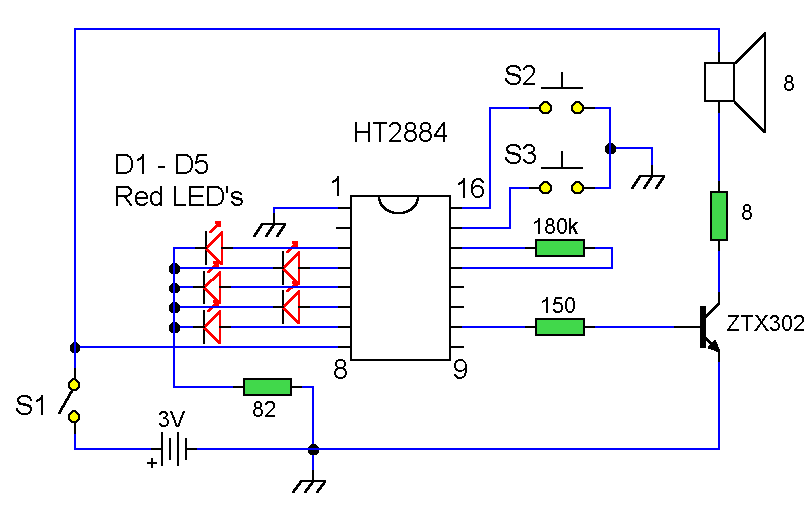
Eliminate hum instrumentation amplifier INA101 circuit
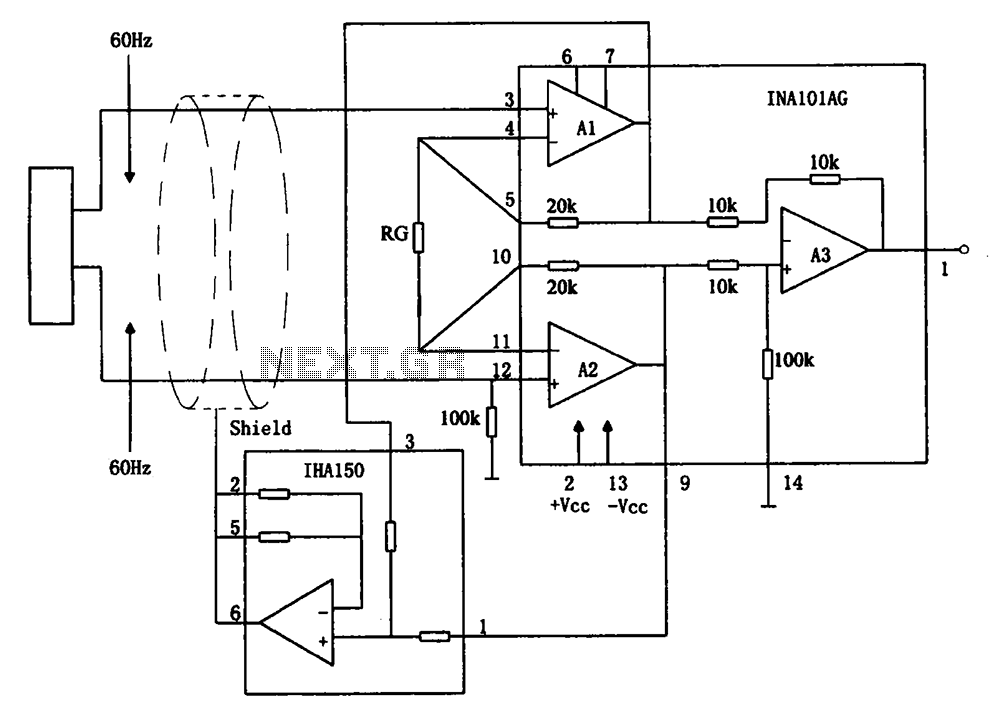
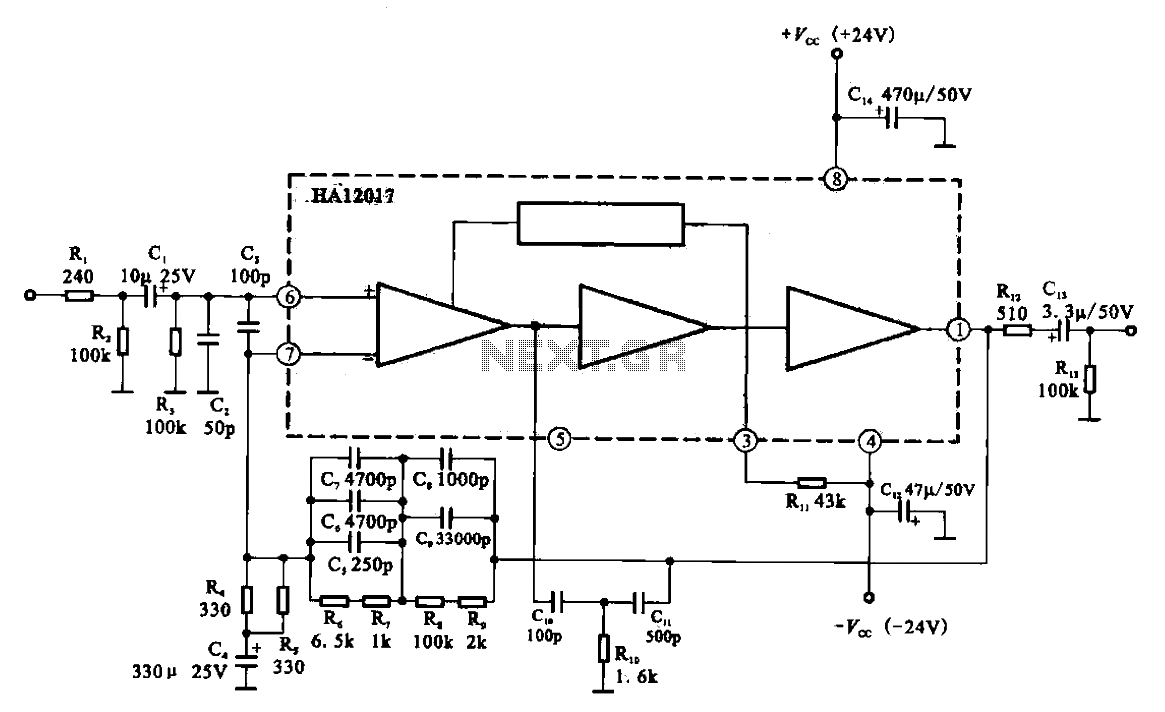
The circuit diagram illustrates a hum elimination instrument amplifier circuit. The amplifier stages A1 and A2 utilize the integrated operational amplifier INA101, followed by stage A3 which employs the INA105. A feedback circuit is incorporated to reduce the power of the interference hum.
The instrument amplifier circuit is designed to effectively eliminate hum and noise from audio signals, enhancing the overall signal quality. The INA101 operational amplifier is chosen for stages A1 and A2 due to its high common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR) and low noise characteristics, which are essential for precision measurement applications. The INA105 in stage A3 serves a similar role, providing additional amplification while maintaining the integrity of the signal.
The feedback circuit plays a crucial role in stabilizing the amplifier's gain and reducing unwanted interference. By carefully selecting resistors and capacitors within the feedback loop, the circuit can be tuned to target specific frequencies of hum, commonly arising from AC power sources. This targeted approach allows for effective suppression of noise without significantly affecting the desired signal.
In designing the circuit, attention must be given to the layout to minimize inductive and capacitive coupling, which can introduce additional noise. Proper grounding techniques and the use of twisted pair wiring for signal paths can further enhance performance. Additionally, bypass capacitors should be placed close to the power supply pins of the operational amplifiers to filter out high-frequency noise.
Overall, this hum elimination instrument amplifier circuit provides a robust solution for applications requiring high-fidelity signal processing, ensuring that the output is clean and free from unwanted hum interference. As shown in FIG To eliminate hum instrument amplifier circuit. FIG amplifier stage A1, A2 selected integrated operational amplifier INA101, followed by level A3 selection INA10 5, INA105 and with similar form a feedback circuit connected to to curb the power of the interference hum.
