Electrical transformer tutorial
Afroman explains the fundamentals of transformer operation, where to purchase step-down mains transformers, and how to safely wire one to mains voltages. The discussion includes both European and North American wiring standards. The presentation concludes with a brief example of converting AC to DC in an unregulated dual-rail power supply. It is important to include a fuse in series with the mains wiring. The next segment will focus on diodes as part of the series on building a stable power supply.
Transformers are crucial components in power supply design, functioning to convert voltage levels while isolating different sections of a circuit. A step-down transformer reduces high mains voltage to a lower, more manageable level suitable for various applications. When selecting a transformer, it is essential to consider factors such as power rating, input and output voltages, and the frequency of operation.
In wiring a transformer to mains voltages, safety is paramount. Proper insulation, secure connections, and adherence to local electrical codes are essential to prevent electrical hazards. The wiring practices differ between European and North American standards, with European systems typically employing a three-phase system and North American systems often using single-phase configurations.
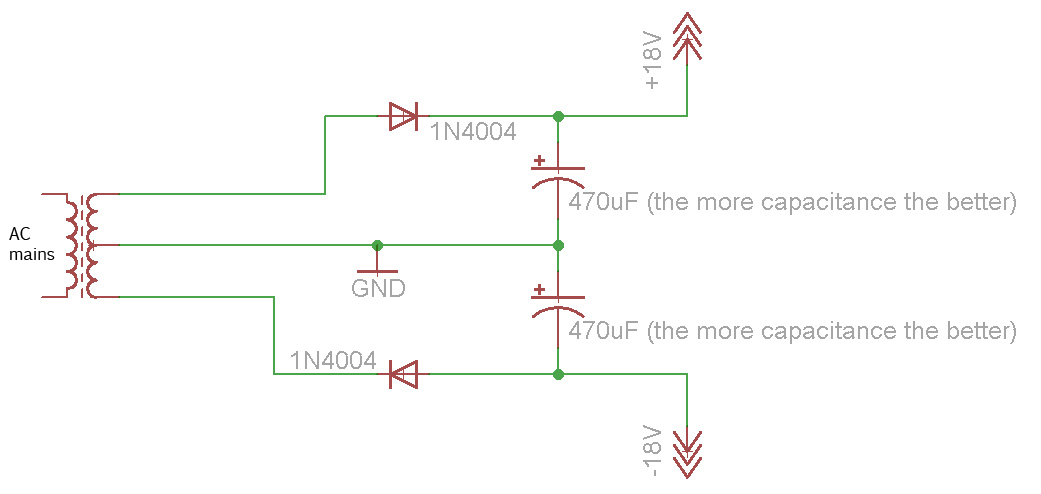
The example of AC to DC conversion in an unregulated dual-rail power supply illustrates the practical application of transformers in power electronics. The unregulated power supply typically consists of a transformer, rectifier diodes, and smoothing capacitors. The transformer steps down the AC voltage, which is then rectified by diodes that convert the AC to pulsating DC. The dual-rail configuration provides both positive and negative voltage rails, which are often required for operational amplifiers and other analog circuits.
Incorporating a fuse in series with the mains wiring serves as a critical safety feature, protecting the circuit from overcurrent conditions that could lead to component damage or fire hazards. The next part of the series will delve into diode functionality, providing insights into their role in rectification and voltage regulation, further enhancing the understanding of building reliable power supplies.Afroman covers the basics of how transformers work, where to shop for step down mains transformers, and how to wire one up to mains voltages without killing yourself. European and North American wiring is discussed. He finishes up with a quick example of AC to DC conversion in an unregulated dual rail power supply. Remember to add a fuse in series with the mains wiring. The diode tutorial is the next part in the trilogy of how to build a stable power supply. 🔗 External reference
Transformers are crucial components in power supply design, functioning to convert voltage levels while isolating different sections of a circuit. A step-down transformer reduces high mains voltage to a lower, more manageable level suitable for various applications. When selecting a transformer, it is essential to consider factors such as power rating, input and output voltages, and the frequency of operation.
In wiring a transformer to mains voltages, safety is paramount. Proper insulation, secure connections, and adherence to local electrical codes are essential to prevent electrical hazards. The wiring practices differ between European and North American standards, with European systems typically employing a three-phase system and North American systems often using single-phase configurations.
The example of AC to DC conversion in an unregulated dual-rail power supply illustrates the practical application of transformers in power electronics. The unregulated power supply typically consists of a transformer, rectifier diodes, and smoothing capacitors. The transformer steps down the AC voltage, which is then rectified by diodes that convert the AC to pulsating DC. The dual-rail configuration provides both positive and negative voltage rails, which are often required for operational amplifiers and other analog circuits.
Incorporating a fuse in series with the mains wiring serves as a critical safety feature, protecting the circuit from overcurrent conditions that could lead to component damage or fire hazards. The next part of the series will delve into diode functionality, providing insights into their role in rectification and voltage regulation, further enhancing the understanding of building reliable power supplies.Afroman covers the basics of how transformers work, where to shop for step down mains transformers, and how to wire one up to mains voltages without killing yourself. European and North American wiring is discussed. He finishes up with a quick example of AC to DC conversion in an unregulated dual rail power supply. Remember to add a fuse in series with the mains wiring. The diode tutorial is the next part in the trilogy of how to build a stable power supply. 🔗 External reference