FM by a timer ME555 circuit
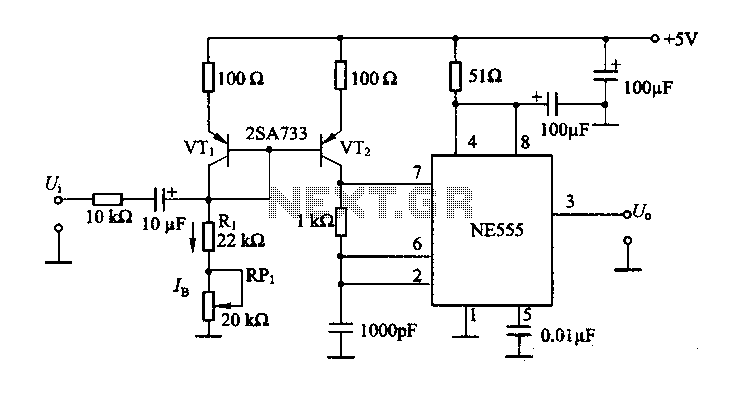
The circuit consists of a NE555 timer and a frequency modulation circuit that modifies the self-excited multivibrator NE555 by adjusting the charging current for frequency modulation. The components VT1 and VT2 form a current mirror circuit, which generates a charging current. The magnitude of this current is determined by resistors R1 and RRP1. A low-frequency modulation signal is superimposed on the bias current IB, resulting in variations in the oscillation frequency. The design also attempts to incorporate a current Miller circuit within the tube configuration.
The NE555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit used for generating precise timing and oscillation. In this application, it operates as a multivibrator, wherein the charging current influences the output frequency. The circuit configuration allows for frequency modulation by altering the charging time, which is directly influenced by the resistors R1 and RRP1.
The current mirror circuit, composed of transistors VT1 and VT2, plays a crucial role in maintaining a consistent charging current. This is essential for stabilizing the oscillation frequency of the NE555 timer. The current mirror ensures that the current flowing through R1 and RRP1 is mirrored accurately, allowing for predictable changes in frequency modulation based on the input signal.
The low-frequency modulation signal applied to the bias current IB allows for dynamic adjustments to the output frequency of the NE555. This modulation can enable various applications, such as tone generation or signal processing, where frequency variability is necessary. The inclusion of a current Miller circuit in the tube configuration further enhances the circuit's ability to manage and utilize the current effectively, providing additional control over the modulation process.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies the integration of a NE555 timer with a current mirror and modulation capabilities, showcasing its applicability in electronic signal generation and manipulation.The figure is composed by a NE555 and other withered frequency circuit by changing the self-excited multivibrator NE555 charging current to frequency modulation. The circuit is VT1 and VT2 constitute a current mirror circuit, the charging current can be generated in the charging circuit, the current size is determined by R1 and RRP1. Low frequency modulation signal superimposed to the bias current IB after the oscillation frequency changes. Try to use the current Miller circuit on the tube.
The NE555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit used for generating precise timing and oscillation. In this application, it operates as a multivibrator, wherein the charging current influences the output frequency. The circuit configuration allows for frequency modulation by altering the charging time, which is directly influenced by the resistors R1 and RRP1.
The current mirror circuit, composed of transistors VT1 and VT2, plays a crucial role in maintaining a consistent charging current. This is essential for stabilizing the oscillation frequency of the NE555 timer. The current mirror ensures that the current flowing through R1 and RRP1 is mirrored accurately, allowing for predictable changes in frequency modulation based on the input signal.
The low-frequency modulation signal applied to the bias current IB allows for dynamic adjustments to the output frequency of the NE555. This modulation can enable various applications, such as tone generation or signal processing, where frequency variability is necessary. The inclusion of a current Miller circuit in the tube configuration further enhances the circuit's ability to manage and utilize the current effectively, providing additional control over the modulation process.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies the integration of a NE555 timer with a current mirror and modulation capabilities, showcasing its applicability in electronic signal generation and manipulation.The figure is composed by a NE555 and other withered frequency circuit by changing the self-excited multivibrator NE555 charging current to frequency modulation. The circuit is VT1 and VT2 constitute a current mirror circuit, the charging current can be generated in the charging circuit, the current size is determined by R1 and RRP1. Low frequency modulation signal superimposed to the bias current IB after the oscillation frequency changes. Try to use the current Miller circuit on the tube.