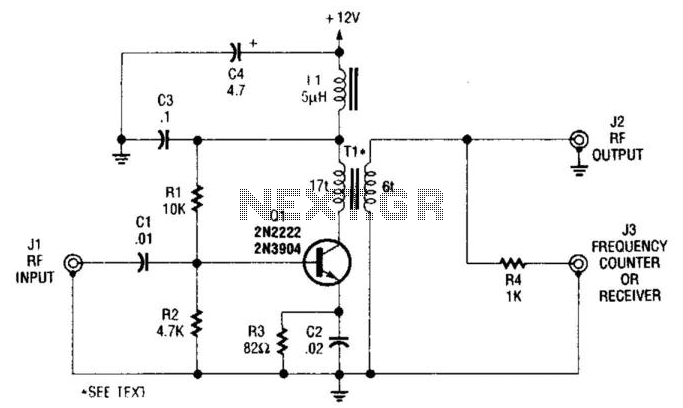
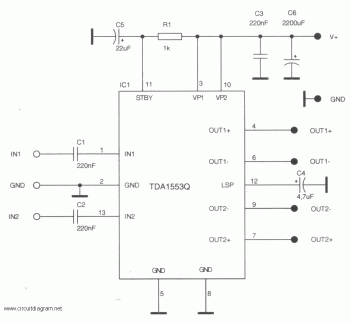
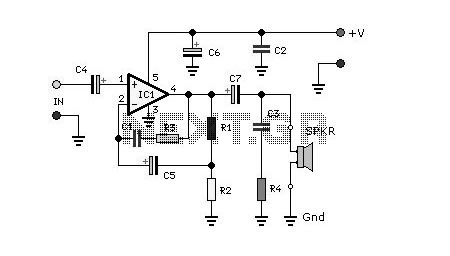
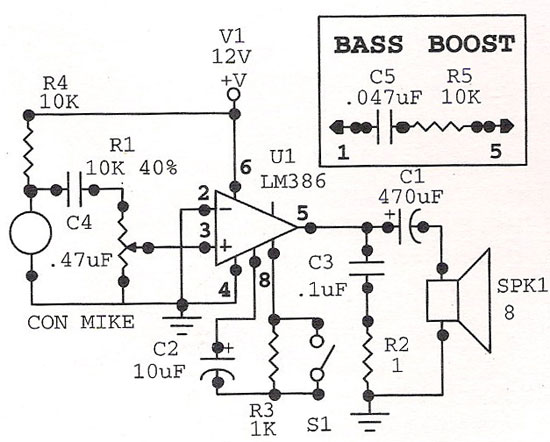
Electret Condenser Microphone Amplifier
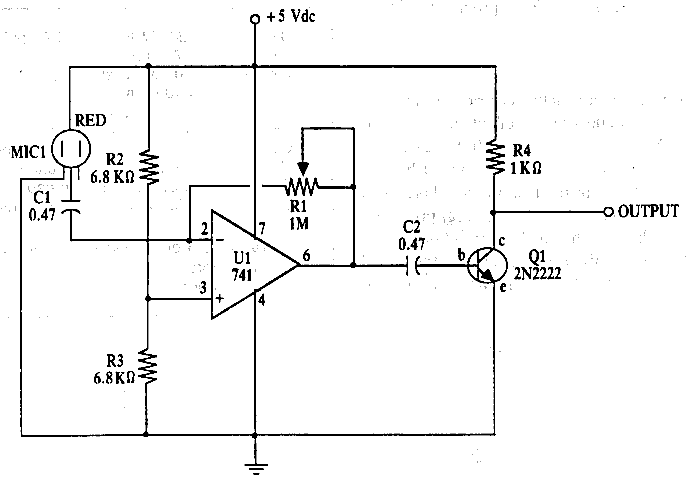
Amplifier circuit for electret microphones (condenser microphones). It amplifies the audio signals picked up by the electret microphone using a 741 op-amp and a 2N2222 transistor.
The amplifier circuit designed for electret microphones utilizes a combination of a 741 operational amplifier (op-amp) and a 2N2222 transistor to enhance the weak audio signals captured by the microphone. The electret microphone, which operates on a low voltage and requires a biasing voltage, is typically connected to the non-inverting input of the op-amp.
The 741 op-amp serves as the primary amplification stage. It is configured in a non-inverting configuration to provide high input impedance, ensuring minimal loading on the microphone. The gain of the op-amp can be set using external resistors connected between the output and the inverting input. This configuration allows for precise control over the amplification factor, which is crucial for optimizing the signal level for further processing.
Following the op-amp stage, the amplified signal is fed into a 2N2222 transistor, which acts as a buffer and additional amplification stage. The transistor is configured in a common-emitter arrangement, providing further gain while offering the ability to drive larger loads. The output from the transistor stage can be connected to other audio processing components, such as filters or audio processors, ensuring that the amplified signal is suitable for various applications.
The circuit may also include additional components such as capacitors for AC coupling to eliminate DC bias and resistors for setting the operating point of the transistor. Proper power supply decoupling is essential to maintain stability and minimize noise in the circuit. Overall, this amplifier circuit effectively enhances the audio signals from electret microphones, making it suitable for applications in audio recording, communication devices, and various electronic projects.Amplifier circuit for electret microphones (condenser microphones). Amplifier the audio signals picked up by the electret microphone, using 741 op-amp and a 2N2222 transistor.. 🔗 External reference
The amplifier circuit designed for electret microphones utilizes a combination of a 741 operational amplifier (op-amp) and a 2N2222 transistor to enhance the weak audio signals captured by the microphone. The electret microphone, which operates on a low voltage and requires a biasing voltage, is typically connected to the non-inverting input of the op-amp.
The 741 op-amp serves as the primary amplification stage. It is configured in a non-inverting configuration to provide high input impedance, ensuring minimal loading on the microphone. The gain of the op-amp can be set using external resistors connected between the output and the inverting input. This configuration allows for precise control over the amplification factor, which is crucial for optimizing the signal level for further processing.
Following the op-amp stage, the amplified signal is fed into a 2N2222 transistor, which acts as a buffer and additional amplification stage. The transistor is configured in a common-emitter arrangement, providing further gain while offering the ability to drive larger loads. The output from the transistor stage can be connected to other audio processing components, such as filters or audio processors, ensuring that the amplified signal is suitable for various applications.
The circuit may also include additional components such as capacitors for AC coupling to eliminate DC bias and resistors for setting the operating point of the transistor. Proper power supply decoupling is essential to maintain stability and minimize noise in the circuit. Overall, this amplifier circuit effectively enhances the audio signals from electret microphones, making it suitable for applications in audio recording, communication devices, and various electronic projects.Amplifier circuit for electret microphones (condenser microphones). Amplifier the audio signals picked up by the electret microphone, using 741 op-amp and a 2N2222 transistor.. 🔗 External reference