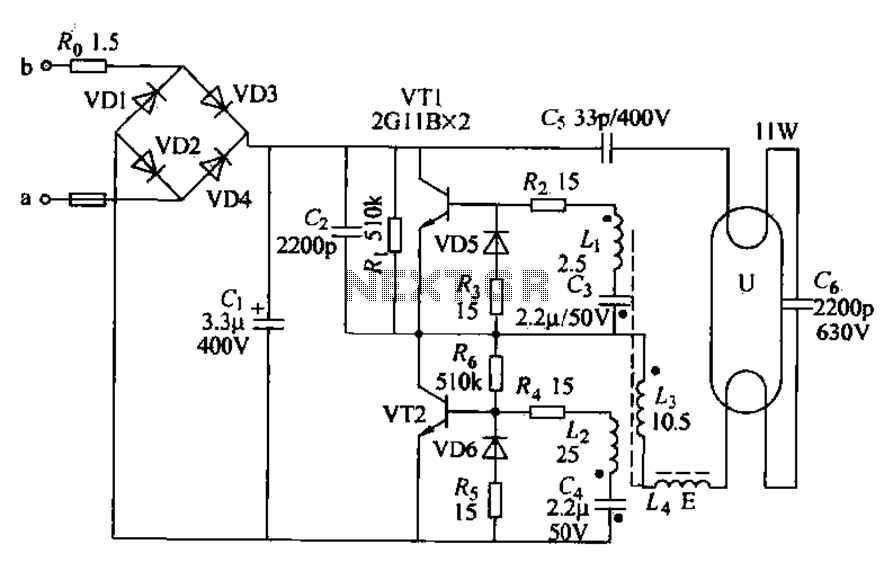
Belt conveyor interlock motor operation sequence control circuit
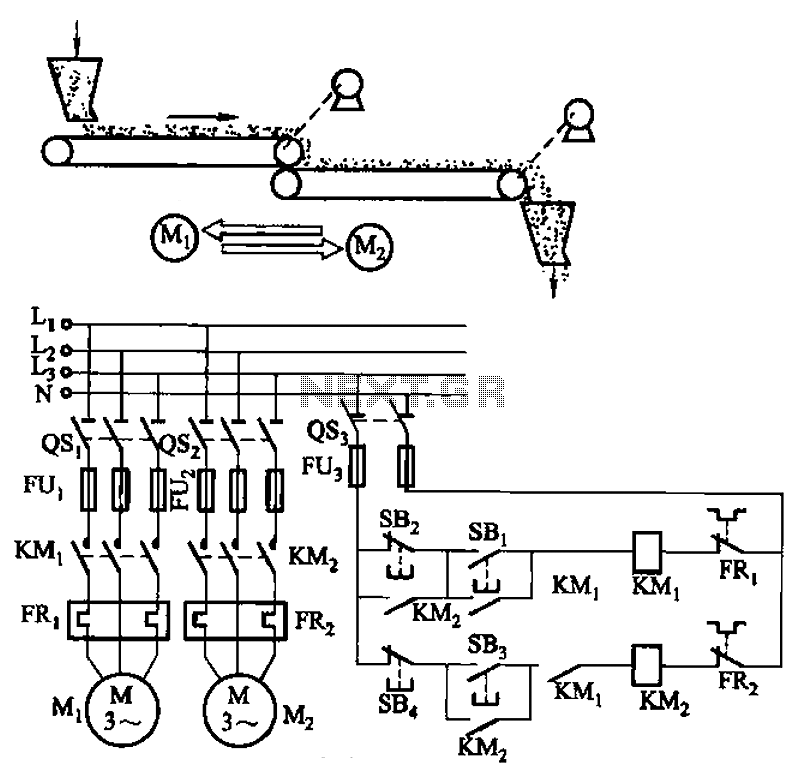
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-86 utilizes a line utilization time relay to control two motors, starting one before the other after an initial stall. The time relay KTi can be adjusted to modify the starting interval of the two electric motors. Additionally, adjusting KT2 allows for changes to the downtime interval between motor activations.
The circuit operates by employing a time relay system that ensures a sequential start of two electric motors, preventing potential overloads or mechanical stress that could occur if both motors were to start simultaneously. The time relay KTi is crucial for setting the delay time before the second motor is activated after the first motor has been started. This adjustment is essential for applications where staggered motor operation is required to manage load conditions effectively.
Furthermore, the second time relay, KT2, provides an adjustable downtime interval between the operations of the motors. This feature is particularly useful in applications where the motors are not required to run continuously and need to be cycled on and off at specific intervals. The ability to fine-tune both the start and downtime intervals enhances the flexibility of the circuit, allowing it to be tailored to the specific operational needs of the machinery involved.
The circuit should include proper protection mechanisms, such as fuses or circuit breakers, to safeguard against potential electrical faults. Additionally, the relay contacts should be rated appropriately to handle the load of the motors being controlled. Proper wiring and layout considerations must also be taken into account to minimize electromagnetic interference and ensure reliable operation.
Overall, this time relay-controlled motor circuit is suitable for various industrial applications, providing an efficient solution for managing motor operations with adjustable timing features. Circuit shown in Figure 3-86. The line utilization time relay to control two motors, one of the first than the other after starting stall. Adjust the time relay KTi, two electr ic motors can change the interval start; adjust KT2, two Taipower can change the interval motivation downtime.
The circuit operates by employing a time relay system that ensures a sequential start of two electric motors, preventing potential overloads or mechanical stress that could occur if both motors were to start simultaneously. The time relay KTi is crucial for setting the delay time before the second motor is activated after the first motor has been started. This adjustment is essential for applications where staggered motor operation is required to manage load conditions effectively.
Furthermore, the second time relay, KT2, provides an adjustable downtime interval between the operations of the motors. This feature is particularly useful in applications where the motors are not required to run continuously and need to be cycled on and off at specific intervals. The ability to fine-tune both the start and downtime intervals enhances the flexibility of the circuit, allowing it to be tailored to the specific operational needs of the machinery involved.
The circuit should include proper protection mechanisms, such as fuses or circuit breakers, to safeguard against potential electrical faults. Additionally, the relay contacts should be rated appropriately to handle the load of the motors being controlled. Proper wiring and layout considerations must also be taken into account to minimize electromagnetic interference and ensure reliable operation.
Overall, this time relay-controlled motor circuit is suitable for various industrial applications, providing an efficient solution for managing motor operations with adjustable timing features. Circuit shown in Figure 3-86. The line utilization time relay to control two motors, one of the first than the other after starting stall. Adjust the time relay KTi, two electr ic motors can change the interval start; adjust KT2, two Taipower can change the interval motivation downtime.