
Field Strength Meter
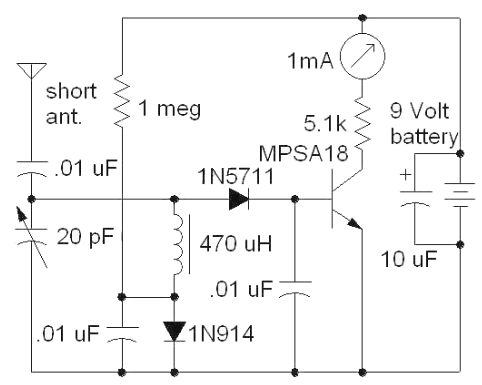
The following circuit illustrates a Field Strength Meter Circuit Diagram. Features: it is useful for radio frequency hobbyists and enthusiasts, and it uses only...
The Field Strength Meter circuit is designed to measure the strength of radio frequency (RF) signals in a given area. This type of circuit is particularly valuable for radio frequency hobbyists and enthusiasts who require a practical tool for evaluating signal strength during the development and testing of RF devices.
The circuit typically consists of a few essential components, including a diode, an operational amplifier (op-amp), a microcontroller, and a display unit. The diode is used to rectify the RF signal, converting it into a direct current (DC) voltage that can be processed. The op-amp amplifies this rectified signal, allowing for better sensitivity and accuracy in measurements.
A microcontroller may be implemented to digitize the amplified signal, facilitating the integration of additional features such as calibration, data logging, or signal processing. The output from the microcontroller can be displayed on an LCD or LED screen, providing a visual representation of the field strength.
Power supply requirements for the circuit can vary, but it is common to use a battery or a regulated power supply to ensure stable operation. Additionally, the circuit design may include input impedance matching components to optimize performance across a range of frequencies.
Overall, the Field Strength Meter circuit is a practical tool for anyone working with radio frequencies, enabling effective measurement and analysis of signal strengths in various applications.The following circuit shows about Field Strength Meter Circuit Diagram. Features: useful for radio frequency hobbyist and enthusiast, uses only .. 🔗 External reference
The Field Strength Meter circuit is designed to measure the strength of radio frequency (RF) signals in a given area. This type of circuit is particularly valuable for radio frequency hobbyists and enthusiasts who require a practical tool for evaluating signal strength during the development and testing of RF devices.
The circuit typically consists of a few essential components, including a diode, an operational amplifier (op-amp), a microcontroller, and a display unit. The diode is used to rectify the RF signal, converting it into a direct current (DC) voltage that can be processed. The op-amp amplifies this rectified signal, allowing for better sensitivity and accuracy in measurements.
A microcontroller may be implemented to digitize the amplified signal, facilitating the integration of additional features such as calibration, data logging, or signal processing. The output from the microcontroller can be displayed on an LCD or LED screen, providing a visual representation of the field strength.
Power supply requirements for the circuit can vary, but it is common to use a battery or a regulated power supply to ensure stable operation. Additionally, the circuit design may include input impedance matching components to optimize performance across a range of frequencies.
Overall, the Field Strength Meter circuit is a practical tool for anyone working with radio frequencies, enabling effective measurement and analysis of signal strengths in various applications.The following circuit shows about Field Strength Meter Circuit Diagram. Features: useful for radio frequency hobbyist and enthusiast, uses only .. 🔗 External reference

.gif)