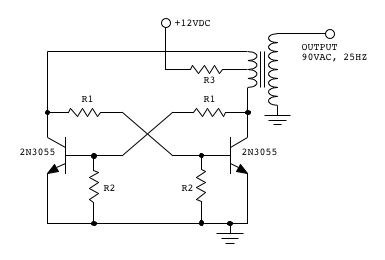
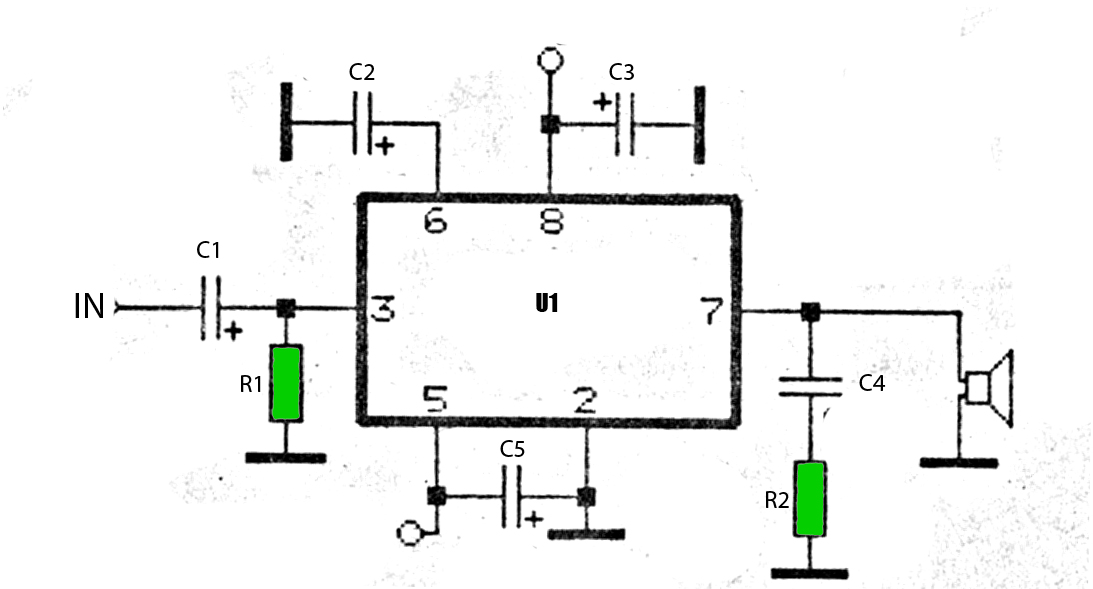
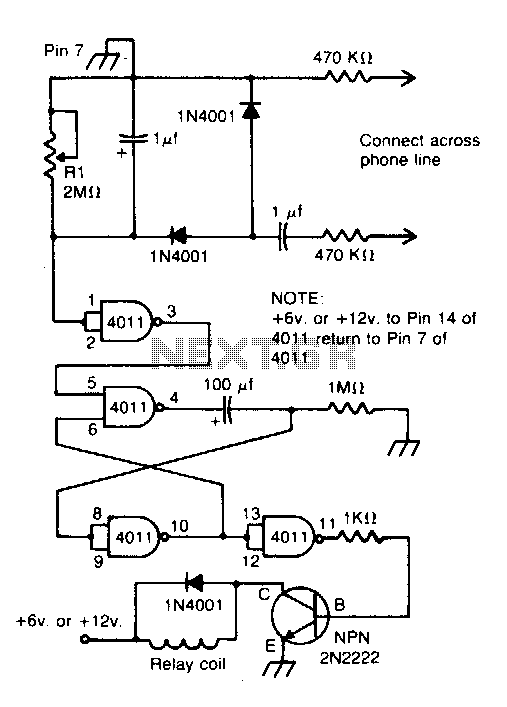
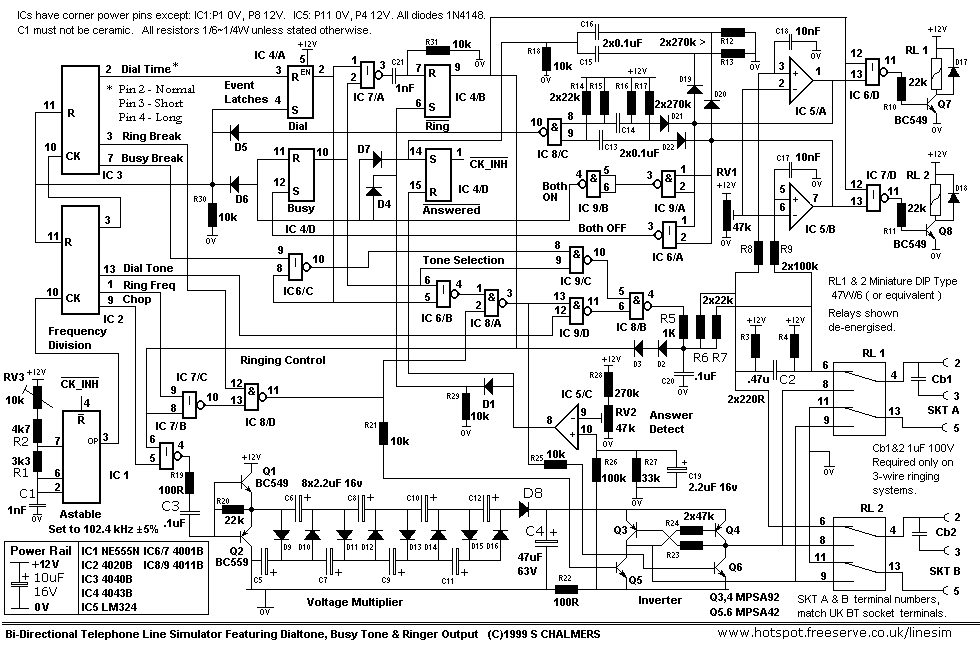
fm telephone circuits

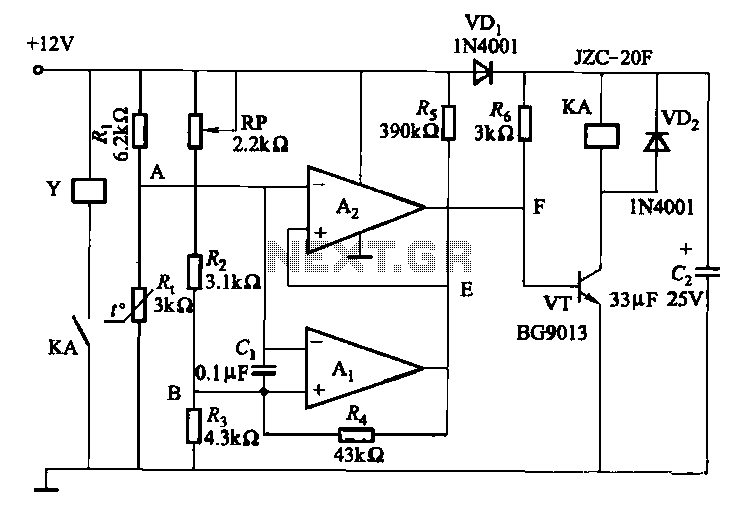
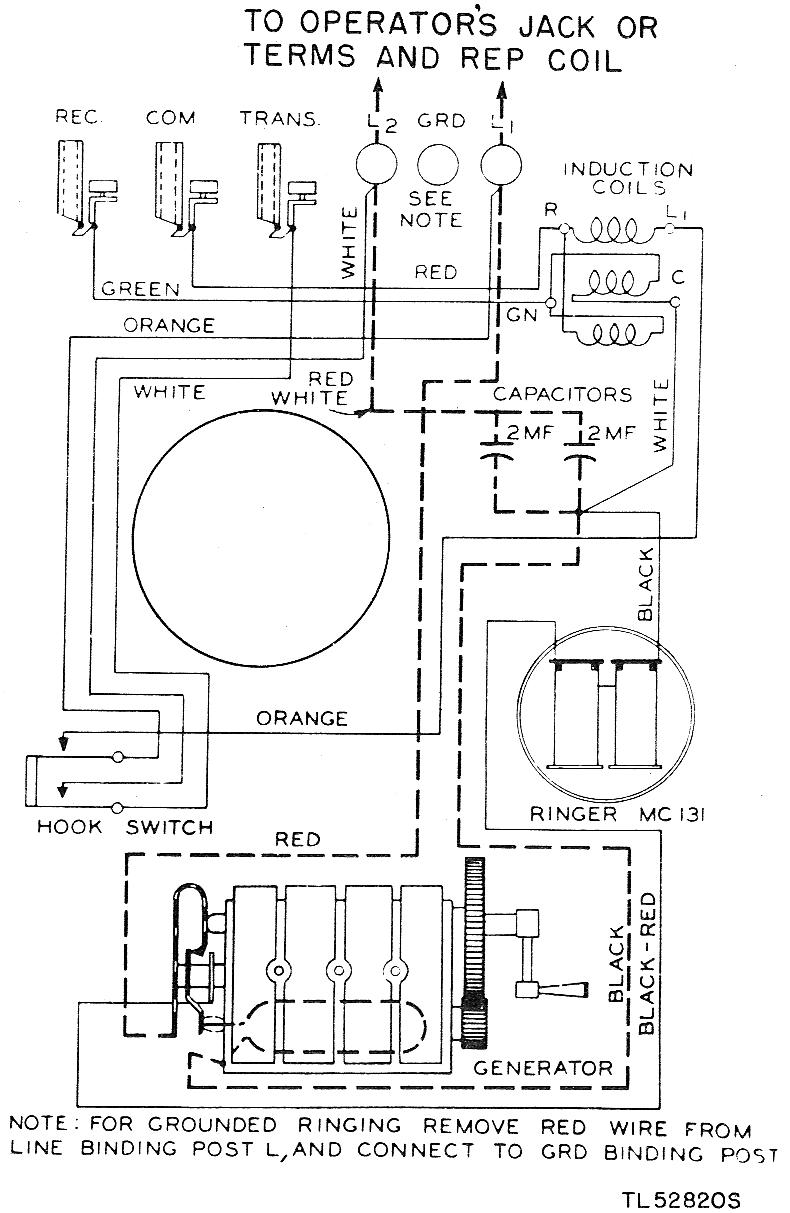
The FM telephone circuit is constructed on a compact PC board that can be easily integrated into the housing of a telephone, functioning as a pseudo-speak earphone. This FM circuit connects in series with the telephone line, drawing power from it, and transmits audio from both ends of the conversation to an FM radio tuned between 90 and 95 MHz.
The FM telephone circuit operates by utilizing the existing telephone line to power its components, which eliminates the need for an external power source. The circuit is designed to intercept the audio signals from both the microphone and speaker of the telephone. This is achieved through a series connection that allows the circuit to access the audio signals without disrupting the normal operation of the telephone.
The FM transmitter within the circuit modulates the audio signals onto a carrier wave within the specified frequency range of 90 to 95 MHz. This frequency range is chosen to align with standard FM radio frequencies, making the transmitted audio easily receivable by common FM radios. The circuit may include a simple oscillator, a modulator, and an antenna for effective transmission.
