HARTLEY OSCILLATOR
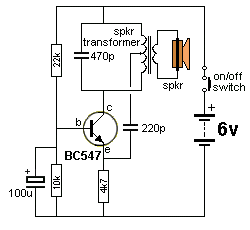
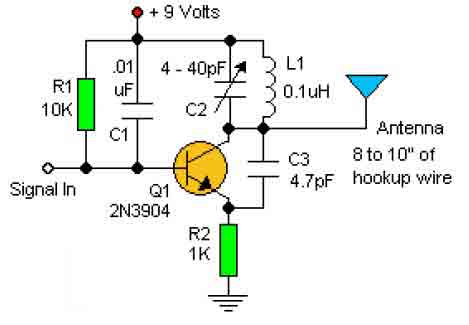
The Hartley Oscillator is characterized by an LC circuit in its collector. The base of the transistor is held steady, and a small amount of signal is taken from a tapping on the inductor and fed to the emitter to maintain the transistor in oscillation.
The Hartley Oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves, primarily used in radio frequency applications. It employs a tank circuit composed of an inductor (L) and a capacitor (C) to produce oscillations. The oscillator's operation is based on the feedback principle, where a portion of the output signal is fed back to the input to sustain oscillations.
In a typical Hartley Oscillator configuration, the circuit consists of a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or field-effect transistor (FET) with the LC tank circuit connected to its collector. The inductor in the tank circuit is often split into two parts, which allows for a tapping point to be established between them. This tapping point is crucial as it provides the necessary feedback signal to the emitter of the transistor.
The base of the transistor is biased with a steady voltage, ensuring that the transistor remains in the active region for amplification. The small feedback signal from the tapping on the inductor is coupled to the emitter, where it influences the transistor's operation, thereby sustaining the oscillation process. The oscillation frequency is determined by the values of the inductance and capacitance in the tank circuit, calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{LC}} \]
where \( f \) is the frequency of oscillation, \( L \) is the total inductance, and \( C \) is the capacitance.
The Hartley Oscillator is favored for its simplicity and ease of tuning, making it suitable for various applications including signal generation, RF amplification, and as a local oscillator in superheterodyne receivers. Proper design considerations, such as component selection and layout, are essential to ensure stable oscillation and minimize unwanted harmonics.The Hartley Oscillator is characterised by an LC circuit in its collector. The base of the transistor is held steady and a small amount of signal is taken from a tapping on the inductor and fed to the emitter to keep the transistor in oscillation. 🔗 External reference
The Hartley Oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves, primarily used in radio frequency applications. It employs a tank circuit composed of an inductor (L) and a capacitor (C) to produce oscillations. The oscillator's operation is based on the feedback principle, where a portion of the output signal is fed back to the input to sustain oscillations.
In a typical Hartley Oscillator configuration, the circuit consists of a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or field-effect transistor (FET) with the LC tank circuit connected to its collector. The inductor in the tank circuit is often split into two parts, which allows for a tapping point to be established between them. This tapping point is crucial as it provides the necessary feedback signal to the emitter of the transistor.
The base of the transistor is biased with a steady voltage, ensuring that the transistor remains in the active region for amplification. The small feedback signal from the tapping on the inductor is coupled to the emitter, where it influences the transistor's operation, thereby sustaining the oscillation process. The oscillation frequency is determined by the values of the inductance and capacitance in the tank circuit, calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{LC}} \]
where \( f \) is the frequency of oscillation, \( L \) is the total inductance, and \( C \) is the capacitance.
The Hartley Oscillator is favored for its simplicity and ease of tuning, making it suitable for various applications including signal generation, RF amplification, and as a local oscillator in superheterodyne receivers. Proper design considerations, such as component selection and layout, are essential to ensure stable oscillation and minimize unwanted harmonics.The Hartley Oscillator is characterised by an LC circuit in its collector. The base of the transistor is held steady and a small amount of signal is taken from a tapping on the inductor and fed to the emitter to keep the transistor in oscillation. 🔗 External reference