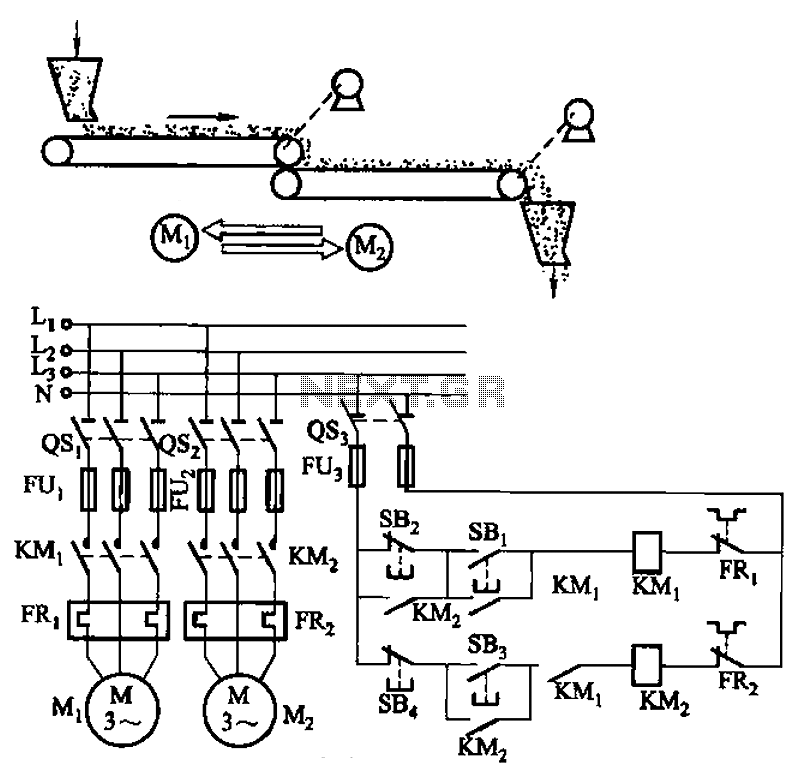
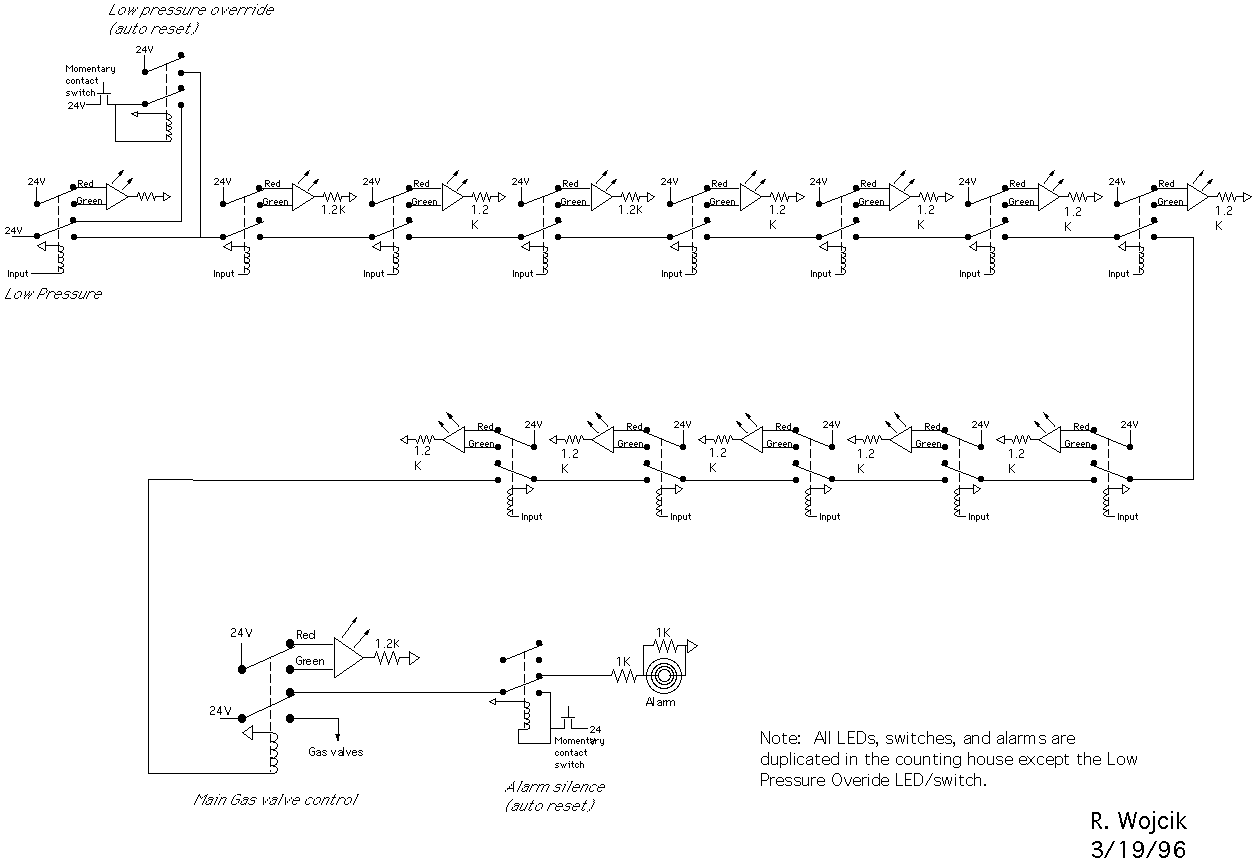
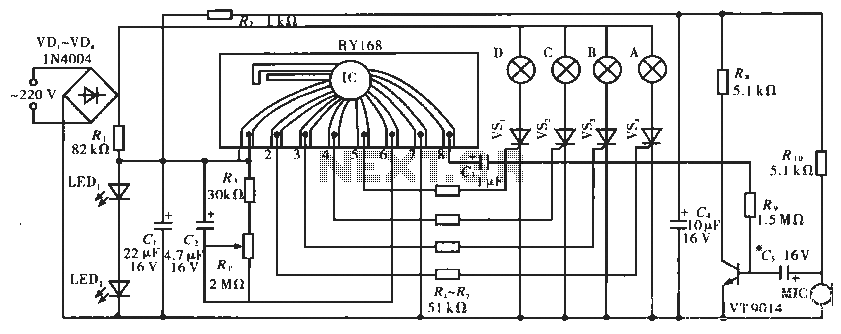
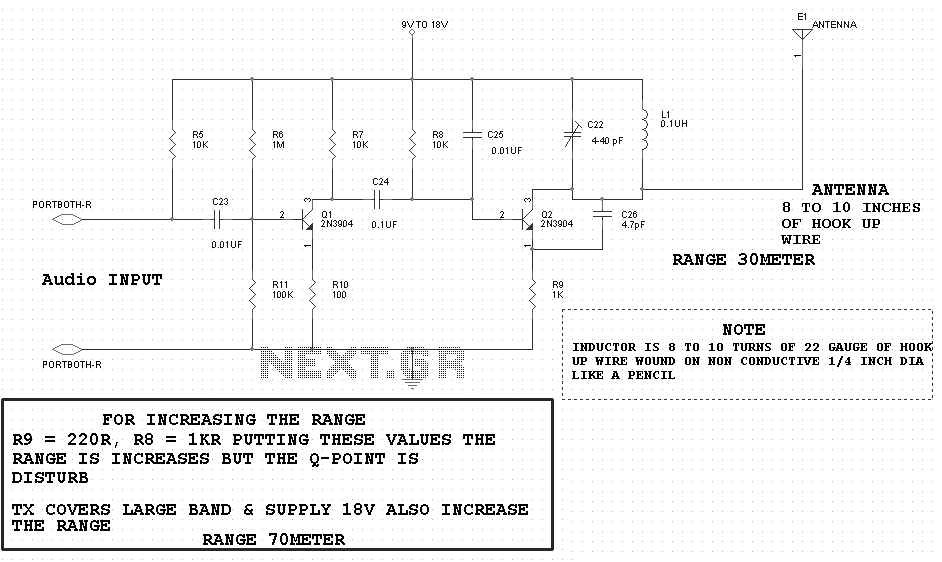
F/V Converter in CLosed Loop Motor Speed Control System
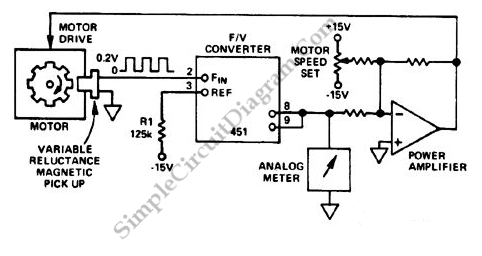
A closed-loop or servo system has the capability to stabilize the controlled plant at a specified operating condition. The plant, which is the controlled sub-system, can be...
A closed-loop control system, commonly referred to as a servo system, is designed to maintain a desired output by continuously monitoring and adjusting the input based on feedback from the system. This type of system is essential in applications where precise control is required, such as in robotics, industrial automation, and aerospace engineering.
In a typical closed-loop system, the key components include a controller, a sensor, an actuator, and the plant itself. The controller processes the error signal, which is the difference between the desired setpoint and the actual output measured by the sensor. The controller then generates a control signal that is sent to the actuator, which modifies the input to the plant to achieve the desired output.
The plant represents the process or system being controlled, which can include mechanical, electrical, thermal, or fluid systems. The stability of the closed-loop system is crucial; it ensures that the output remains within the desired range even in the presence of disturbances or changes in system dynamics.
Feedback mechanisms play a vital role in maintaining system stability. Positive feedback can lead to instability, while negative feedback is employed to reduce the error signal and stabilize the system. Various control strategies, such as proportional-integral-derivative (PID) control, are often implemented to enhance the performance of closed-loop systems by optimizing the response time and minimizing overshoot.
