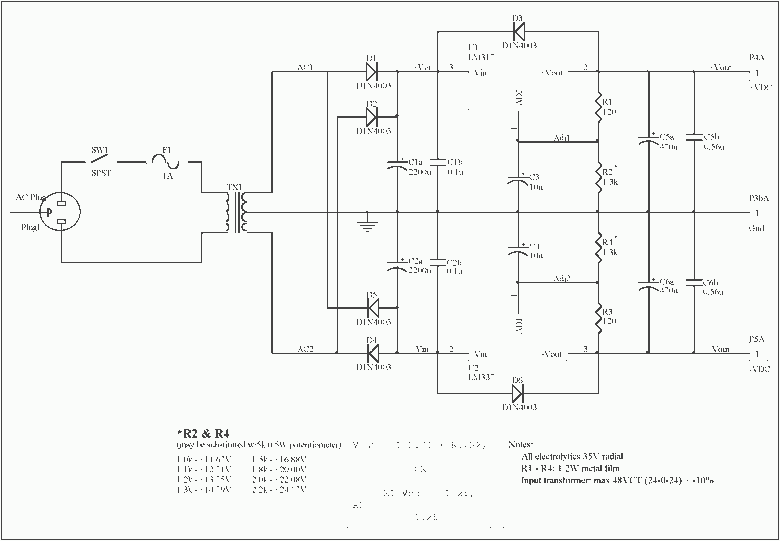
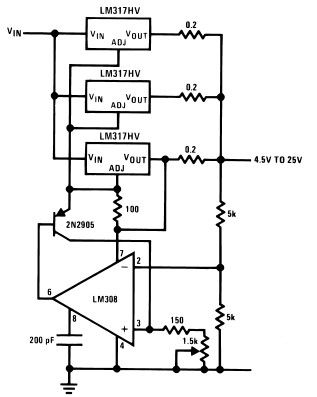
Dual polarity power supply
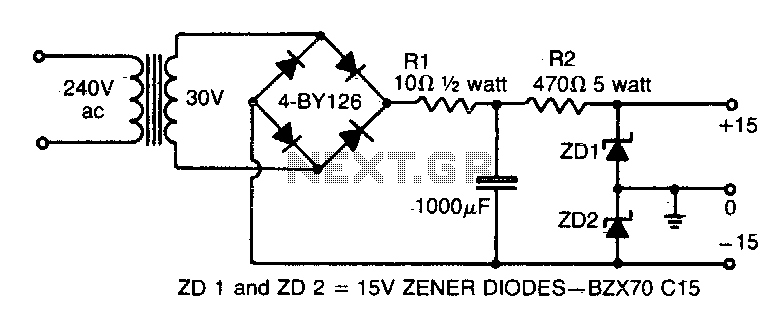
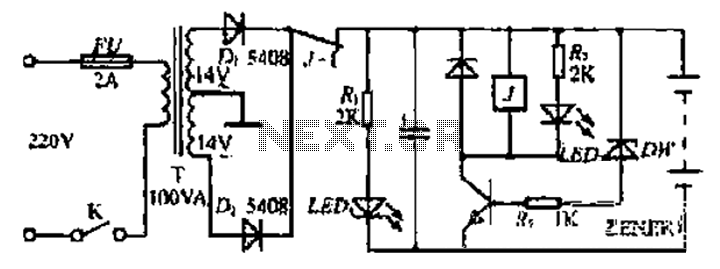
This simple circuit provides both a positive and negative supply from a single transformer winding and a full-wave bridge rectifier. Two zener diodes connected in series create a voltage division, with their junction point grounded. It is important to note that the filter capacitor should not be grounded through its case.
This circuit operates by utilizing a single transformer winding to supply alternating current (AC) to a full-wave bridge rectifier, which converts the AC voltage into direct current (DC). The bridge rectifier consists of four diodes arranged in a configuration that allows current to flow through the load during both halves of the AC cycle, thus providing a more stable output voltage.
The two zener diodes are employed to create a dual voltage output. By placing the zener diodes in series, each diode can be selected to have a specific breakdown voltage, allowing for precise voltage regulation. The center point between the two zener diodes serves as the ground reference for the circuit, effectively splitting the output into positive and negative voltages relative to this ground point.
In addition, the filter capacitor is essential for smoothing the rectified voltage. It stores charge and releases it when the rectified voltage drops, thus reducing ripple in the output. Care must be taken to ensure that the capacitor is not grounded through its case, as this could introduce noise and instability into the circuit. Instead, the capacitor should be connected to the appropriate points in the circuit to maintain the integrity of the voltage levels and ensure reliable performance.
This configuration is commonly used in various applications where dual power supplies are required, such as operational amplifiers, analog circuits, and signal processing systems. Proper selection of the transformer, zener diodes, and filter capacitor values is critical to achieving the desired output characteristics and ensuring the circuit operates within its intended specifications.This simple circuit gives a positive and negative supply from a single transformer winding and one full-wave bridge. Two zener diodes in series provide the voltage division and their centerpoint is grounded (The filter capacitor must not be grounded via its case).
This circuit operates by utilizing a single transformer winding to supply alternating current (AC) to a full-wave bridge rectifier, which converts the AC voltage into direct current (DC). The bridge rectifier consists of four diodes arranged in a configuration that allows current to flow through the load during both halves of the AC cycle, thus providing a more stable output voltage.
The two zener diodes are employed to create a dual voltage output. By placing the zener diodes in series, each diode can be selected to have a specific breakdown voltage, allowing for precise voltage regulation. The center point between the two zener diodes serves as the ground reference for the circuit, effectively splitting the output into positive and negative voltages relative to this ground point.
In addition, the filter capacitor is essential for smoothing the rectified voltage. It stores charge and releases it when the rectified voltage drops, thus reducing ripple in the output. Care must be taken to ensure that the capacitor is not grounded through its case, as this could introduce noise and instability into the circuit. Instead, the capacitor should be connected to the appropriate points in the circuit to maintain the integrity of the voltage levels and ensure reliable performance.
This configuration is commonly used in various applications where dual power supplies are required, such as operational amplifiers, analog circuits, and signal processing systems. Proper selection of the transformer, zener diodes, and filter capacitor values is critical to achieving the desired output characteristics and ensuring the circuit operates within its intended specifications.This simple circuit gives a positive and negative supply from a single transformer winding and one full-wave bridge. Two zener diodes in series provide the voltage division and their centerpoint is grounded (The filter capacitor must not be grounded via its case).