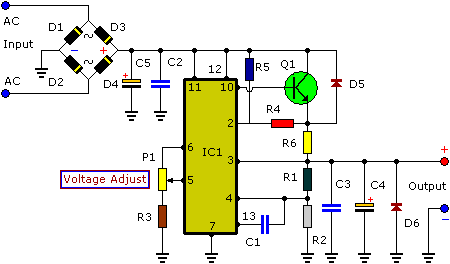
Fast acting power supply protection
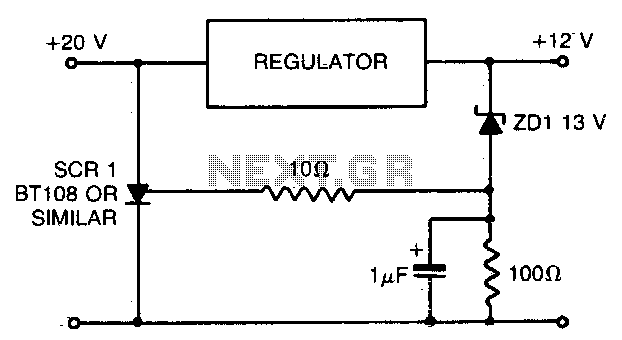
When using a regulated power supply to lower a supply voltage, there is always a risk that a failure in the power supply could result in a significant overvoltage condition across the load. To address overvoltage situations, the circuit is designed to protect the load during such conditions. The component values provided are for a 20 V supply with a regulated output of 12 V. The zener diode can be replaced with one that corresponds to the desired maximum voltage.
If the voltage at the regulator output exceeds 13 V, the zener diode enters breakdown mode and activates the thyristor, which then shorts the supply line and causes the main fuse to blow.
The described circuit provides a robust solution for overvoltage protection in regulated power supply systems. The primary components include a voltage regulator, a zener diode, a thyristor, and a fuse. The voltage regulator is responsible for maintaining a stable output voltage, while the zener diode serves as a voltage reference. When the output voltage approaches the predefined threshold of 13 V, the zener diode will conduct in reverse breakdown, allowing current to flow through it.
This current triggers the thyristor, a semiconductor device that can conduct current in one direction when it is activated. Once the thyristor is turned on, it creates a low-resistance path to ground, effectively shorting the power supply output. This action diverts the excess voltage away from the load, preventing damage to sensitive components. The main fuse in the circuit is designed to protect the entire system by breaking the circuit if the current exceeds a safe level, thus ensuring that no further damage occurs.
The choice of the zener diode is critical; it should be rated for the maximum voltage that the circuit is intended to handle. Adjusting the zener diode value allows for customization of the overvoltage threshold, making the circuit adaptable to various applications. The overall design emphasizes reliability and safety, ensuring that the load remains protected even in the event of a fault in the power supply.When using a regulated power supply to reduce a supply voltage, there is always the danger that component failure in the power supply might lead to a severe overvoltage condition across the load. To cope with overvoltage situations, the circuit is designed to protect the load under overyoltage conditions.
Component values given are for a 20 V supply with regulated output at 12 V. The zener diode can be changed according to whatever voltage is to be the maximum If the voltage at the regulator output rises to 13 V or above, the zener diode breaks down and triggers the thyristor which shorts out the supply line and blows the main fuse.
If the voltage at the regulator output exceeds 13 V, the zener diode enters breakdown mode and activates the thyristor, which then shorts the supply line and causes the main fuse to blow.
The described circuit provides a robust solution for overvoltage protection in regulated power supply systems. The primary components include a voltage regulator, a zener diode, a thyristor, and a fuse. The voltage regulator is responsible for maintaining a stable output voltage, while the zener diode serves as a voltage reference. When the output voltage approaches the predefined threshold of 13 V, the zener diode will conduct in reverse breakdown, allowing current to flow through it.
This current triggers the thyristor, a semiconductor device that can conduct current in one direction when it is activated. Once the thyristor is turned on, it creates a low-resistance path to ground, effectively shorting the power supply output. This action diverts the excess voltage away from the load, preventing damage to sensitive components. The main fuse in the circuit is designed to protect the entire system by breaking the circuit if the current exceeds a safe level, thus ensuring that no further damage occurs.
The choice of the zener diode is critical; it should be rated for the maximum voltage that the circuit is intended to handle. Adjusting the zener diode value allows for customization of the overvoltage threshold, making the circuit adaptable to various applications. The overall design emphasizes reliability and safety, ensuring that the load remains protected even in the event of a fault in the power supply.When using a regulated power supply to reduce a supply voltage, there is always the danger that component failure in the power supply might lead to a severe overvoltage condition across the load. To cope with overvoltage situations, the circuit is designed to protect the load under overyoltage conditions.
Component values given are for a 20 V supply with regulated output at 12 V. The zener diode can be changed according to whatever voltage is to be the maximum If the voltage at the regulator output rises to 13 V or above, the zener diode breaks down and triggers the thyristor which shorts out the supply line and blows the main fuse.