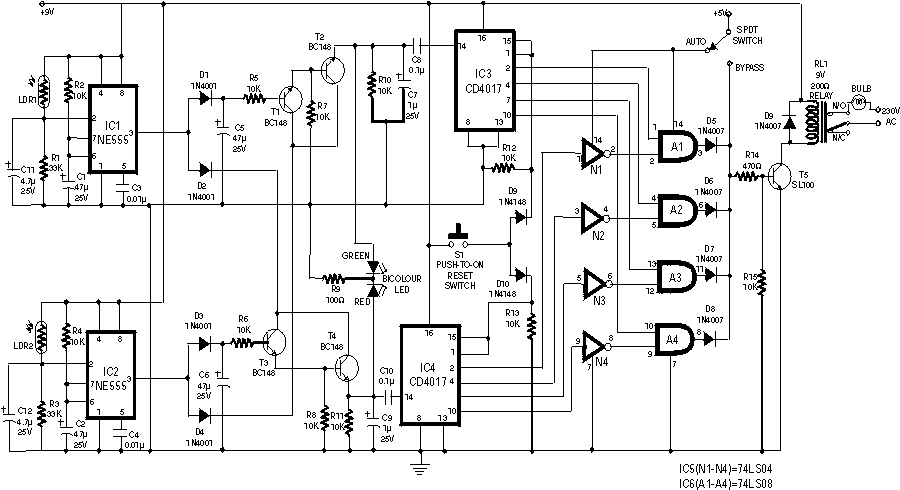
Ground-Fault Hall Sensor
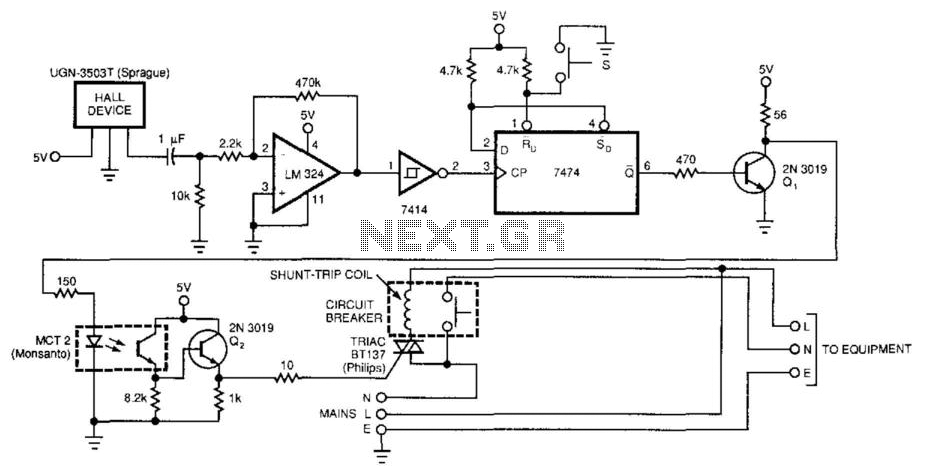
No electrical contact exists between the circuit and the conductor. The 7474 flip-flop is triggered by the output from the Hall sensor, op amp, and Schmitt trigger. This triggering activates the optocoupler, turns on the triac, and trips the circuit breaker.
The circuit operates without any direct electrical contact between the main circuit and the conductor, ensuring electrical isolation. The 7474 flip-flop serves as a bistable multivibrator, receiving its triggering input from the combined outputs of a Hall effect sensor, an operational amplifier (op amp), and a Schmitt trigger.
The Hall sensor detects magnetic fields and converts this information into an electrical signal. The op amp amplifies this signal, ensuring that it is strong enough to be processed. The Schmitt trigger provides a clean digital output by eliminating noise and ensuring sharp transitions, which is essential for reliable triggering of the flip-flop.
Once the 7474 flip-flop receives a trigger signal, it changes its state, which in turn activates the optocoupler. The optocoupler provides electrical isolation between the input and output sides of the circuit, allowing the control signal to turn on the triac without direct electrical contact. The triac, a semiconductor device used for switching and controlling power, will then conduct current, effectively controlling the load connected to the circuit.
Finally, this action can trip a circuit breaker, providing a safety mechanism that interrupts the current flow in case of an overload or fault condition. The entire arrangement ensures that the circuit operates safely and efficiently while maintaining electrical isolation, thereby protecting sensitive components and enhancing the overall reliability of the system. No electrical contact exists between the circuit and the conductor. The 7474 flip-flop is triggered by the output from the Hall sensor, op amp, and Schmitt trigger. This triggering activates the optocoupler, turns on the triac, and trips the circuit breaker.
The circuit operates without any direct electrical contact between the main circuit and the conductor, ensuring electrical isolation. The 7474 flip-flop serves as a bistable multivibrator, receiving its triggering input from the combined outputs of a Hall effect sensor, an operational amplifier (op amp), and a Schmitt trigger.
The Hall sensor detects magnetic fields and converts this information into an electrical signal. The op amp amplifies this signal, ensuring that it is strong enough to be processed. The Schmitt trigger provides a clean digital output by eliminating noise and ensuring sharp transitions, which is essential for reliable triggering of the flip-flop.
Once the 7474 flip-flop receives a trigger signal, it changes its state, which in turn activates the optocoupler. The optocoupler provides electrical isolation between the input and output sides of the circuit, allowing the control signal to turn on the triac without direct electrical contact. The triac, a semiconductor device used for switching and controlling power, will then conduct current, effectively controlling the load connected to the circuit.
Finally, this action can trip a circuit breaker, providing a safety mechanism that interrupts the current flow in case of an overload or fault condition. The entire arrangement ensures that the circuit operates safely and efficiently while maintaining electrical isolation, thereby protecting sensitive components and enhancing the overall reliability of the system. No electrical contact exists between the circuit and the conductor. The 7474 flip-flop is triggered by the output from the Hall sensor, op amp, and Schmitt trigger. This triggering activates the optocoupler, turns on the triac, and trips the circuit breaker.