Dual Polarity Power Supply
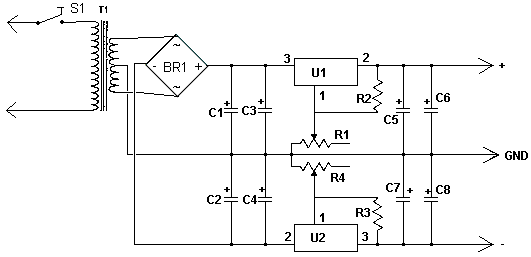
This dual polarity power supply is simple to construct, requires minimal components, and is adjustable from 0 to 15 volts. It is suitable for powering operational amplifier circuits as well as other circuits that necessitate a dual supply voltage. The components U1 and U2 have a minimum output of ±1.2V. To achieve lower voltages, two 1N4003 diodes can be added in series with the output of the regulator. Each diode causes a voltage drop of approximately 0.6V, enabling the supply to reach 0 volts. However, this modification will also reduce the maximum output voltage by 1.2V.
This dual polarity power supply circuit is designed to provide a stable voltage output ranging from 0 to 15 volts, making it versatile for various electronic applications. The circuit is built around two voltage regulators, denoted as U1 and U2, which are responsible for generating the positive and negative voltage rails. The use of operational amplifiers in circuits often necessitates a dual supply, and this design effectively meets that requirement with ease of assembly and minimal component count.
The voltage regulators selected for this circuit typically have a minimum output voltage of ±1.2V. In scenarios where lower voltage outputs are needed, the addition of two 1N4003 diodes in series with the output of the regulators is recommended. Each diode introduces a forward voltage drop of approximately 0.6V, which allows the output voltage to be adjusted down to 0 volts. It is important to note that incorporating these diodes will also reduce the maximum output voltage of the power supply by a total of 1.2V, which must be considered in the design phase.
The circuit layout should include appropriate filtering capacitors at the input and output of the voltage regulators to ensure stable operation and minimize ripple voltage. Additionally, heat sinks may be required depending on the load current to maintain the thermal stability of the regulators. Proper attention to the layout and grounding techniques will enhance performance and reliability, making this dual polarity power supply an excellent choice for experimental and prototyping environments.This dual polarity power supply is easy to build, requires few parts, and is adjustable from 0-15 volts. It is great for powering op amp circuits, as well as other circuits that require a dual supply voltage.
4. U1 and U2 can only go down to a minimum of +-1. 2V. If you need to go lower, you can add two 1N4003 diodes in series with the output of th e regulator. The diodes drop about 0. 6V each, which will allow the supply to go to 0. Note that this will also decrease your maximum output voltage by 1. 2V. (Thanks to Steve Horvath, horvaths@techcomnet. com for the suggestion). 🔗 External reference
This dual polarity power supply circuit is designed to provide a stable voltage output ranging from 0 to 15 volts, making it versatile for various electronic applications. The circuit is built around two voltage regulators, denoted as U1 and U2, which are responsible for generating the positive and negative voltage rails. The use of operational amplifiers in circuits often necessitates a dual supply, and this design effectively meets that requirement with ease of assembly and minimal component count.
The voltage regulators selected for this circuit typically have a minimum output voltage of ±1.2V. In scenarios where lower voltage outputs are needed, the addition of two 1N4003 diodes in series with the output of the regulators is recommended. Each diode introduces a forward voltage drop of approximately 0.6V, which allows the output voltage to be adjusted down to 0 volts. It is important to note that incorporating these diodes will also reduce the maximum output voltage of the power supply by a total of 1.2V, which must be considered in the design phase.
The circuit layout should include appropriate filtering capacitors at the input and output of the voltage regulators to ensure stable operation and minimize ripple voltage. Additionally, heat sinks may be required depending on the load current to maintain the thermal stability of the regulators. Proper attention to the layout and grounding techniques will enhance performance and reliability, making this dual polarity power supply an excellent choice for experimental and prototyping environments.This dual polarity power supply is easy to build, requires few parts, and is adjustable from 0-15 volts. It is great for powering op amp circuits, as well as other circuits that require a dual supply voltage.
4. U1 and U2 can only go down to a minimum of +-1. 2V. If you need to go lower, you can add two 1N4003 diodes in series with the output of th e regulator. The diodes drop about 0. 6V each, which will allow the supply to go to 0. Note that this will also decrease your maximum output voltage by 1. 2V. (Thanks to Steve Horvath, horvaths@techcomnet. com for the suggestion). 🔗 External reference