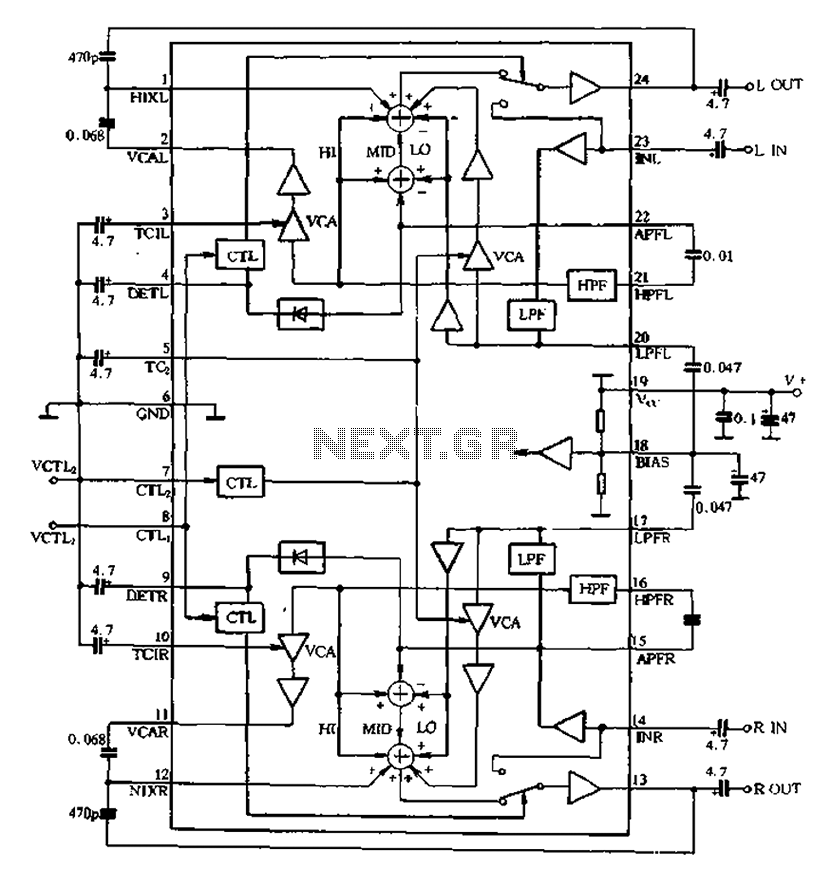
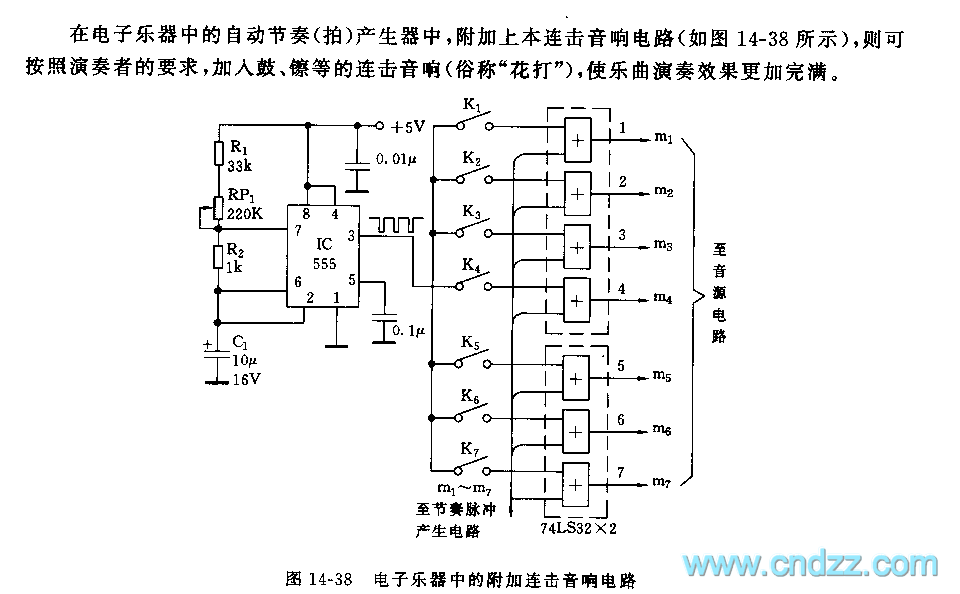
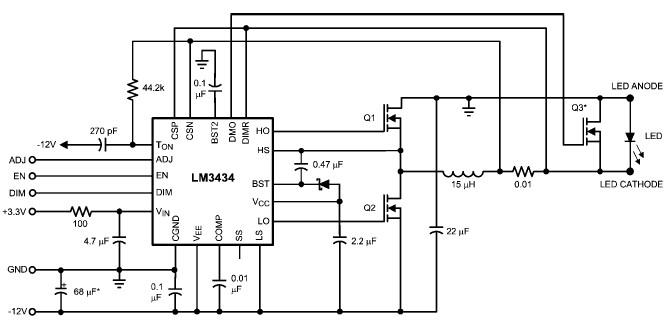
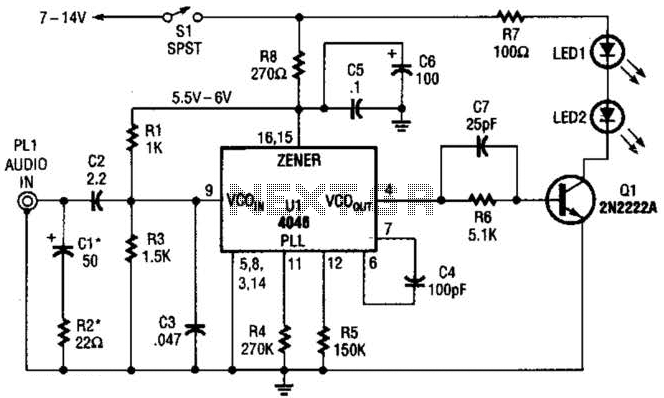
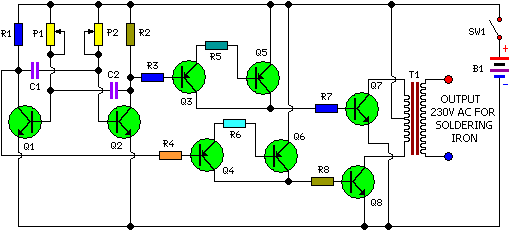
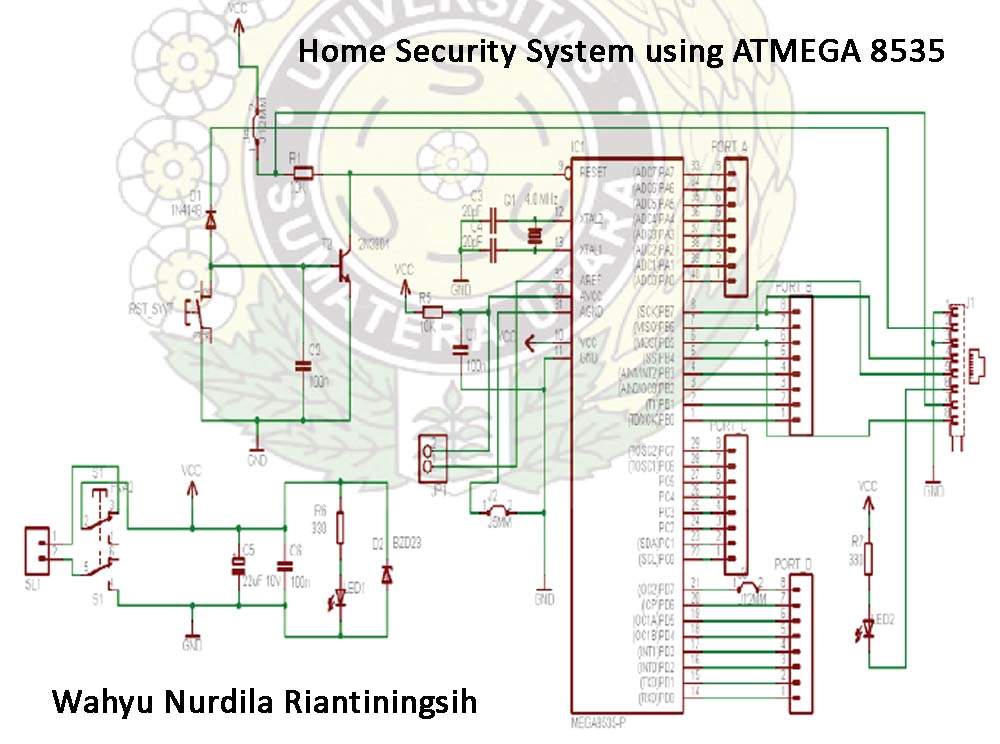
Easy Crystal Impedance Checker Circuit
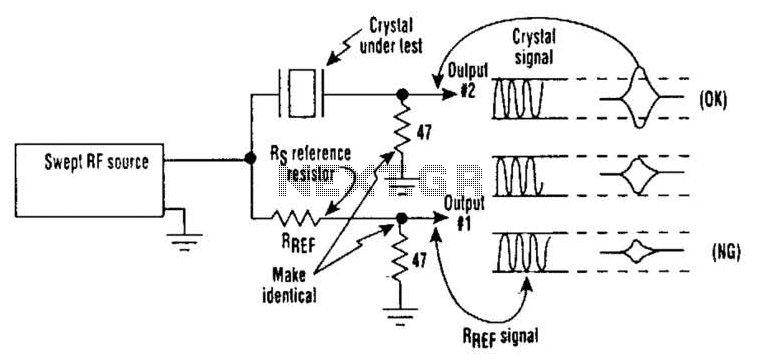
Occasionally, microprocessors and microcomputers may not be compatible with certain microprocessor crystals. Many data sheets for microprocessors specify maximum values for a crystal's equivalent series resistance (Rs), which may not be met by some crystals marketed for use with these devices. Consequently, a crystal with an Rs value exceeding the maximum specified for the microprocessor may lead to issues, such as an unreliable or non-functional clock oscillator. To address this issue, a suspected crystal can be quickly tested for Rs using a simple setup that includes a sweep generator, an oscilloscope, and three resistors. When the frequency source is adjusted to match the crystal's frequency, output 2 will reach its maximum. If this output exceeds the amplitude of output 1, the crystal's Rs value is lower than that of the reference resistor. Conversely, if it does not exceed output 1's amplitude, the crystal's Rs value is too high.