The instrument amplifier circuit is designed to effectively eliminate hum and noise from audio signals, enhancing the overall signal quality. The INA101 operational amplifier is chosen for stages A1 and A2 due to its high common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR) and low noise characteristics, which are essential for precision measurement applications. The INA105 in stage A3 serves a similar role, providing additional amplification while maintaining the integrity of the signal.
The feedback circuit plays a crucial role in stabilizing the amplifier's gain and reducing unwanted interference. By carefully selecting resistors and capacitors within the feedback loop, the circuit can be tuned to target specific frequencies of hum, commonly arising from AC power sources. This targeted approach allows for effective suppression of noise without significantly affecting the desired signal.
In designing the circuit, attention must be given to the layout to minimize inductive and capacitive coupling, which can introduce additional noise. Proper grounding techniques and the use of twisted pair wiring for signal paths can further enhance performance. Additionally, bypass capacitors should be placed close to the power supply pins of the operational amplifiers to filter out high-frequency noise.
Overall, this hum elimination instrument amplifier circuit provides a robust solution for applications requiring high-fidelity signal processing, ensuring that the output is clean and free from unwanted hum interference. As shown in FIG To eliminate hum instrument amplifier circuit. FIG amplifier stage A1, A2 selected integrated operational amplifier INA101, followed by level A3 selection INA10 5, INA105 and with similar form a feedback circuit connected to to curb the power of the interference hum.