Good/Bad Transistor Tester
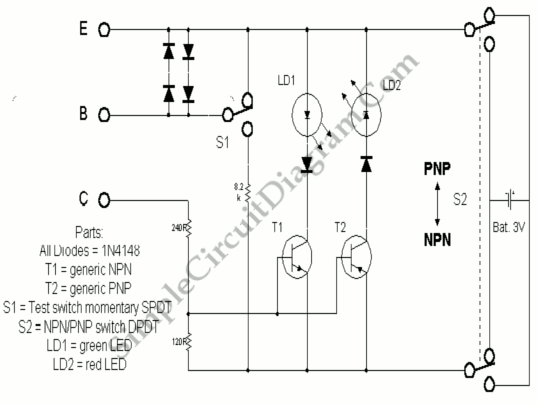
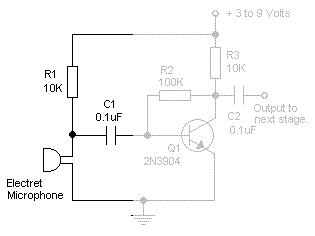
A good/bad transistor tester is an instrument designed to determine the operational status of a transistor, indicating whether it is functional or defective. This device provides a simple binary assessment, confirming if the transistor has a gain equal to or greater than 30.
A good/bad transistor tester typically operates by applying a small voltage to the transistor terminals and measuring the resulting current flow. The tester assesses the transistor's gain, which is a crucial parameter indicating its ability to amplify signals. If the gain is equal to or exceeds the threshold value of 30, the transistor is classified as "good"; otherwise, it is deemed "bad."
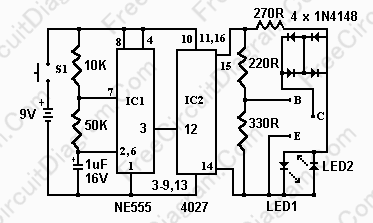
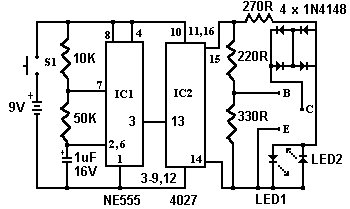
The circuit design of a good/bad transistor tester usually incorporates a few essential components, including a power supply, a current measuring device (often an analog or digital multimeter), and a switching mechanism to connect the transistor under test. The tester may feature a simple LED indicator or a digital readout to provide visual feedback on the transistor's status.
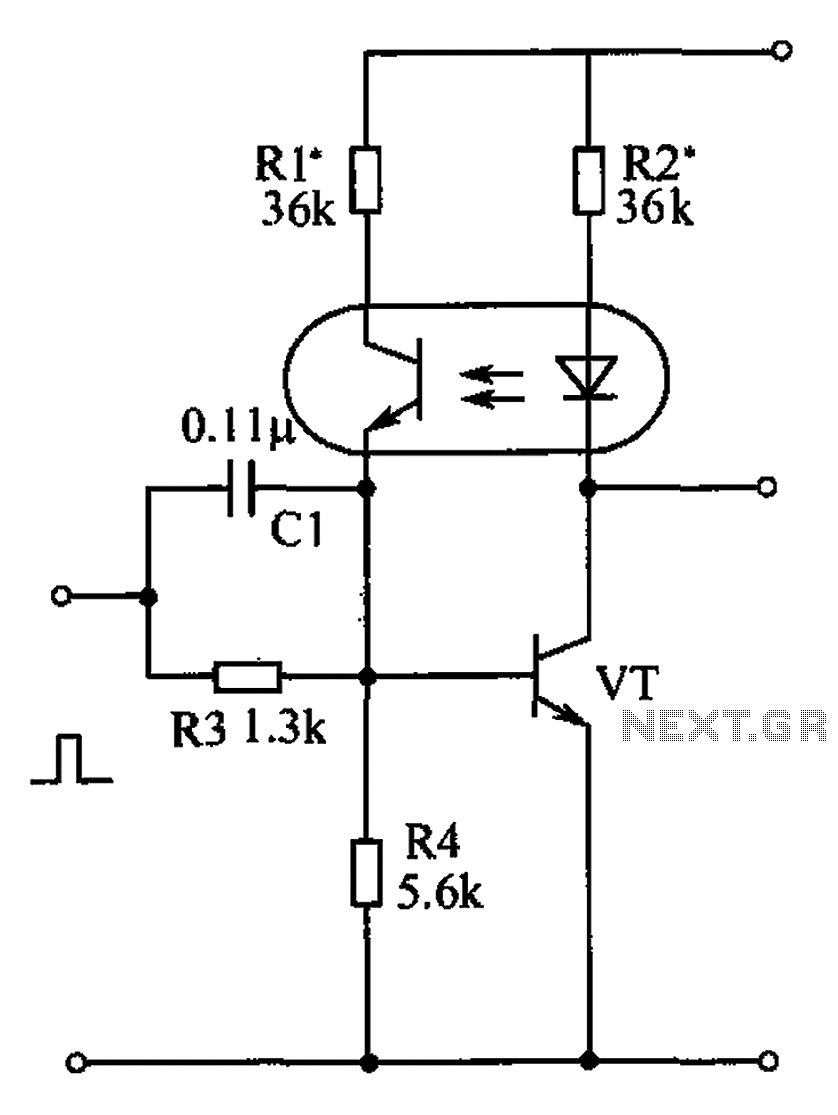
In terms of construction, the tester circuit can be built using common electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors. A typical configuration might include a biasing network to ensure the transistor is operating in the correct region of its characteristic curve. The output stage may utilize an op-amp or a comparator to compare the measured gain against the predefined threshold.
Moreover, the tester can be designed to accommodate various transistor types, including NPN and PNP configurations, by incorporating a switch or jumper settings to adjust the biasing conditions accordingly. This versatility enhances the utility of the tester in diagnosing a wide range of transistors found in electronic devices.
In summary, a good/bad transistor tester is a straightforward yet effective tool for quickly assessing the functionality of transistors, making it an essential instrument for electronics repair and maintenance. Its design emphasizes simplicity and reliability, ensuring accurate results in determining the operational status of transistors.Good/Bad transistor tester means that this instrument can only determine if the transistor is good or bad, nothing more. Any transistor with gain equal to 30.. 🔗 External reference