Testing the equivalent series resistance (Rs) of a crystal oscillator is crucial for ensuring compatibility with microprocessors and microcomputers. Incompatible crystals may lead to malfunctioning circuits, which can compromise the performance of electronic devices. The described testing setup leverages a sweep generator to provide a frequency signal that is varied until it matches the resonant frequency of the crystal under test. An oscilloscope is employed to visualize the output signals, allowing for real-time analysis of the crystal's behavior.
The three resistors in the circuit serve specific roles: one acts as a reference resistor, while the others may be used to create voltage dividers or limit current in the testing circuit. The relationship between the amplitudes of output 1 and output 2 provides critical information about the crystal's Rs value. If output 2 surpasses output 1, it indicates that the crystal's Rs is lower than the reference, suggesting it is suitable for use. If output 2 does not exceed output 1, this indicates that the Rs is too high, which could lead to inefficiencies or failure in the oscillator circuit.
This testing method is advantageous due to its simplicity and effectiveness, allowing engineers to quickly ascertain the suitability of a crystal for a given microprocessor application. Proper selection and testing of crystals can significantly enhance the reliability and performance of electronic systems, particularly in timing applications where precision is paramount. On occasion, microprocessors/microcomputers and microprocessor crystals just aren`t compatible with each other. Many microprocessor data sheets specify maximum values for a crystal`s equivalent series resistance (Rs) that aren`t met by some crystals advertised for microprocessor/ microcomputer use.
As a result, a crystal with an Rs value greater than the maximum specified for the chip might cause problems, such as a balky or even inoperative clock oscillator. To tackle this problem, a suspected crystal can be given a quick check for Rs with a simple test setup that consists of a sweep generator, oscilloscope, and three resistors (see the figure).
When the frequency source is brought to the crystal`s frequency, output 2 will maximize. If it exceeds the amplitude of output 1, the crystal`s Rs value will be less than the Rs reference resistor`s value. If it doesn`t exceed output l`s amplitude, the crystal`s Rs value is too large.
Testing the equivalent series resistance (Rs) of a crystal oscillator is crucial for ensuring compatibility with microprocessors and microcomputers. Incompatible crystals may lead to malfunctioning circuits, which can compromise the performance of electronic devices. The described testing setup leverages a sweep generator to provide a frequency signal that is varied until it matches the resonant frequency of the crystal under test. An oscilloscope is employed to visualize the output signals, allowing for real-time analysis of the crystal's behavior.
The three resistors in the circuit serve specific roles: one acts as a reference resistor, while the others may be used to create voltage dividers or limit current in the testing circuit. The relationship between the amplitudes of output 1 and output 2 provides critical information about the crystal's Rs value. If output 2 surpasses output 1, it indicates that the crystal's Rs is lower than the reference, suggesting it is suitable for use. If output 2 does not exceed output 1, this indicates that the Rs is too high, which could lead to inefficiencies or failure in the oscillator circuit.
This testing method is advantageous due to its simplicity and effectiveness, allowing engineers to quickly ascertain the suitability of a crystal for a given microprocessor application. Proper selection and testing of crystals can significantly enhance the reliability and performance of electronic systems, particularly in timing applications where precision is paramount. On occasion, microprocessors/microcomputers and microprocessor crystals just aren`t compatible with each other. Many microprocessor data sheets specify maximum values for a crystal`s equivalent series resistance (Rs) that aren`t met by some crystals advertised for microprocessor/ microcomputer use.
As a result, a crystal with an Rs value greater than the maximum specified for the chip might cause problems, such as a balky or even inoperative clock oscillator. To tackle this problem, a suspected crystal can be given a quick check for Rs with a simple test setup that consists of a sweep generator, oscilloscope, and three resistors (see the figure).
When the frequency source is brought to the crystal`s frequency, output 2 will maximize. If it exceeds the amplitude of output 1, the crystal`s Rs value will be less than the Rs reference resistor`s value. If it doesn`t exceed output l`s amplitude, the crystal`s Rs value is too large.