Overall, closed-loop systems are fundamental in modern engineering, enabling precise control and automation across a wide range of applications.Closed loop or servo system has the ability to stabilize the controlled plant at a specified operating condition. The plant, the controlled sub-system, can be.. 🔗 External reference
A closed-loop control system, commonly referred to as a servo system, is designed to maintain a desired output by continuously monitoring and adjusting the input based on feedback from the system. This type of system is essential in applications where precise control is required, such as in robotics, industrial automation, and aerospace engineering.
In a typical closed-loop system, the key components include a controller, a sensor, an actuator, and the plant itself. The controller processes the error signal, which is the difference between the desired setpoint and the actual output measured by the sensor. The controller then generates a control signal that is sent to the actuator, which modifies the input to the plant to achieve the desired output.
The plant represents the process or system being controlled, which can include mechanical, electrical, thermal, or fluid systems. The stability of the closed-loop system is crucial; it ensures that the output remains within the desired range even in the presence of disturbances or changes in system dynamics.
Feedback mechanisms play a vital role in maintaining system stability. Positive feedback can lead to instability, while negative feedback is employed to reduce the error signal and stabilize the system. Various control strategies, such as proportional-integral-derivative (PID) control, are often implemented to enhance the performance of closed-loop systems by optimizing the response time and minimizing overshoot.
Overall, closed-loop systems are fundamental in modern engineering, enabling precise control and automation across a wide range of applications.Closed loop or servo system has the ability to stabilize the controlled plant at a specified operating condition. The plant, the controlled sub-system, can be.. 🔗 External reference