The compact design of the PC board is critical, as it must fit within the limited space of the telephone housing. Components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits are selected for their small size and low power consumption. The use of surface-mount technology (SMT) may be employed to further reduce the footprint of the circuit.
In practical applications, users can tune their FM radios to the designated frequency to listen to the conversation taking place on the telephone. This feature can be useful for various purposes, including monitoring calls or for hands-free operation. However, it is essential to consider legal regulations regarding the interception of telephone conversations in the applicable jurisdiction before using such a device.The FM telephone circuit is built on a PC board that is so small it can easily be fitted inside the housing of a telephone making it an instant pseudo-speak earphone. This FM circuit connects in series with telephone line, steals power from it, and transmit at both sides of the conversation to an FM radio tuned between 90 and 95 MHz.
🔗 External reference
The FM telephone circuit operates by utilizing the existing telephone line to power its components, which eliminates the need for an external power source. The circuit is designed to intercept the audio signals from both the microphone and speaker of the telephone. This is achieved through a series connection that allows the circuit to access the audio signals without disrupting the normal operation of the telephone.
The FM transmitter within the circuit modulates the audio signals onto a carrier wave within the specified frequency range of 90 to 95 MHz. This frequency range is chosen to align with standard FM radio frequencies, making the transmitted audio easily receivable by common FM radios. The circuit may include a simple oscillator, a modulator, and an antenna for effective transmission.
The compact design of the PC board is critical, as it must fit within the limited space of the telephone housing. Components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits are selected for their small size and low power consumption. The use of surface-mount technology (SMT) may be employed to further reduce the footprint of the circuit.
In practical applications, users can tune their FM radios to the designated frequency to listen to the conversation taking place on the telephone. This feature can be useful for various purposes, including monitoring calls or for hands-free operation. However, it is essential to consider legal regulations regarding the interception of telephone conversations in the applicable jurisdiction before using such a device.The FM telephone circuit is built on a PC board that is so small it can easily be fitted inside the housing of a telephone making it an instant pseudo-speak earphone. This FM circuit connects in series with telephone line, steals power from it, and transmit at both sides of the conversation to an FM radio tuned between 90 and 95 MHz.
🔗 External reference