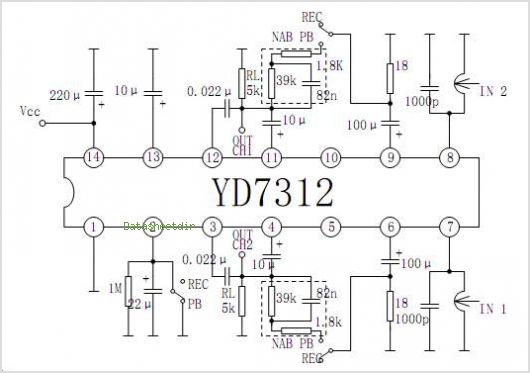
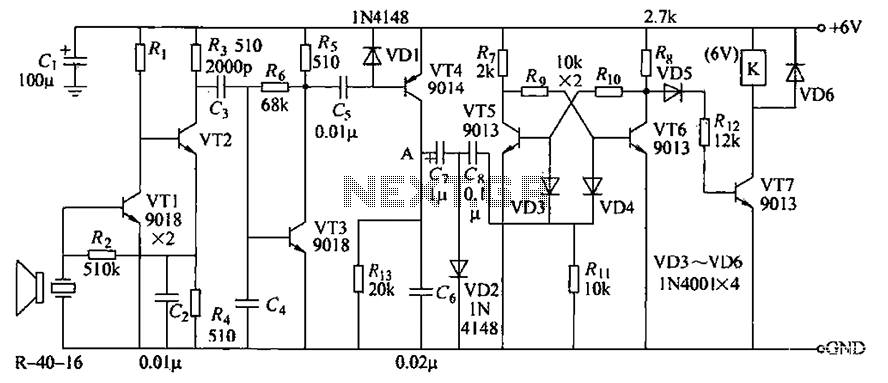
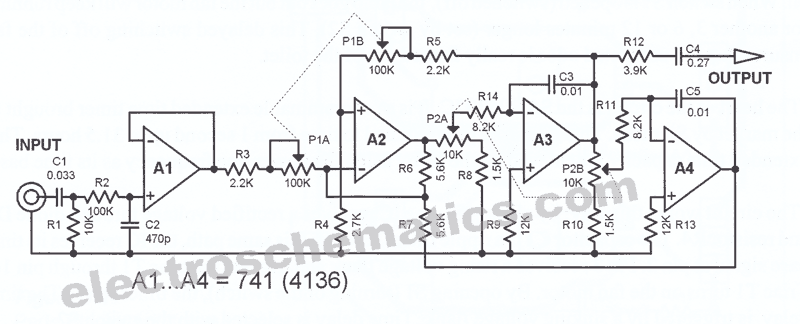
Dual Tone Sounder Circuit
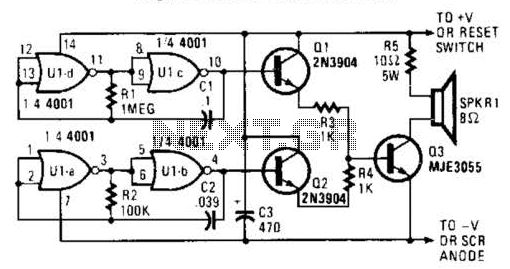
An external horn-type speaker is optimal for this circuit. However, such devices demand significant power, so this sounder should only be employed in alarm circuits utilizing at least a 6-A SCR as the sounder driver. The circuit incorporates a single CMOS 4001 quad 2-input NOR gate, two 2N3904 general-purpose NPN transistors, and a single MJE3055 power transistor to produce a two-tone output. Gates U1-a and U1-b are configured as a basic feedback oscillator, with R2 and C2 determining the oscillator's frequency. With the specified values, the circuit oscillates at approximately 500 Hz. Gates U1-c and U1-d are arranged in a similar oscillator configuration, but they function at a significantly lower frequency.
The oscillator frequencies (and consequently the tones they generate) can be modified by adjusting the values of R1 and C7 for the low-frequency oscillator, and R2 and C2 for the high-frequency oscillator. Reducing the values of these components will increase the frequency, while increasing their values will decrease the frequency. The outputs from the two oscillators are fed into separate amplifiers configured as emitter followers, which drive a single power transistor (Q3, an MJE3055). A 10- or 5-ohm resistor, R5, is utilized to limit the current flowing through the speaker and Q3 to a safe level. To enhance the sound output, R5 can be substituted with an additional speaker.
This circuit design is primarily aimed at generating distinct audio tones suitable for alarm applications. The use of a horn-type speaker allows for increased sound projection, making it effective for alerting purposes in various environments. The choice of components, including the CMOS NOR gates and NPN transistors, facilitates the creation of the desired audio frequencies through feedback oscillation.
