Doorbell Warning Switch
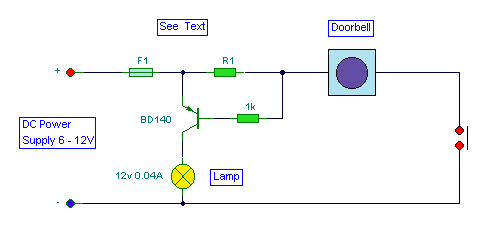
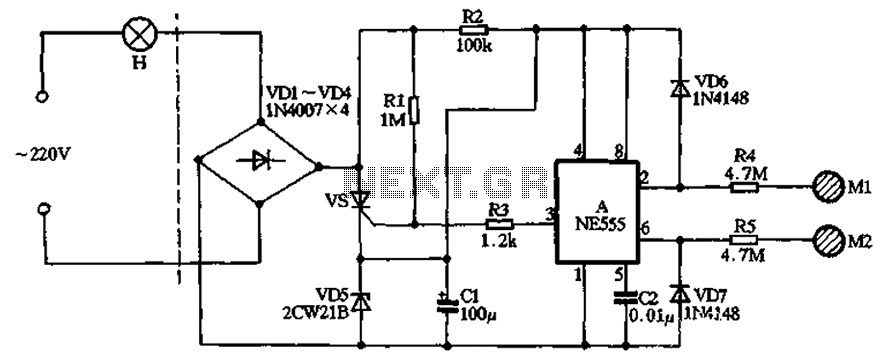
This circuit activates a lamp at a remote location when the doorbell switch is pressed. It is designed specifically for solenoid-type doorbells, as electronic doorbells that play tunes are incompatible. The circuit addresses the issue of potentially missing the sound of a doorbell while engaged in other activities, such as watching television, by providing a visual indicator. An LED may also be used as an alternative indicator. Simply connecting a lamp in parallel with the doorbell could result in additional power drain from the doorbell's batteries or transformer. Instead, a series resistor, R1, is included in series with the doorbell to reduce current flow and extend battery life. The value of R1 is selected to develop approximately 0.6 to 0.7 volts across it when the doorbell switch is activated. A combination of a 22-ohm resistor in parallel with a 50-ohm resistor is utilized. The voltage drop across R1 is sufficient to activate a transistor, which in turn illuminates the lamp connected in series with the collector. Additionally, an electromechanical counter is employed in parallel with the lamp.
This circuit serves as an effective solution for enhancing the visibility of a doorbell alert, particularly in environments where audio cues may be missed. The design incorporates a solenoid-type doorbell, ensuring compatibility and reliable operation. The inclusion of a series resistor, R1, is crucial; it limits the current flowing through the doorbell when the switch is engaged. The calculated voltage drop across R1 not only ensures that the transistor is activated but also minimizes power consumption, thereby prolonging the life of the power source.
The choice of resistors (22 ohms and 50 ohms in parallel) allows for a precise voltage drop that is tailored to the specific requirements of the circuit. This configuration enables the transistor to switch on effectively, allowing for the lamp to illuminate brightly when the doorbell is pressed. The electromechanical counter adds an additional layer of functionality, providing a count of the number of times the doorbell has been activated, which can be useful in monitoring visitor frequency.
Overall, this circuit design is a practical enhancement for doorbell systems, integrating visual indicators and counters while maintaining energy efficiency. Proper selection of components and careful consideration of circuit parameters are essential for achieving optimal performance and reliability.This circuit will light a lamp at a remote location when the doorbell switch is pressed. This circuit should only be used with the solenoid type doorbells, the electronic type that play tunes will not work here. It is quite easy to miss the sound of a doorbell if you are watching TV, this circuit gets round the problem by providing a visual indic
ation. As an alternative, a LED could also be used. You could just parallel a lamp across the doorbell, but this would mean extra drain from the doorbell batteries or transformer. A series resistor, R1 is wired in series with the doorbell and reduces current flow, thereby increasing battery life.
The value of R1 is chosen so that about 0. 6 to 0. 7 volts is developed across it, when the doorbell switch is pressed. I used a combination of a 22 ohm resistor in parallel with a 50 ohm. The voltage drop across R1 is sufficient to switch on the transistor, the lamp in series with the collector will then illuminate. I also used an electromechanical counter in parallel with the lamp. 🔗 External reference
This circuit serves as an effective solution for enhancing the visibility of a doorbell alert, particularly in environments where audio cues may be missed. The design incorporates a solenoid-type doorbell, ensuring compatibility and reliable operation. The inclusion of a series resistor, R1, is crucial; it limits the current flowing through the doorbell when the switch is engaged. The calculated voltage drop across R1 not only ensures that the transistor is activated but also minimizes power consumption, thereby prolonging the life of the power source.
The choice of resistors (22 ohms and 50 ohms in parallel) allows for a precise voltage drop that is tailored to the specific requirements of the circuit. This configuration enables the transistor to switch on effectively, allowing for the lamp to illuminate brightly when the doorbell is pressed. The electromechanical counter adds an additional layer of functionality, providing a count of the number of times the doorbell has been activated, which can be useful in monitoring visitor frequency.
Overall, this circuit design is a practical enhancement for doorbell systems, integrating visual indicators and counters while maintaining energy efficiency. Proper selection of components and careful consideration of circuit parameters are essential for achieving optimal performance and reliability.This circuit will light a lamp at a remote location when the doorbell switch is pressed. This circuit should only be used with the solenoid type doorbells, the electronic type that play tunes will not work here. It is quite easy to miss the sound of a doorbell if you are watching TV, this circuit gets round the problem by providing a visual indic
ation. As an alternative, a LED could also be used. You could just parallel a lamp across the doorbell, but this would mean extra drain from the doorbell batteries or transformer. A series resistor, R1 is wired in series with the doorbell and reduces current flow, thereby increasing battery life.
The value of R1 is chosen so that about 0. 6 to 0. 7 volts is developed across it, when the doorbell switch is pressed. I used a combination of a 22 ohm resistor in parallel with a 50 ohm. The voltage drop across R1 is sufficient to switch on the transistor, the lamp in series with the collector will then illuminate. I also used an electromechanical counter in parallel with the lamp. 🔗 External reference