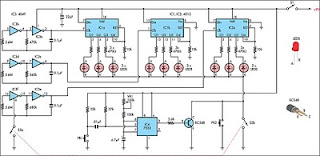
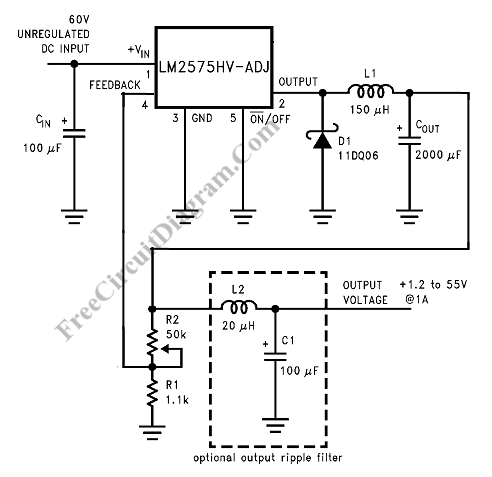
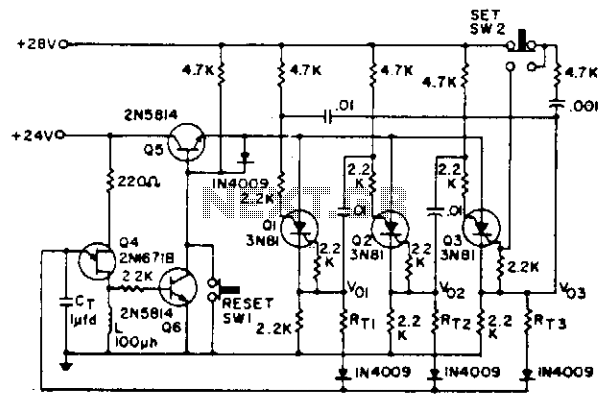
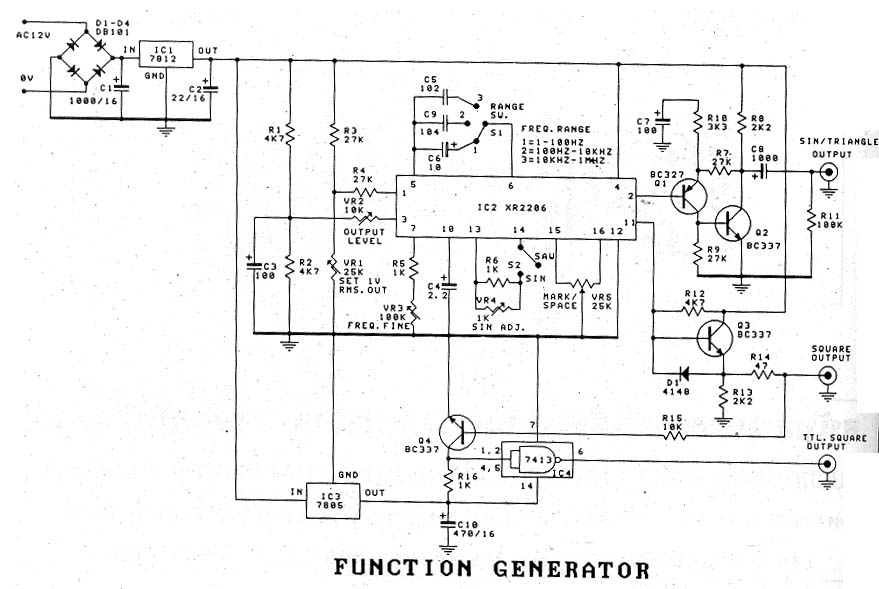
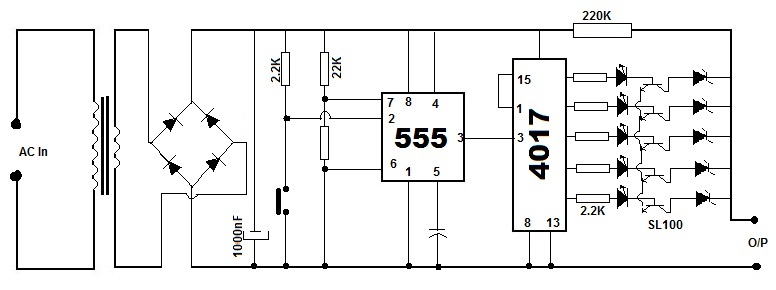
extended counter using cd4017

At the initial state, all pin 15 connections are grounded, causing resistor R0 to be energized. A 555 multivibrator generates a clock signal to IC1, activating the outputs from R0 to R8. This basic circuit can be employed to drive a monostable relay via a single button switch. In the initial state, the relay remains inactive. When the button (P) is pressed, transistor T1 is energized through resistors R1 and R2, allowing the capacitor to charge. The coil is then activated.