The oscillator configuration is crucial for achieving the required sound characteristics. By carefully selecting resistor and capacitor values, the designer can fine-tune the output frequencies to meet specific requirements. The integration of emitter follower amplifiers ensures that the signal strength is adequate to drive the power transistor, which in turn powers the speaker without risking damage to the components.
In practical applications, attention must be paid to power management, particularly when utilizing a high-power SCR for driving the sounder. The circuit’s design allows for flexibility in sound output, and the option to replace the current-limiting resistor with an additional speaker provides an opportunity to amplify the sound further, catering to environments where high sound levels are necessary for effective alerting. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a robust solution for alarm systems requiring reliable and powerful audio output. An outside horn-type speaker works best with the circuit. However, such devices require a great deal of power, so this sounder should only be used in alarm circuits where at least a 6-A SCR is used as the sounder driver. A single CMOS 4001 quad 2-input NOR gate, two 2N3904 general- purpose npri transistors, and a single MJE3055 power transistor combine to generate a two-tone output.
Gates Ul-a and Ul-b are configured as a simple feedback oscillator with R2 and C2 setting the oscillator`s frequency. With the values shown, the circuit oscillates at about 500 Hz. Gates Ul-c and Ul-d are connected in a similar oscillator circuit, but they operate at a much lower frequency.
The oscillator frequencies (and thus the tones that they produce) can be altered by increasing or decreasing, the values of Rl and C7] for the low-frequency oscillator and R2 and C2 for the high-frequency oscillator. Decreasing the values of those components will increase the frequency; increasing their values will decrease the frequency.
The two oscillator outputs are connected to separate amplifiers (configured as emitter followers), whose outputs are used to drive a single power transistor (Q3, an MJE3055). 10-, 5-W resistor, R5, is used to limit the current through the speaker and Q3 to a safe level. To boost the sound level, R5 can be replaced with another speaker.
The oscillator frequencies (and consequently the tones they generate) can be modified by adjusting the values of R1 and C7 for the low-frequency oscillator, and R2 and C2 for the high-frequency oscillator. Reducing the values of these components will increase the frequency, while increasing their values will decrease the frequency. The outputs from the two oscillators are fed into separate amplifiers configured as emitter followers, which drive a single power transistor (Q3, an MJE3055). A 10- or 5-ohm resistor, R5, is utilized to limit the current flowing through the speaker and Q3 to a safe level. To enhance the sound output, R5 can be substituted with an additional speaker.
This circuit design is primarily aimed at generating distinct audio tones suitable for alarm applications. The use of a horn-type speaker allows for increased sound projection, making it effective for alerting purposes in various environments. The choice of components, including the CMOS NOR gates and NPN transistors, facilitates the creation of the desired audio frequencies through feedback oscillation.
The oscillator configuration is crucial for achieving the required sound characteristics. By carefully selecting resistor and capacitor values, the designer can fine-tune the output frequencies to meet specific requirements. The integration of emitter follower amplifiers ensures that the signal strength is adequate to drive the power transistor, which in turn powers the speaker without risking damage to the components.
In practical applications, attention must be paid to power management, particularly when utilizing a high-power SCR for driving the sounder. The circuit’s design allows for flexibility in sound output, and the option to replace the current-limiting resistor with an additional speaker provides an opportunity to amplify the sound further, catering to environments where high sound levels are necessary for effective alerting. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a robust solution for alarm systems requiring reliable and powerful audio output. An outside horn-type speaker works best with the circuit. However, such devices require a great deal of power, so this sounder should only be used in alarm circuits where at least a 6-A SCR is used as the sounder driver. A single CMOS 4001 quad 2-input NOR gate, two 2N3904 general- purpose npri transistors, and a single MJE3055 power transistor combine to generate a two-tone output.
Gates Ul-a and Ul-b are configured as a simple feedback oscillator with R2 and C2 setting the oscillator`s frequency. With the values shown, the circuit oscillates at about 500 Hz. Gates Ul-c and Ul-d are connected in a similar oscillator circuit, but they operate at a much lower frequency.
The oscillator frequencies (and thus the tones that they produce) can be altered by increasing or decreasing, the values of Rl and C7] for the low-frequency oscillator and R2 and C2 for the high-frequency oscillator. Decreasing the values of those components will increase the frequency; increasing their values will decrease the frequency.
The two oscillator outputs are connected to separate amplifiers (configured as emitter followers), whose outputs are used to drive a single power transistor (Q3, an MJE3055). 10-, 5-W resistor, R5, is used to limit the current through the speaker and Q3 to a safe level. To boost the sound level, R5 can be replaced with another speaker.