A good/bad transistor tester typically operates by applying a small voltage to the transistor terminals and measuring the resulting current flow. The tester assesses the transistor's gain, which is a crucial parameter indicating its ability to amplify signals. If the gain is equal to or exceeds the threshold value of 30, the transistor is classified as "good"; otherwise, it is deemed "bad."
The circuit design of a good/bad transistor tester usually incorporates a few essential components, including a power supply, a current measuring device (often an analog or digital multimeter), and a switching mechanism to connect the transistor under test. The tester may feature a simple LED indicator or a digital readout to provide visual feedback on the transistor's status.
In terms of construction, the tester circuit can be built using common electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors. A typical configuration might include a biasing network to ensure the transistor is operating in the correct region of its characteristic curve. The output stage may utilize an op-amp or a comparator to compare the measured gain against the predefined threshold.
Moreover, the tester can be designed to accommodate various transistor types, including NPN and PNP configurations, by incorporating a switch or jumper settings to adjust the biasing conditions accordingly. This versatility enhances the utility of the tester in diagnosing a wide range of transistors found in electronic devices.
In summary, a good/bad transistor tester is a straightforward yet effective tool for quickly assessing the functionality of transistors, making it an essential instrument for electronics repair and maintenance. Its design emphasizes simplicity and reliability, ensuring accurate results in determining the operational status of transistors.Good/Bad transistor tester means that this instrument can only determine if the transistor is good or bad, nothing more. Any transistor with gain equal to 30.. 🔗 External reference