This circuit utilizes a 555 timer configured in astable mode to produce a continuous clock signal. The output from the 555 timer (IC1) is connected to a series of output pins (R0 to R8), which can be used to control various devices or components in the circuit. The initial grounding of pin 15 ensures that the circuit remains in a stable state until the button is pressed.
When the button (P) is activated, it creates a path for current to flow through resistors R1 and R2, which serves to limit the current to the base of transistor T1. This action turns on T1, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter, effectively energizing the relay coil. As the relay is activated, it can switch larger loads or control other circuits.
Additionally, the capacitor connected in the circuit plays a crucial role in timing and stabilization. It charges through the resistors, and once a certain voltage threshold is reached, it can influence the behavior of the circuit, such as providing a delay or smoothing out voltage fluctuations.
In summary, this simple yet effective circuit design demonstrates how a 555 timer can be employed to control a relay through a button press, utilizing basic components such as resistors, a transistor, and a capacitor to achieve desired functionality. Proper component selection and configuration are essential to ensure reliable operation and performance of the circuit.At the start condition all pin 15 are connected to the ground, so R0 is energized. A 555multivibrator sendsthe clock signalto IC1, which activates the outputs from R0 to R8. This simple circuit can be utilized to drive a monostable relay through a single button switch. At the start condition the relay does not work. When I press the button (P) T1 is energized through R1 and R2, and the capacitor charges. The coil is jumped by 🔗 External reference
This circuit utilizes a 555 timer configured in astable mode to produce a continuous clock signal. The output from the 555 timer (IC1) is connected to a series of output pins (R0 to R8), which can be used to control various devices or components in the circuit. The initial grounding of pin 15 ensures that the circuit remains in a stable state until the button is pressed.
When the button (P) is activated, it creates a path for current to flow through resistors R1 and R2, which serves to limit the current to the base of transistor T1. This action turns on T1, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter, effectively energizing the relay coil. As the relay is activated, it can switch larger loads or control other circuits.
Additionally, the capacitor connected in the circuit plays a crucial role in timing and stabilization. It charges through the resistors, and once a certain voltage threshold is reached, it can influence the behavior of the circuit, such as providing a delay or smoothing out voltage fluctuations.
In summary, this simple yet effective circuit design demonstrates how a 555 timer can be employed to control a relay through a button press, utilizing basic components such as resistors, a transistor, and a capacitor to achieve desired functionality. Proper component selection and configuration are essential to ensure reliable operation and performance of the circuit.At the start condition all pin 15 are connected to the ground, so R0 is energized. A 555multivibrator sendsthe clock signalto IC1, which activates the outputs from R0 to R8. This simple circuit can be utilized to drive a monostable relay through a single button switch. At the start condition the relay does not work. When I press the button (P) T1 is energized through R1 and R2, and the capacitor charges. The coil is jumped by 🔗 External reference
%2Bdecoder%2BCircuit%2Bschematic%2Busing%2BM8870.png)