance, if the load current is 1A, the voltage drop across R3 would be 0.4V, resulting in a current of 1mA flowing through Rs, which produces a 1V drop. The conversion ratio is 2 blocks at 1V/A, 1 block at 10V/A, and 3 blocks at 0.4V/A. The display driver circuit utilizes a linear ten-point/line driver such as the LM3914 IC, with a 7-pin output reference voltage of 1.25V sourced from an internal voltage divider. The reference voltage also determines the operating current size of LEDs, typically calculated as IF = 1.25 x 10/RP. To enhance stability, a filter capacitor (C3) should be placed close to the positive power supply pin. Resistors R3 and R4 are high precision, ideally at a tolerance level of 1%. Should the load current increase, an operational amplifier IC with high input impedance, such as CA3130, CA340, LF356, or TL081, is recommended. It is important to note that the circuit in Figure 2-66 (a) is designed for a supply voltage of +3 to 18V. Additionally, the display range and resolution of the load current estimates can vary, with increased load current leading to coarser resolution results. To address this, the circuit in Figure 2-66 (b) can be utilized, which reduces the range resolution by half compared to the circuit in Figure 2-66 (a).
The circuit design involves multiple components working together to measure and display load current accurately. The operational amplifier serves as a key element, ensuring high input impedance and facilitating the voltage follower configuration, which minimizes loading effects on the circuit. The precision resistors (R3 and R4) are critical for maintaining measurement accuracy, and their low tolerance is essential for reliable performance.
The LM3914 display driver is configured to translate voltage drops into visual signals, allowing for easy monitoring of load current levels. The internal voltage divider that provides the 1.25V reference voltage is crucial for setting the thresholds for the comparators within the LM3914, ensuring accurate LED illumination corresponding to the measured current.
The filter capacitor (C3) plays a vital role in stabilizing the power supply to the operational amplifier, minimizing noise and fluctuations that could affect measurement accuracy. The choice of high-precision components and careful layout considerations contribute to the overall reliability and performance of the circuit.
In summary, this circuit design is suited for applications requiring precise measurement and display of load currents, with considerations for component selection, configuration, and power supply stability being paramount to its successful operation.Fig. A, b, c for the test rod end clip, a positive power supply terminating test equipment, b, c end series with the load, where c is the negative side of the device. Shu is th e sensing resistance measurements, loads of people because of its string loop, so it has a direct perception of the size of the load current. Since the product is less resistance, without affecting the load are functioning properly. Op amp IC. And BG composition suspension voltage follower, so flow through R, the load current is generated by the same pressure drop and the pressure drop on R3, Ding is flowing through the current and the voltage drop is proportional to Ri on R3, R4.
R5, R6 a current/voltage conversion ratio resistors R3 with its flowing through the same current, the resulting voltage drop that is on behalf of the table the size of the load current. Such as K 2 block is located, if the load current is 1A, then the pressure drop immediately to O.IV, also O.IV drop on R3, which the current imA, then the voltage drop across Rs is 1V, because this 2 block conversion ratio IV/a.
Similarly, the conversion ratio is 1 block 10V/A, 3-speed conversion ratio O.IV/A. Shaped display driver circuit consists of a linear ten point/line driver as the LM3914, IC, 7-pin output reference voltage of 1.25V, obtained from the RP IV sent an internal voltage divider as ten comparator reference voltage, while RP also determines the LEDl - LEDio operating current size, generally IF 1.25 x 10/RP. To make IC2 stable, filter capacitor C 3 is preferably close to the positive power supply pin. Fig 2 - 66 (a) of the resistor horse, R3, R4 Yun high precision, the general should be up to l% level.
If the load current is greater, Shu can take 0010, op amp Ic, should take the high input impedance type, such as CA3130, CA340, LF356, TL081 and the like. It is noteworthy that in Figure 2- 66 (a) applies only to the supply voltage +3 a 18V device estimate.
Figure 2 - 66 (Japan) also found that the current estimate of the display range Display resolution section of its tenth, and the load current increases, the more coarse resolution estimate results. To this end, FIG. 2 - 66 (a) may be employed in the right side of the broken line in Fig. 2 - 66 (b) bar-shaped display shown, this circuit is range resolution than Figure 2 - 66 (a) circuit is reduced by half.
The circuit design involves multiple components working together to measure and display load current accurately. The operational amplifier serves as a key element, ensuring high input impedance and facilitating the voltage follower configuration, which minimizes loading effects on the circuit. The precision resistors (R3 and R4) are critical for maintaining measurement accuracy, and their low tolerance is essential for reliable performance.
The LM3914 display driver is configured to translate voltage drops into visual signals, allowing for easy monitoring of load current levels. The internal voltage divider that provides the 1.25V reference voltage is crucial for setting the thresholds for the comparators within the LM3914, ensuring accurate LED illumination corresponding to the measured current.
The filter capacitor (C3) plays a vital role in stabilizing the power supply to the operational amplifier, minimizing noise and fluctuations that could affect measurement accuracy. The choice of high-precision components and careful layout considerations contribute to the overall reliability and performance of the circuit.
In summary, this circuit design is suited for applications requiring precise measurement and display of load currents, with considerations for component selection, configuration, and power supply stability being paramount to its successful operation.Fig. A, b, c for the test rod end clip, a positive power supply terminating test equipment, b, c end series with the load, where c is the negative side of the device. Shu is th e sensing resistance measurements, loads of people because of its string loop, so it has a direct perception of the size of the load current. Since the product is less resistance, without affecting the load are functioning properly. Op amp IC. And BG composition suspension voltage follower, so flow through R, the load current is generated by the same pressure drop and the pressure drop on R3, Ding is flowing through the current and the voltage drop is proportional to Ri on R3, R4.
R5, R6 a current/voltage conversion ratio resistors R3 with its flowing through the same current, the resulting voltage drop that is on behalf of the table the size of the load current. Such as K 2 block is located, if the load current is 1A, then the pressure drop immediately to O.IV, also O.IV drop on R3, which the current imA, then the voltage drop across Rs is 1V, because this 2 block conversion ratio IV/a.
Similarly, the conversion ratio is 1 block 10V/A, 3-speed conversion ratio O.IV/A. Shaped display driver circuit consists of a linear ten point/line driver as the LM3914, IC, 7-pin output reference voltage of 1.25V, obtained from the RP IV sent an internal voltage divider as ten comparator reference voltage, while RP also determines the LEDl - LEDio operating current size, generally IF 1.25 x 10/RP. To make IC2 stable, filter capacitor C 3 is preferably close to the positive power supply pin. Fig 2 - 66 (a) of the resistor horse, R3, R4 Yun high precision, the general should be up to l% level.
If the load current is greater, Shu can take 0010, op amp Ic, should take the high input impedance type, such as CA3130, CA340, LF356, TL081 and the like. It is noteworthy that in Figure 2- 66 (a) applies only to the supply voltage +3 a 18V device estimate.
Figure 2 - 66 (Japan) also found that the current estimate of the display range Display resolution section of its tenth, and the load current increases, the more coarse resolution estimate results. To this end, FIG. 2 - 66 (a) may be employed in the right side of the broken line in Fig. 2 - 66 (b) bar-shaped display shown, this circuit is range resolution than Figure 2 - 66 (a) circuit is reduced by half.