Flashing Light with Triacs
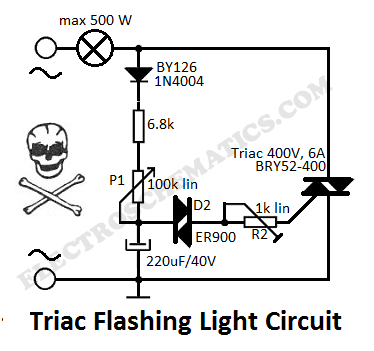
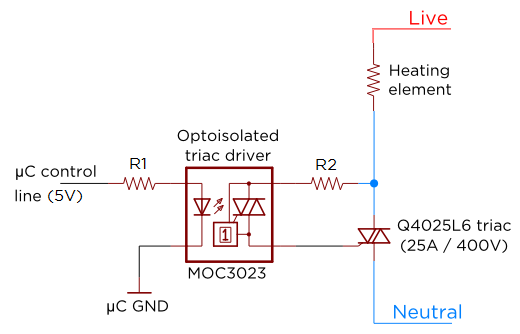
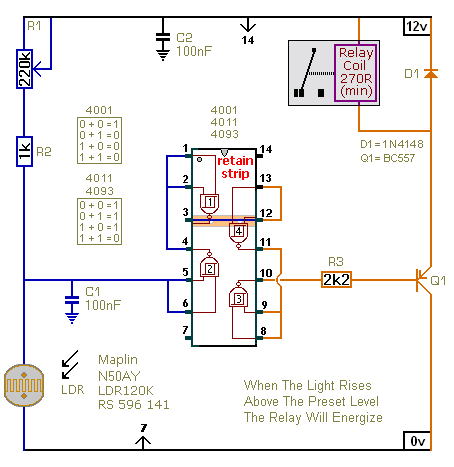
This flashing light circuit utilizes triacs to produce an intermittent light with variable frequency. Additional components include the D1 diode and a semi-adjustable resistor.
The flashing light circuit is designed to create a visual indication through intermittent illumination, which can be adjusted in frequency to suit various applications. At the core of the circuit are triacs, which are semiconductor devices capable of controlling power. They allow the circuit to switch on and off rapidly, producing the desired flashing effect.
The D1 diode serves a critical function in this circuit by providing rectification, ensuring that the current flows in a single direction. This is essential for the proper operation of the triacs, as they require a specific polarity to function effectively. The semi-adjustable resistor, often a potentiometer, allows for fine-tuning of the circuit's frequency. By adjusting this resistor, the user can change the amount of current flowing through the circuit, thereby altering the flashing rate of the light.
The circuit may also include additional components such as capacitors or resistors to stabilize the operation and enhance performance. Capacitors can be used to filter out noise and provide a smoother operation, while resistors can limit current to protect sensitive components.
In summary, this circuit is a versatile solution for creating variable frequency flashing lights, suitable for applications ranging from decorative lighting to signaling devices. The use of triacs, along with the diode and adjustable resistor, ensures efficient operation and customization of the flashing frequency.This flashing light circuit uses triacs to generate an intermittent light with variable frequency. Additional components are the D1 diode and semi adjustab.. 🔗 External reference
The flashing light circuit is designed to create a visual indication through intermittent illumination, which can be adjusted in frequency to suit various applications. At the core of the circuit are triacs, which are semiconductor devices capable of controlling power. They allow the circuit to switch on and off rapidly, producing the desired flashing effect.
The D1 diode serves a critical function in this circuit by providing rectification, ensuring that the current flows in a single direction. This is essential for the proper operation of the triacs, as they require a specific polarity to function effectively. The semi-adjustable resistor, often a potentiometer, allows for fine-tuning of the circuit's frequency. By adjusting this resistor, the user can change the amount of current flowing through the circuit, thereby altering the flashing rate of the light.
The circuit may also include additional components such as capacitors or resistors to stabilize the operation and enhance performance. Capacitors can be used to filter out noise and provide a smoother operation, while resistors can limit current to protect sensitive components.
In summary, this circuit is a versatile solution for creating variable frequency flashing lights, suitable for applications ranging from decorative lighting to signaling devices. The use of triacs, along with the diode and adjustable resistor, ensures efficient operation and customization of the flashing frequency.This flashing light circuit uses triacs to generate an intermittent light with variable frequency. Additional components are the D1 diode and semi adjustab.. 🔗 External reference